SPWM inverters produce smooth, pure sine wave output ideal for sensitive electronics, while square wave inverters generate a rougher waveform that can cause noise and potential damage to devices. Discover how choosing the right inverter can protect Your equipment and improve efficiency by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
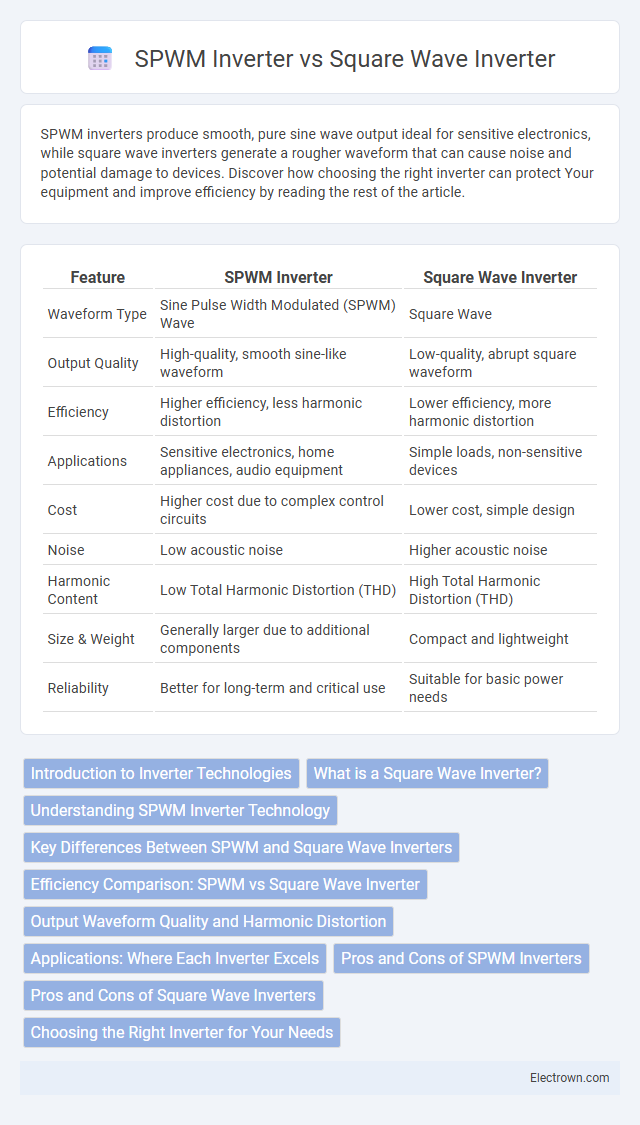
| Feature | SPWM Inverter | Square Wave Inverter |
|---|---|---|
| Waveform Type | Sine Pulse Width Modulated (SPWM) Wave | Square Wave |
| Output Quality | High-quality, smooth sine-like waveform | Low-quality, abrupt square waveform |
| Efficiency | Higher efficiency, less harmonic distortion | Lower efficiency, more harmonic distortion |
| Applications | Sensitive electronics, home appliances, audio equipment | Simple loads, non-sensitive devices |
| Cost | Higher cost due to complex control circuits | Lower cost, simple design |
| Noise | Low acoustic noise | Higher acoustic noise |
| Harmonic Content | Low Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) | High Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) |
| Size & Weight | Generally larger due to additional components | Compact and lightweight |
| Reliability | Better for long-term and critical use | Suitable for basic power needs |
Introduction to Inverter Technologies
Sinusoidal Pulse Width Modulation (SPWM) inverters generate outputs that closely mimic pure sine waves by modulating pulse width to control voltage and frequency, enhancing efficiency and reducing harmonic distortion. Square wave inverters produce a simpler, less refined output with abrupt voltage transitions, causing higher harmonic content and potential damage to sensitive electronic devices. SPWM technology is preferred for applications requiring clean power and improved performance, while square wave inverters are limited to basic, cost-sensitive uses.
What is a Square Wave Inverter?
A Square Wave Inverter converts DC power into a basic square wave AC output, characterized by abrupt voltage transitions between high and low states. This type of inverter is simple and cost-effective but generates higher harmonic distortion, causing inefficient operation and potential interference with sensitive electronic devices. Compared to SPWM inverters, square wave inverters produce less smooth and less sinusoidal output, resulting in reduced compatibility with most household appliances.
Understanding SPWM Inverter Technology
SPWM (Sinusoidal Pulse Width Modulation) inverter technology produces a smooth and efficient output waveform by modulating pulse widths to approximate a sine wave, reducing harmonic distortion compared to the harsh, stepped output of square wave inverters. This results in improved power quality, increased device compatibility, and enhanced energy efficiency, especially critical for sensitive electronics and renewable energy systems. Understanding SPWM inverters allows you to select more reliable solutions that ensure stable operation and longer equipment lifespan.
Key Differences Between SPWM and Square Wave Inverters
SPWM (Sinusoidal Pulse Width Modulation) inverters produce a smooth, sinusoidal output waveform ideal for sensitive electronics by modulating the width of pulses to simulate sine waves, while square wave inverters generate a simple, abrupt on/off waveform causing more harmonic distortion and potential damage to appliances. SPWM inverters offer higher efficiency, reduced electromagnetic interference, and better power quality compared to the cheaper but less efficient square wave inverters. Your choice between these two impacts device performance, energy consumption, and lifespan, especially in applications demanding stable and clean power supply.
Efficiency Comparison: SPWM vs Square Wave Inverter
SPWM inverters provide significantly higher efficiency compared to square wave inverters due to their ability to generate a smooth sinusoidal output waveform, resulting in reduced harmonic distortion and lower power loss in connected devices. Square wave inverters produce a waveform with abrupt transitions, causing increased heat dissipation and inefficiencies in inductive loads such as motors and transformers. Consequently, SPWM technology enhances overall system performance and energy savings in applications requiring clean power output.
Output Waveform Quality and Harmonic Distortion
Sinusoidal Pulse Width Modulation (SPWM) inverters produce a smooth, near-sinusoidal output waveform with low harmonic distortion, enhancing the efficiency and lifespan of connected devices. Square wave inverters generate a simple, stepped waveform that causes higher harmonic distortion, which can lead to overheating and reduced performance in sensitive equipment. Choosing an SPWM inverter ensures superior output waveform quality, protecting your appliances from electrical noise and potential damage.
Applications: Where Each Inverter Excels
SPWM inverters excel in applications requiring high-quality, low-distortion AC power such as sensitive electronics, renewable energy systems, and precision motor drives, providing efficient and smooth voltage output. Square wave inverters are suitable for simple, cost-effective applications like basic lighting, heaters, and some tools where waveform purity is less critical. Your choice depends on whether the application demands high power quality or prioritizes affordability and simplicity.
Pros and Cons of SPWM Inverters
SPWM (Sinusoidal Pulse Width Modulation) inverters offer high efficiency and produce a nearly pure sine wave output, reducing harmonic distortion and minimizing interference with sensitive electronic devices. Their complex design and higher cost compared to square wave inverters make them less suitable for low-budget or simple applications. SPWM inverters also generate less heat and noise, enhancing the overall reliability and lifespan of connected equipment.
Pros and Cons of Square Wave Inverters
Square wave inverters offer a simple design and lower cost compared to SPWM inverters, making them suitable for basic power applications with resistive loads. However, they produce higher harmonic distortion, leading to inefficient power delivery and potential damage to sensitive electronic devices or inductive loads. Your choice depends on whether cost savings or power quality holds greater priority for your application.
Choosing the Right Inverter for Your Needs
Selecting the right inverter depends on the quality of output waveform required for your devices; SPWM (Sinusoidal Pulse Width Modulation) inverters produce a smooth sine wave that closely mimics utility power, making them ideal for sensitive electronics and high-efficiency applications. In contrast, square wave inverters generate a simpler, less refined waveform suitable for basic tools and appliances that do not require precise power quality. Evaluating device compatibility, power efficiency, and total harmonic distortion levels is crucial when deciding between SPWM and square wave inverters for optimal performance and longevity.
spwm inverter vs square wave inverter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com