SiC diodes offer superior performance over Si diodes, including higher efficiency, faster switching speeds, and greater thermal stability, making them ideal for high-power and high-frequency applications. Explore the rest of the article to discover how choosing the right diode can enhance Your electronic system's reliability and efficiency.
Table of Comparison
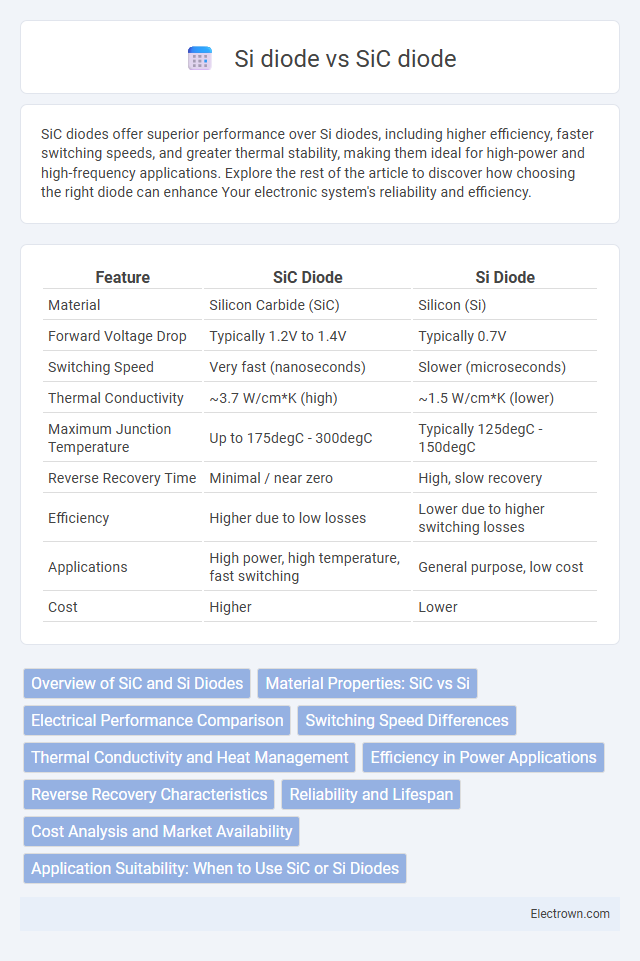
| Feature | SiC Diode | Si Diode |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Silicon (Si) |
| Forward Voltage Drop | Typically 1.2V to 1.4V | Typically 0.7V |
| Switching Speed | Very fast (nanoseconds) | Slower (microseconds) |
| Thermal Conductivity | ~3.7 W/cm*K (high) | ~1.5 W/cm*K (lower) |
| Maximum Junction Temperature | Up to 175degC - 300degC | Typically 125degC - 150degC |
| Reverse Recovery Time | Minimal / near zero | High, slow recovery |
| Efficiency | Higher due to low losses | Lower due to higher switching losses |
| Applications | High power, high temperature, fast switching | General purpose, low cost |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Overview of SiC and Si Diodes
Silicon Carbide (SiC) diodes offer superior performance compared to traditional Silicon (Si) diodes due to their higher breakdown voltage, faster switching speeds, and better thermal conductivity. SiC diodes are ideal for high-power and high-temperature applications, reducing energy losses and improving efficiency. Your choice between SiC and Si diodes depends on the specific electrical and thermal requirements of your device or system.
Material Properties: SiC vs Si
Silicon Carbide (SiC) diodes exhibit superior material properties compared to Silicon (Si) diodes, including higher breakdown electric field, greater thermal conductivity, and wider bandgap energy. These characteristics enable SiC diodes to operate efficiently at higher voltages, temperatures, and switching frequencies, enhancing performance in demanding power electronics applications. Your choice of SiC over Si diodes can result in improved reliability and reduced energy losses, crucial for advanced semiconductor devices.
Electrical Performance Comparison
SiC diodes exhibit superior electrical performance compared to Si diodes, characterized by higher breakdown voltage and faster switching speeds, which result in reduced power losses and improved efficiency in power conversion applications. The wide bandgap of SiC enables higher temperature operation and lower reverse recovery charge, minimizing energy dissipation and thermal management requirements. Consequently, SiC diodes are favored for high-voltage, high-frequency environments where enhanced electrical robustness and reliability are critical.
Switching Speed Differences
SiC diodes exhibit significantly faster switching speeds than Si diodes due to their wide bandgap semiconductor properties, which reduce charge carrier recombination and energy loss during transitions. This results in lower switching losses, improved efficiency, and enhanced performance in high-frequency applications such as power converters and inverters. Your circuits benefit from reduced heat generation and smaller passive components, enabling more compact and reliable designs.
Thermal Conductivity and Heat Management
Silicon Carbide (SiC) diodes exhibit significantly higher thermal conductivity, typically around 3.7 W/cm*K, compared to Silicon (Si) diodes, which have thermal conductivity near 1.5 W/cm*K, enabling superior heat dissipation. This enhanced thermal conductivity allows SiC diodes to operate efficiently at higher temperatures and reduces the need for bulky cooling systems. Effective heat management in SiC devices leads to improved reliability and performance in high-power and high-frequency applications.
Efficiency in Power Applications
SiC diodes exhibit significantly higher efficiency in power applications compared to traditional Si diodes due to their lower forward voltage drop and faster switching speeds. This results in reduced power losses and enhanced thermal management, enabling devices to operate at higher temperatures with improved reliability. Consequently, SiC diodes are preferred in high-performance applications such as electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and industrial power supplies.
Reverse Recovery Characteristics
SiC diodes exhibit significantly faster reverse recovery times compared to Si diodes, resulting in lower reverse recovery charge and reduced switching losses. This makes SiC diodes ideal for high-frequency and high-efficiency power conversion applications. Your choice of SiC diodes over traditional Si diodes can greatly enhance performance in circuits requiring rapid switching and minimal energy dissipation during reverse recovery.
Reliability and Lifespan
SiC diodes exhibit superior reliability and longer lifespan compared to traditional Si diodes due to their high thermal conductivity and robust material properties. These characteristics allow SiC diodes to operate efficiently under higher temperatures and harsh conditions, reducing failure rates and maintenance needs. Your systems benefit from SiC diodes' enhanced durability, ensuring sustained performance and lower replacement costs over time.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
SiC diodes typically have a higher upfront cost compared to traditional Si diodes due to advanced manufacturing processes and raw material expenses. Despite the premium price, SiC diodes offer superior efficiency and thermal performance, leading to long-term savings in power electronics applications. Your choice should consider SiC diodes' increasing market availability, as broader adoption is driving prices down and improving accessibility.
Application Suitability: When to Use SiC or Si Diodes
SiC diodes excel in high-voltage, high-frequency, and high-temperature applications such as electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and industrial power supplies due to their superior efficiency and thermal stability. Si diodes remain suitable for low to medium voltage and cost-sensitive applications like consumer electronics and standard rectification tasks, where switching speed and heat dissipation demands are moderate. Choose SiC diodes for enhanced performance in demanding environments, while Si diodes provide reliable, cost-effective solutions for everyday electronic devices.
SiC diode vs Si diode Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com