Snubberless triacs offer improved switching performance and reduced electromagnetic interference by eliminating the need for an external snubber circuit, making them more reliable in sensitive electronic applications. Discover how choosing between snubberless and standard triacs can impact your device's efficiency and durability in the full article.
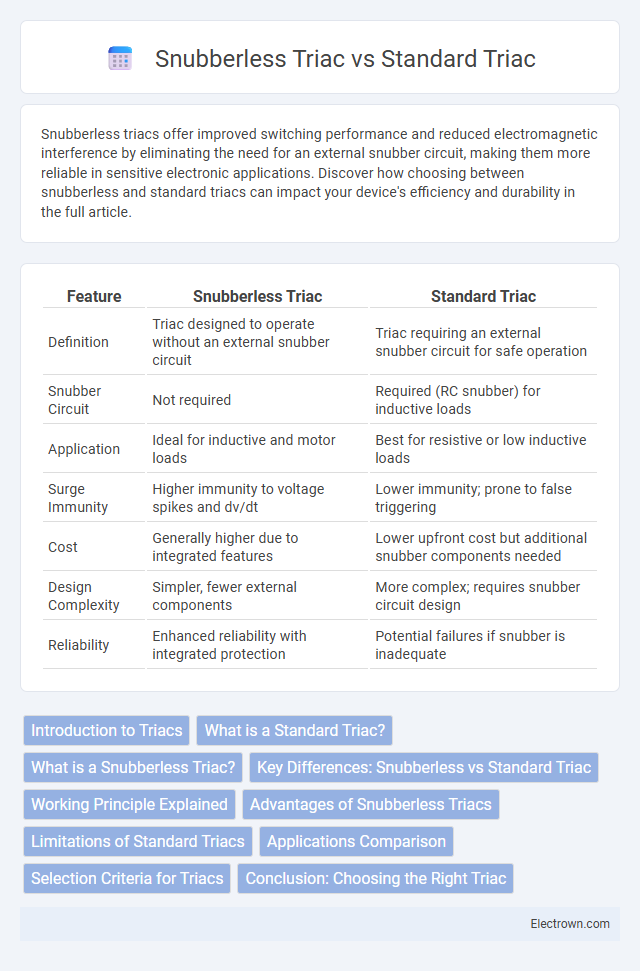
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Snubberless Triac | Standard Triac |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Triac designed to operate without an external snubber circuit | Triac requiring an external snubber circuit for safe operation |
| Snubber Circuit | Not required | Required (RC snubber) for inductive loads |
| Application | Ideal for inductive and motor loads | Best for resistive or low inductive loads |
| Surge Immunity | Higher immunity to voltage spikes and dv/dt | Lower immunity; prone to false triggering |
| Cost | Generally higher due to integrated features | Lower upfront cost but additional snubber components needed |
| Design Complexity | Simpler, fewer external components | More complex; requires snubber circuit design |
| Reliability | Enhanced reliability with integrated protection | Potential failures if snubber is inadequate |
Introduction to Triacs
Triacs are semiconductor devices used to control AC power by switching currents in both directions. Standard triacs often require snubber circuits to prevent false triggering caused by voltage spikes or rapid changes in current. Snubberless triacs incorporate advanced gate designs that enable reliable operation without external snubber components, improving circuit simplicity and reducing overall component count.
What is a Standard Triac?
A standard triac is a semiconductor device used for controlling AC power by switching electrical currents in both directions. It requires an external snubber circuit to protect it from voltage spikes and ensure stable operation during switching transitions. Compared to snubberless triacs, standard triacs have slower switching speeds and are more sensitive to inductive loads, impacting their performance and durability.
What is a Snubberless Triac?
A Snubberless Triac is a semiconductor device designed to switch AC power without the need for an external snubber circuit, which is typically used to protect Standard Triacs from voltage spikes and noise. It integrates improved gate sensitivity and robust dv/dt (rate of voltage change) handling capabilities, making it suitable for applications with inductive loads and minimizing electromagnetic interference. This design enhances durability and reliability in motor control, lighting, and heater circuits compared to conventional Standard Triacs that require additional snubber components.
Key Differences: Snubberless vs Standard Triac
Snubberless triacs feature built-in dv/dt protection, eliminating the need for external snubber circuits commonly required by standard triacs to prevent false triggering from voltage spikes. Standard triacs typically demand additional snubber components for reliable operation in inductive loads, while snubberless triacs ensure improved reliability and simplified circuit design. Your choice between these components hinges on the application's sensitivity to transient voltages and the desire for reduced component count.
Working Principle Explained
Snubberless triacs operate without an external snubber circuit due to their built-in sensitivities to voltage and current changes, enabling them to switch loads more efficiently and reduce electromagnetic interference. Standard triacs require an external snubber circuit to manage voltage spikes and prevent false triggering, ensuring stable operation in inductive load applications. Your choice depends on the specific load characteristics and circuit complexity, with snubberless triacs simplifying design in many cases.
Advantages of Snubberless Triacs
Snubberless triacs eliminate the need for external snubber circuits, reducing component count and overall system cost. They offer improved reliability and simpler circuit design by integrating built-in gate triggering and dv/dt immunity. Enhanced switching performance in inductive loads and lower electromagnetic interference (EMI) make snubberless triacs ideal for modern AC power control applications.
Limitations of Standard Triacs
Standard triacs often face limitations such as sensitivity to voltage spikes and the need for external snubber circuits to prevent false triggering and device damage. These triacs struggle with high dv/dt conditions, leading to unintended switching and reduced reliability in complex AC loads. You can overcome these issues by opting for snubberless triacs, which integrate built-in protection to enhance performance and durability.
Applications Comparison
Snubberless triacs are preferred in applications involving inductive loads and environments with high electromagnetic interference due to their integrated snubber circuitry, which enhances switching reliability and reduces external component count. Standard triacs require external snubber circuits for protection against voltage spikes and are commonly used in resistive load applications such as light dimmers or simple motor controls. The choice between snubberless and standard triacs depends on the complexity of the load and the need for compact, robust designs in industrial automation or consumer electronics.
Selection Criteria for Triacs
Selection criteria for triacs include voltage and current ratings, switching speed, and snubber circuit requirements. Snubberless triacs are preferred when operating in inductive loads with built-in dV/dt immunity, reducing the need for external snubber circuits and improving reliability. Standard triacs require additional snubber components to handle high dV/dt conditions, making them suitable for less demanding applications or where cost constraints are prioritized.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Triac
Snubberless triacs offer superior performance in circuits with inductive loads by eliminating the need for external snubber circuits, reducing component count and increasing reliability. Standard triacs require snubber networks to prevent false triggering and manage voltage spikes, making them suitable for resistive loads and simpler applications. Selecting the right triac depends on load type and circuit complexity, where snubberless triacs are preferred for cost-effective, compact designs handling inductive loads, while standard triacs remain effective for basic resistive switching.
Snubberless triac vs Standard triac Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com