Isolated gate drivers provide electrical isolation between control and power circuits, enhancing safety and noise immunity, while non-isolated gate drivers directly connect both circuits, offering simpler design and lower cost. Explore the rest of the article to understand which gate driver best suits your application's needs.
Table of Comparison
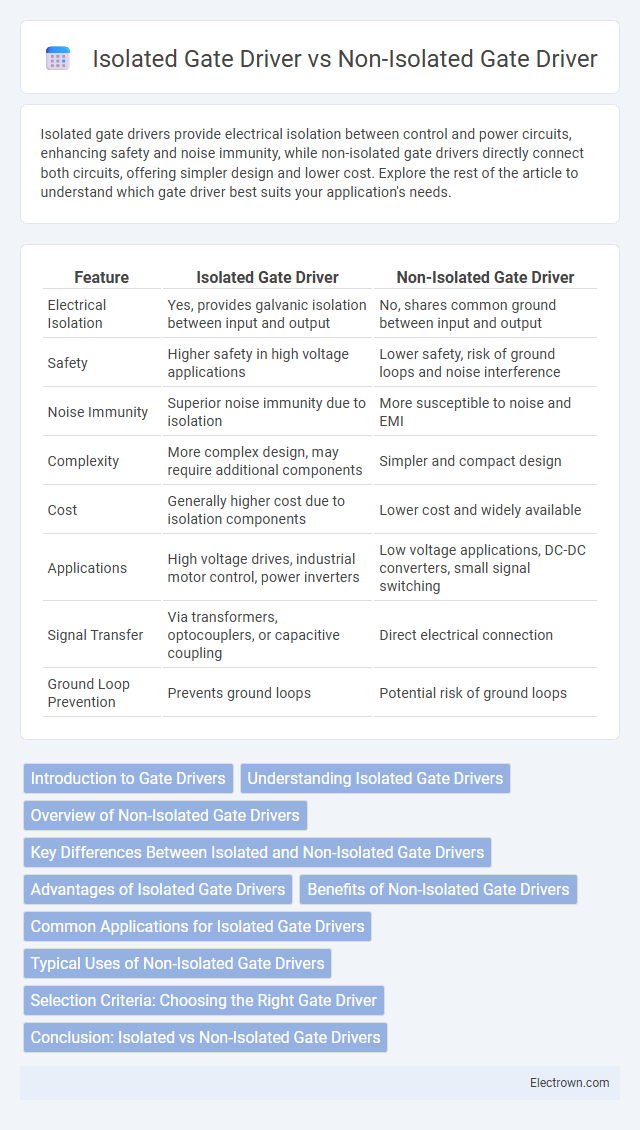
| Feature | Isolated Gate Driver | Non-Isolated Gate Driver |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Isolation | Yes, provides galvanic isolation between input and output | No, shares common ground between input and output |
| Safety | Higher safety in high voltage applications | Lower safety, risk of ground loops and noise interference |
| Noise Immunity | Superior noise immunity due to isolation | More susceptible to noise and EMI |
| Complexity | More complex design, may require additional components | Simpler and compact design |
| Cost | Generally higher cost due to isolation components | Lower cost and widely available |
| Applications | High voltage drives, industrial motor control, power inverters | Low voltage applications, DC-DC converters, small signal switching |
| Signal Transfer | Via transformers, optocouplers, or capacitive coupling | Direct electrical connection |
| Ground Loop Prevention | Prevents ground loops | Potential risk of ground loops |
Introduction to Gate Drivers
Gate drivers are essential components in power electronics, enabling efficient switching of power transistors such as MOSFETs and IGBTs. Isolated gate drivers provide galvanic isolation between input and output, enhancing safety and noise immunity, while non-isolated gate drivers offer direct electrical coupling, often resulting in faster signal transmission and lower cost. Understanding your application's voltage isolation requirements helps determine the optimal gate driver choice for reliable and efficient performance.
Understanding Isolated Gate Drivers
Isolated gate drivers provide electrical isolation between the control circuitry and the power stage, enhancing safety and reducing noise interference in high-voltage applications. Non-isolated gate drivers lack this separation, making them suitable for low-voltage or less complex systems where isolation is not critical. Understanding isolated gate drivers is essential for designing reliable power electronics systems that require protection against voltage spikes and ground loops.
Overview of Non-Isolated Gate Drivers
Non-isolated gate drivers share a common reference ground with the power stage, enabling direct control signals and simpler circuit design. They are typically used in low- to medium-voltage applications where the ground potential difference is minimal, allowing efficient switching performance without isolation barriers. Non-isolated gate drivers offer cost-effective solutions with reduced complexity but lack the noise immunity and safety benefits provided by isolated counterparts.
Key Differences Between Isolated and Non-Isolated Gate Drivers
Isolated gate drivers provide galvanic isolation between the control and power circuits, enhancing safety and noise immunity in high-voltage applications, whereas non-isolated gate drivers lack this separation, making them suitable for low-voltage or single-ground systems. Isolated drivers Typically incorporate transformers or optocouplers to achieve isolation, effectively preventing ground loop issues and voltage spikes from damaging control electronics. Non-isolated gate drivers offer simpler design and lower cost but may suffer from interference and signal integrity problems in high-voltage environments.
Advantages of Isolated Gate Drivers
Isolated gate drivers provide superior electrical isolation between the control and power circuits, significantly enhancing safety and reducing the risk of ground loop interference. They improve signal integrity and protect sensitive components from high voltage transients, making them ideal for applications in industrial automation and renewable energy systems. Your system benefits from enhanced reliability and noise immunity when using isolated gate drivers compared to non-isolated alternatives.
Benefits of Non-Isolated Gate Drivers
Non-isolated gate drivers offer significant benefits such as simpler circuit design, lower cost, and improved efficiency due to direct reference to the same ground as the power stage. These drivers reduce complexity and size by eliminating the need for isolation components like transformers or optocouplers, which is ideal for applications with a common ground. Your system can achieve faster switching speeds and enhanced performance with non-isolated gate drivers in low-voltage, single-ended power configurations.
Common Applications for Isolated Gate Drivers
Isolated gate drivers are predominantly used in high-voltage power conversion applications, such as motor drives, renewable energy systems like solar inverters, and industrial power supplies, where electrical isolation is critical for safety and noise immunity. They enable reliable signal transmission between control circuits and power devices in environments with significant voltage differences, enhancing system protection and performance. Non-isolated gate drivers, in contrast, are typically found in low-voltage, low-noise environments where isolation is not required.
Typical Uses of Non-Isolated Gate Drivers
Non-isolated gate drivers are typically used in applications where the driver and power stage share a common ground, such as in DC-DC converters, motor control circuits, and power inverters. These drivers provide efficient switching control for power transistors like MOSFETs and IGBTs without the complexity of galvanic isolation. Your choice of a non-isolated gate driver is ideal when cost, size, and simplicity are priorities over isolation requirements.
Selection Criteria: Choosing the Right Gate Driver
Selecting the right gate driver depends on your application's voltage isolation requirements and system complexity. Isolated gate drivers are essential in high-voltage environments, providing galvanic isolation to protect sensitive control circuitry and ensure signal integrity. Non-isolated gate drivers suit low-voltage, single-ground systems where simplicity and cost-effectiveness are priorities.
Conclusion: Isolated vs Non-Isolated Gate Drivers
Isolated gate drivers provide enhanced safety and noise immunity by electrically separating the control and power circuits, making them ideal for high-voltage applications and complex power systems. Non-isolated gate drivers offer simpler design and lower cost but lack isolation, which may expose Your system to noise interference and safety risks in sensitive environments. Choosing between isolated and non-isolated gate drivers depends on Your specific application requirements, balancing isolation needs, system complexity, and budget constraints.
isolated gate driver vs non-isolated gate driver Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com