Schottky diodes offer lower forward voltage drop and faster switching speeds compared to fast recovery diodes, making them ideal for high-efficiency power applications. Discover the key differences and choose the best diode to optimize your electronic circuits by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
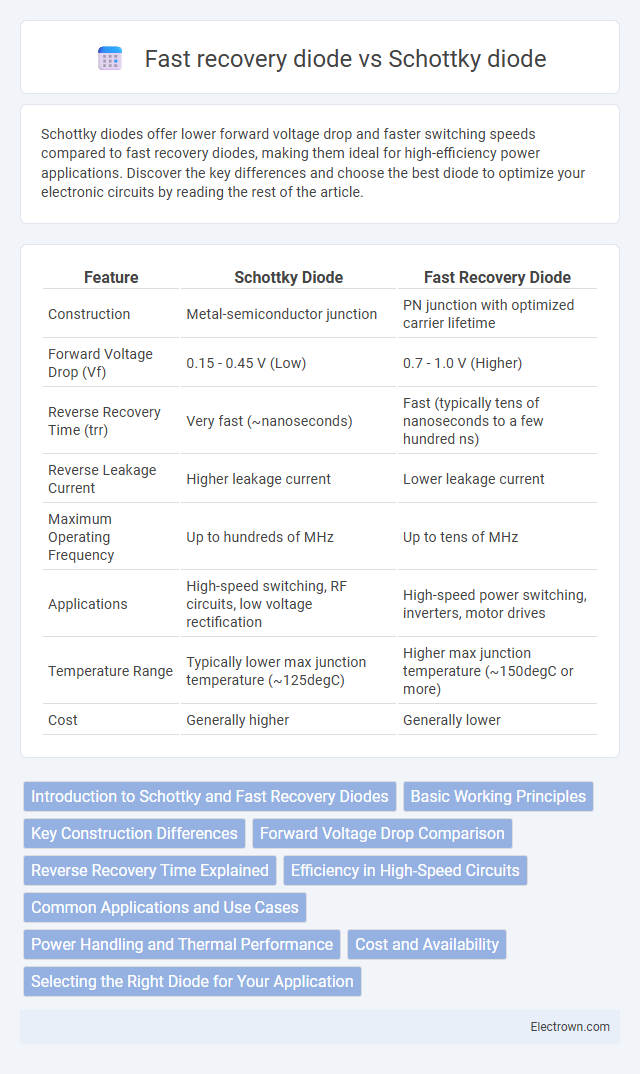
| Feature | Schottky Diode | Fast Recovery Diode |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | Metal-semiconductor junction | PN junction with optimized carrier lifetime |
| Forward Voltage Drop (Vf) | 0.15 - 0.45 V (Low) | 0.7 - 1.0 V (Higher) |
| Reverse Recovery Time (trr) | Very fast (~nanoseconds) | Fast (typically tens of nanoseconds to a few hundred ns) |
| Reverse Leakage Current | Higher leakage current | Lower leakage current |
| Maximum Operating Frequency | Up to hundreds of MHz | Up to tens of MHz |
| Applications | High-speed switching, RF circuits, low voltage rectification | High-speed power switching, inverters, motor drives |
| Temperature Range | Typically lower max junction temperature (~125degC) | Higher max junction temperature (~150degC or more) |
| Cost | Generally higher | Generally lower |
Introduction to Schottky and Fast Recovery Diodes
Schottky diodes feature a metal-semiconductor junction that enables ultra-fast switching speeds and low forward voltage drop, making them ideal for high-frequency applications and power efficiency. Fast recovery diodes utilize a p-n junction with optimized semiconductor materials and fabrication techniques to significantly reduce reverse recovery time compared to standard diodes, enhancing performance in switching power supplies and inverters. Both diodes serve critical roles in power electronics, where Schottky diodes offer superior conduction efficiency and fast recovery diodes provide balanced switching speed with higher voltage tolerance.
Basic Working Principles
Schottky diodes operate based on the metal-semiconductor junction, allowing majority carriers to cross with minimal charge storage, resulting in low forward voltage drop and near-instantaneous switching. Fast recovery diodes rely on a p-n junction designed to reduce reverse recovery time by minimizing stored minority carriers, enabling quicker transition from conducting to blocking state. The fundamental difference lies in charge carrier dynamics, where Schottky diodes favor majority carrier conduction, whereas fast recovery diodes optimize minority carrier removal for speed.
Key Construction Differences
Schottky diodes feature a metal-semiconductor junction, typically between a metal and an N-type semiconductor, enabling a low forward voltage drop and fast switching speed. Fast recovery diodes use a p-n junction with a specialized doping profile to minimize charge storage and reduce recovery time during reverse switching. The fundamental construction difference lies in the Schottky diode's metal-semiconductor barrier versus the fast recovery diode's tailored p-n junction, directly impacting their electrical performance and switching characteristics.
Forward Voltage Drop Comparison
Schottky diodes typically exhibit a lower forward voltage drop, usually around 0.2 to 0.3 volts, making them more efficient for low-voltage applications. Fast recovery diodes generally have a higher forward voltage drop, approximately 0.7 volts, due to their PN junction structure. Your choice depends on the need for energy efficiency and switching speed, where Schottky diodes minimize power loss during conduction.
Reverse Recovery Time Explained
Reverse recovery time is the duration a diode takes to switch from conducting to blocking state, crucial for switching efficiency in power electronics. Schottky diodes have very low reverse recovery times, often in the nanosecond range, due to their majority carrier conduction, making them ideal for high-frequency applications. Fast recovery diodes, while faster than standard PN diodes, still exhibit longer reverse recovery times than Schottky diodes, impacting switching losses and thermal performance in your circuits.
Efficiency in High-Speed Circuits
Schottky diodes offer superior efficiency in high-speed circuits due to their low forward voltage drop and minimal reverse recovery time, which reduces switching losses and heat generation. Fast recovery diodes, while better than standard diodes, have longer reverse recovery times causing higher power dissipation and lower switching speed efficiency. Your choice of diode directly impacts the overall performance of high-frequency applications, with Schottky diodes generally providing better efficiency in these scenarios.
Common Applications and Use Cases
Schottky diodes are widely used in low-voltage, high-frequency applications such as power rectification in switched-mode power supplies and RF systems due to their low forward voltage drop and fast switching speed. Fast recovery diodes find common application in high-power circuits like motor drives, inverters, and power factor correction where rapid switching and high surge current capability are critical. Both diodes optimize efficiency in electronic circuits but are selected based on specific needs for speed, voltage, and current handling.
Power Handling and Thermal Performance
Schottky diodes excel in power handling due to their low forward voltage drop, which reduces conduction losses and improves thermal performance in high-frequency applications. Fast recovery diodes, meanwhile, offer superior reverse recovery characteristics, making them suitable for circuits requiring efficient switching but typically generate higher heat under heavy loads. Understanding your power and thermal management needs will help determine the optimal diode choice for maximizing efficiency and reliability in your electronic designs.
Cost and Availability
Schottky diodes generally offer lower cost and higher availability due to their widespread use in low-voltage, high-speed switching applications. Fast recovery diodes tend to be more expensive because they are specialized for high-voltage, high-current circuits requiring rapid turn-off times, and their availability is somewhat limited compared to Schottky types. Both diodes are commonly stocked by major electronic component distributors, but price sensitivity and supply chain factors favor Schottky diodes for cost-conscious designs.
Selecting the Right Diode for Your Application
Selecting the right diode depends on your application's switching speed and efficiency requirements. Schottky diodes offer low forward voltage drop and fast switching suitable for high-frequency circuits, while fast recovery diodes provide better reverse recovery times and higher voltage ratings ideal for power electronics. Understanding these key characteristics ensures optimal performance and longevity in your electronic design.
Schottky diode vs Fast recovery diode Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com