Z-source inverters offer a unique impedance network that enables both voltage boosting and buck-boost capabilities, unlike traditional VSI which can only step down voltage. Discover how your power conversion efficiency can improve by exploring the detailed comparison in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
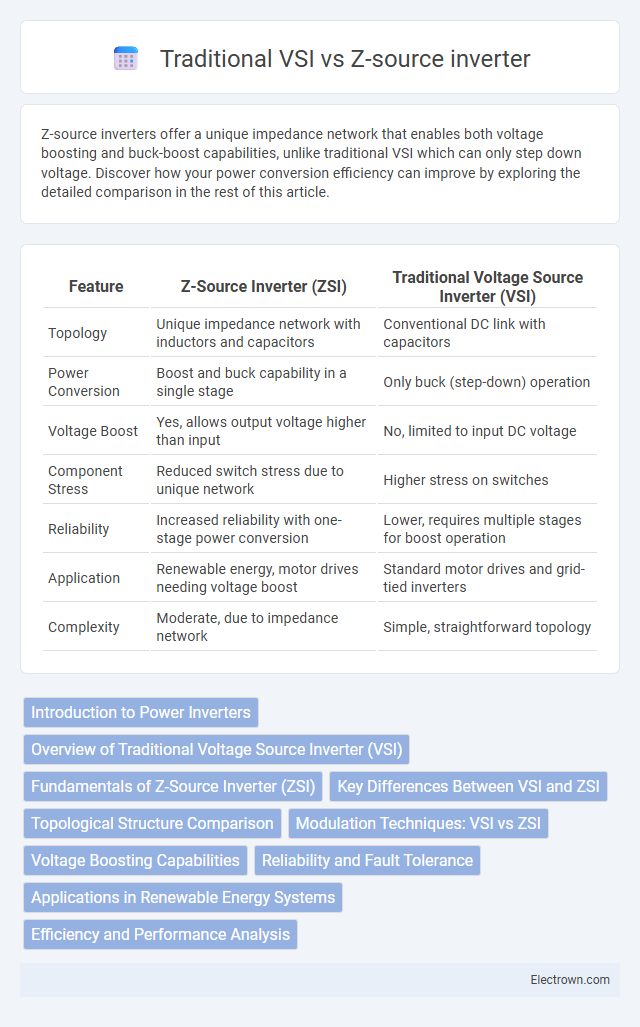
| Feature | Z-Source Inverter (ZSI) | Traditional Voltage Source Inverter (VSI) |
|---|---|---|
| Topology | Unique impedance network with inductors and capacitors | Conventional DC link with capacitors |
| Power Conversion | Boost and buck capability in a single stage | Only buck (step-down) operation |
| Voltage Boost | Yes, allows output voltage higher than input | No, limited to input DC voltage |
| Component Stress | Reduced switch stress due to unique network | Higher stress on switches |
| Reliability | Increased reliability with one-stage power conversion | Lower, requires multiple stages for boost operation |
| Application | Renewable energy, motor drives needing voltage boost | Standard motor drives and grid-tied inverters |
| Complexity | Moderate, due to impedance network | Simple, straightforward topology |
Introduction to Power Inverters
Power inverters convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) to power various electrical devices and systems. The Z-source inverter (ZSI) offers enhanced performance by integrating an impedance network, allowing it to boost voltage and provide ride-through capability without additional components. In contrast, traditional voltage source inverters (VSI) rely on separate DC voltage sources and typically require extra circuitry for voltage boosting, limiting their efficiency and adaptability.
Overview of Traditional Voltage Source Inverter (VSI)
Traditional Voltage Source Inverters (VSIs) convert DC power into AC power using a fixed DC voltage input and a switching network to generate a sinusoidal output waveform. These inverters have a simpler structure but suffer from limited voltage boosting capabilities and poor reliability under voltage sags or transients. Your choice between VSIs and advanced options like Z-source inverters depends on the need for voltage buck-boost capability and enhanced fault tolerance.
Fundamentals of Z-Source Inverter (ZSI)
The Z-source inverter (ZSI) integrates an impedance network composed of inductors and capacitors between the power source and inverter bridge, enabling both buck and boost operations in a single stage. Unlike traditional voltage source inverters (VSI) that rely on a DC-link capacitor and separate boost converters for voltage enhancement, ZSI provides enhanced voltage ride-through capability and improved reliability. The unique shoot-through state in ZSI prevents short circuits while allowing energy storage components to boost the DC voltage, enhancing system efficiency and reducing component count.
Key Differences Between VSI and ZSI
Z-source inverters (ZSI) feature a unique impedance network that allows buck-boost capabilities, unlike traditional voltage source inverters (VSI) which only provide step-down voltage conversion. Your system benefits from ZSI's improved reliability and ability to handle shoot-through states, enhancing power conversion efficiency and extending device lifespan. VSIs operate with simpler circuitry but lack the ZSI's inherent fault tolerance and voltage boost functionality.
Topological Structure Comparison
Z-source inverters feature a unique impedance network consisting of inductors and capacitors between the DC source and inverter, enabling both voltage buck and boost capabilities within a single stage. Traditional Voltage Source Inverters (VSI) rely on a direct DC link capacitor and can only step down voltage, lacking the Z-source's ability to handle voltage sags and generate higher voltage levels without additional converters. Your selection between these topologies should consider the Z-source inverter's enhanced voltage ride-through capability and simpler structure for applications requiring voltage boost functionality.
Modulation Techniques: VSI vs ZSI
Voltage Source Inverters (VSI) typically employ Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) techniques such as Sinusoidal PWM (SPWM) and Space Vector PWM (SVPWM) to control output voltage and frequency, providing precise waveform control. Z-Source Inverters (ZSI) utilize similar PWM strategies but benefit from the unique impedance network that enables voltage boost capabilities without the need for a DC-DC converter stage. The modulation of ZSI involves controlling shoot-through states to enhance voltage gain and improve reliability, differentiating it from traditional VSI modulation approaches.
Voltage Boosting Capabilities
Z-source inverters provide inherent voltage boosting capabilities through their unique impedance network, enabling them to produce output voltages higher than the input DC supply without the need for additional converters. Traditional Voltage Source Inverters (VSIs) rely on the input DC voltage level and cannot boost voltage beyond this limit without external devices such as DC-DC converters. The Z-source inverter's ability to boost voltage improves system efficiency and power density in renewable energy applications and electric vehicle drives.
Reliability and Fault Tolerance
Z-source inverters exhibit higher reliability and fault tolerance compared to traditional Voltage Source Inverters (VSI) due to their unique impedance network that allows enhanced ride-through capability during voltage sags and shoot-through faults. This impedance network prevents device breakdown by blocking shoot-through currents, which traditional VSIs cannot tolerate without damage. Consequently, Z-source inverters provide more robust performance in harsh operating conditions, reducing downtime and maintenance needs in power conversion applications.
Applications in Renewable Energy Systems
Z-source inverters offer enhanced reliability and efficiency in renewable energy systems by enabling buck-boost capability, which allows direct DC voltage boosting without additional converters. Traditional Voltage Source Inverters (VSIs) often require extra DC-DC converters for voltage regulation, increasing system complexity and losses in applications like solar photovoltaic and wind power integration. Your renewable energy setups can benefit from Z-source inverters' unique impedance network that provides better voltage sag ride-through and higher power quality compared to conventional VSIs.
Efficiency and Performance Analysis
Z-source inverters offer higher efficiency and improved performance compared to traditional voltage source inverters (VSI) due to their unique impedance network, which enables buck-boost capability and reduces switching losses. Your system can achieve better voltage regulation and higher reliability under varying load conditions with Z-source technology, especially in renewable energy applications. Performance analysis highlights that Z-source inverters maintain stable output voltage and current waveforms while minimizing harmonic distortion, outperforming conventional VSI designs.
Z-source inverter vs Traditional VSI Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com