SMPS delivers high efficiency and compact size by switching current at high frequencies, while linear power supplies offer simpler design with lower noise but larger size and heat dissipation. Discover which power supply suits your needs best by exploring the detailed comparison in this article.
Table of Comparison
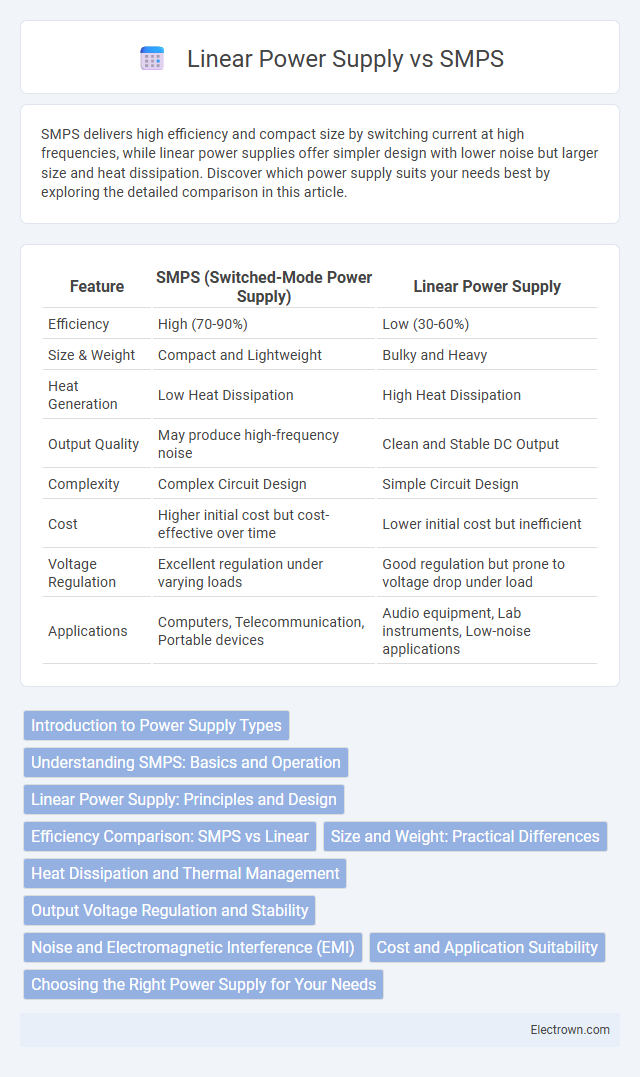
| Feature | SMPS (Switched-Mode Power Supply) | Linear Power Supply |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | High (70-90%) | Low (30-60%) |
| Size & Weight | Compact and Lightweight | Bulky and Heavy |
| Heat Generation | Low Heat Dissipation | High Heat Dissipation |
| Output Quality | May produce high-frequency noise | Clean and Stable DC Output |
| Complexity | Complex Circuit Design | Simple Circuit Design |
| Cost | Higher initial cost but cost-effective over time | Lower initial cost but inefficient |
| Voltage Regulation | Excellent regulation under varying loads | Good regulation but prone to voltage drop under load |
| Applications | Computers, Telecommunication, Portable devices | Audio equipment, Lab instruments, Low-noise applications |
Introduction to Power Supply Types
Switching Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) and Linear Power Supplies are two primary types used to convert electrical energy into usable voltage levels for electronic devices. SMPS offers high efficiency by rapidly switching on and off and regulating output via transformers and inductors, whereas Linear Power Supplies provide stable and low-noise output voltage through voltage regulation using linear components. Understanding the distinctions helps you choose the optimal power supply for your electronic applications based on efficiency, size, and noise requirements.
Understanding SMPS: Basics and Operation
Switched-Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) convert electrical power efficiently by rapidly switching components on and off, regulating voltage through high-frequency transformers and inductors. Unlike Linear power supplies that dissipate excess energy as heat, SMPS offers compact size, lighter weight, and better energy efficiency due to its pulse-width modulation (PWM) control. Understanding your SMPS operation helps optimize energy savings and thermal management in electronics applications.
Linear Power Supply: Principles and Design
Linear power supply operates by using a transformer to step down voltage, followed by rectification and filtering to produce a stable DC output with minimal ripple, ensuring clean and reliable power for sensitive electronics. Its design includes large heat sinks to dissipate excess energy as heat, resulting in lower efficiency but simpler circuitry and reduced electromagnetic interference. You benefit from consistent voltage regulation and superior noise performance, ideal for audio and precision measurement equipment.
Efficiency Comparison: SMPS vs Linear
Switch Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) typically offer efficiency rates between 70% to 90%, significantly higher than Linear Power Supplies, which generally operate around 40% to 60% efficiency due to energy lost as heat. This efficiency advantage of SMPS leads to lower electricity consumption and reduced heat generation, making it ideal for applications requiring energy conservation and compact design. When selecting a power supply for Your device, prioritizing SMPS can result in cost savings and improved thermal management.
Size and Weight: Practical Differences
SMPS (Switched-Mode Power Supply) is significantly smaller and lighter than a linear power supply due to its high-frequency operation and efficient components. This compact size is ideal for applications where space is limited or portability is essential. Your choice of power supply dramatically affects the overall design constraints, making SMPS preferable when minimizing size and weight is critical.
Heat Dissipation and Thermal Management
SMPS (Switched-Mode Power Supply) generates less heat compared to linear power supplies due to higher efficiency achieved by switching elements operating at high frequencies, reducing energy loss. Linear power supplies dissipate significant heat as they regulate voltage by dropping excess voltage as heat through resistive elements, requiring robust heat sinks for thermal management. Effective cooling is crucial for both types, but SMPS designs enable more compact, cooler operation that benefits Your device's overall thermal performance and reliability.
Output Voltage Regulation and Stability
Switch-mode power supplies (SMPS) provide superior output voltage regulation and stability due to their high-frequency switching operation, enabling precise voltage control and minimal ripple, even under varying load conditions. Linear power supplies rely on dissipative voltage regulation with larger heat generation, leading to less efficient voltage stability and more output voltage variation during load changes. The rapid feedback mechanisms in SMPS maintain consistent output voltage, making them ideal for sensitive electronic devices requiring tight voltage tolerances.
Noise and Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
SMPS (Switched-Mode Power Supply) generates higher noise and electromagnetic interference (EMI) due to its high-frequency switching operation, which can affect sensitive electronic components and communication signals. In contrast, linear power supplies produce minimal noise and EMI because they regulate voltage through simple, linear regulation without switching elements. For applications requiring clean power, your choice of a linear power supply can significantly reduce unwanted noise and EMI-related issues.
Cost and Application Suitability
Switch Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) offer higher efficiency and lower manufacturing costs, making them ideal for compact or portable electronic devices where energy conservation and size are critical. Linear power supplies, despite being less efficient and bulkier, provide cleaner and more stable output voltage, which suits applications requiring minimal electrical noise like audio equipment and sensitive laboratory instruments. Your choice between SMPS and linear power supply should consider budget constraints and the specific power quality needs of your device or system.
Choosing the Right Power Supply for Your Needs
Choosing the right power supply involves understanding the differences between SMPS and linear power supplies to match Your device's requirements. SMPS offers higher efficiency, compact size, and better heat dissipation, ideal for energy-sensitive applications and space-constrained setups. Linear power supplies provide cleaner output with minimal noise and stable voltage, making them suitable for sensitive analog equipment requiring precise, low-ripple power.
SMPS vs Linear power supply Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com