OLED encapsulation protects organic layers from moisture and oxygen, enhancing display lifespan and maintaining vibrant colors, while QD encapsulation focuses on preserving quantum dots' efficiency and color purity under environmental stress. Explore the article to understand which encapsulation technology best suits your display needs.
Table of Comparison
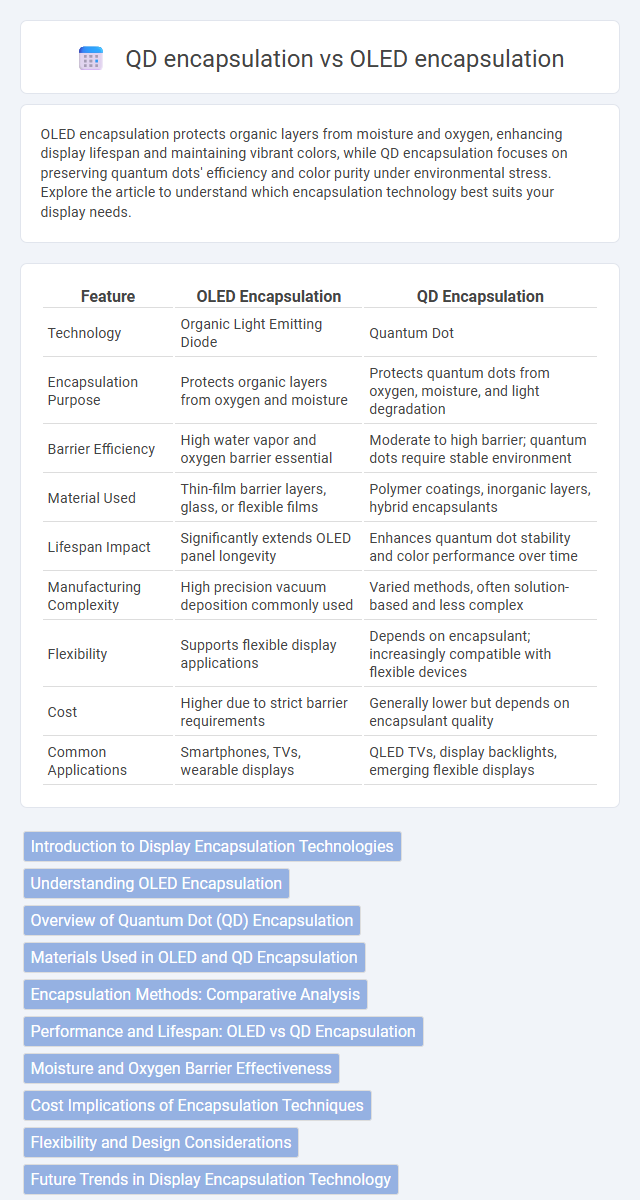
| Feature | OLED Encapsulation | QD Encapsulation |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Organic Light Emitting Diode | Quantum Dot |
| Encapsulation Purpose | Protects organic layers from oxygen and moisture | Protects quantum dots from oxygen, moisture, and light degradation |
| Barrier Efficiency | High water vapor and oxygen barrier essential | Moderate to high barrier; quantum dots require stable environment |
| Material Used | Thin-film barrier layers, glass, or flexible films | Polymer coatings, inorganic layers, hybrid encapsulants |
| Lifespan Impact | Significantly extends OLED panel longevity | Enhances quantum dot stability and color performance over time |
| Manufacturing Complexity | High precision vacuum deposition commonly used | Varied methods, often solution-based and less complex |
| Flexibility | Supports flexible display applications | Depends on encapsulant; increasingly compatible with flexible devices |
| Cost | Higher due to strict barrier requirements | Generally lower but depends on encapsulant quality |
| Common Applications | Smartphones, TVs, wearable displays | QLED TVs, display backlights, emerging flexible displays |
Introduction to Display Encapsulation Technologies
OLED encapsulation employs thin-film barrier layers to protect organic materials from moisture and oxygen, ensuring device longevity and performance. QD encapsulation uses specialized polymer matrices or glass barriers to shield quantum dots from environmental degradation, maintaining color purity and brightness. Both technologies are critical in enhancing display durability and visual quality by preventing contaminants from compromising the active layers.
Understanding OLED Encapsulation
OLED encapsulation uses thin-film barriers or glass to protect organic layers from moisture and oxygen, ensuring device longevity and performance stability. You should note that QD (Quantum Dot) encapsulation involves specialized films that enhance color purity and brightness while providing environmental protection. Comparing both, OLED encapsulation prioritizes flexibility and moisture resistance, whereas QD encapsulation emphasizes color enhancement alongside durability.
Overview of Quantum Dot (QD) Encapsulation
Quantum Dot (QD) encapsulation utilizes nanoscale semiconductor particles to enhance display color accuracy and brightness by converting blue light into highly saturated red and green emissions. This technique offers superior color gamut and energy efficiency compared to traditional OLED encapsulation, which primarily relies on organic layers protected by thin-film barriers. QD encapsulation also improves device longevity by effectively blocking moisture and oxygen, critical factors in preserving display performance.
Materials Used in OLED and QD Encapsulation
OLED encapsulation primarily utilizes thin layers of glass, metal foils, and advanced polymer films such as atomic layer deposition (ALD) grown oxides to prevent oxygen and moisture ingress. QD encapsulation, on the other hand, often relies on hybrid materials combining inorganic barriers like SiOx or AlOx with flexible polymers, optimized for protecting quantum dots from air and light degradation. The choice of materials in both encapsulation techniques directly impacts device lifetime and optical performance by enhancing barrier properties and maintaining structural integrity under environmental stress.
Encapsulation Methods: Comparative Analysis
OLED encapsulation employs thin-film barriers and flexible glass to prevent moisture and oxygen ingress, ensuring device longevity and performance stability. QD encapsulation often utilizes advanced multi-layer encapsulation with inorganic and organic materials to protect quantum dots from degradation while maintaining high color purity and brightness. Compared to OLEDs, QD encapsulation demands superior moisture resistance and UV protection due to quantum dots' sensitivity, resulting in more complex encapsulation architectures optimized for enhanced optical efficiency and device durability.
Performance and Lifespan: OLED vs QD Encapsulation
OLED encapsulation offers excellent flexibility but tends to have a shorter lifespan due to susceptibility to oxygen and moisture damage, affecting long-term performance. QD encapsulation provides superior barrier properties that enhance durability and extend the lifespan of displays by effectively protecting quantum dots from environmental degradation. Your choice between OLED and QD encapsulation significantly impacts display reliability, brightness, and color stability over time.
Moisture and Oxygen Barrier Effectiveness
OLED encapsulation typically employs multilayer thin-film barriers combining inorganic and organic materials, achieving exceptional moisture and oxygen barrier effectiveness with water vapor transmission rates (WVTR) as low as 10^-6 g/m2/day. QD encapsulation often relies on polymer matrices embedded with quantum dots, which can be more permeable and may require additional barrier layers to match the low WVTR levels of OLED encapsulation. Your choice between OLED and QD devices should consider these differences, as superior encapsulation directly impacts device longevity and performance stability under exposure to moisture and oxygen.
Cost Implications of Encapsulation Techniques
OLED encapsulation generally involves higher material and manufacturing costs due to the need for ultra-thin, flexible, and highly durable barrier layers to protect organic materials from moisture and oxygen. QD (Quantum Dot) encapsulation often benefits from lower costs, as it typically employs simpler inorganic layers or hybrid materials that require less stringent environmental control during production. The cost implications significantly affect device pricing and market adoption, with OLED encapsulation driving up expenses in premium display segments compared to more cost-efficient QD solutions.
Flexibility and Design Considerations
OLED encapsulation offers superior flexibility due to its thin, lightweight layers that can bend and conform to curved surfaces, making it ideal for wearable devices and foldable screens. QD encapsulation typically involves rigid barriers to protect quantum dots, which can limit design adaptability and restrict use in flexible or stretchable displays. Design considerations must account for the encapsulation method's impact on durability, breathability, and the device's mechanical stress tolerance.
Future Trends in Display Encapsulation Technology
Future trends in display encapsulation technology emphasize enhanced barrier layers combining inorganic and organic materials to improve OLED lifespan and efficiency. Quantum Dot (QD) encapsulation developments focus on hybrid materials that maintain color purity while offering flexible, robust protection against moisture and oxygen. Innovations in nanolaminate coatings and atomic layer deposition methods drive both OLED and QD displays toward thinner, more durable encapsulation solutions for next-generation flexible and foldable devices.
OLED encapsulation vs QD encapsulation Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com