Full bridge rectifiers provide higher efficiency and better voltage output by converting both halves of the AC waveform into DC, while half bridge rectifiers use fewer components and are simpler but with lower output voltage. Discover how the differences in design affect your power supply's performance by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
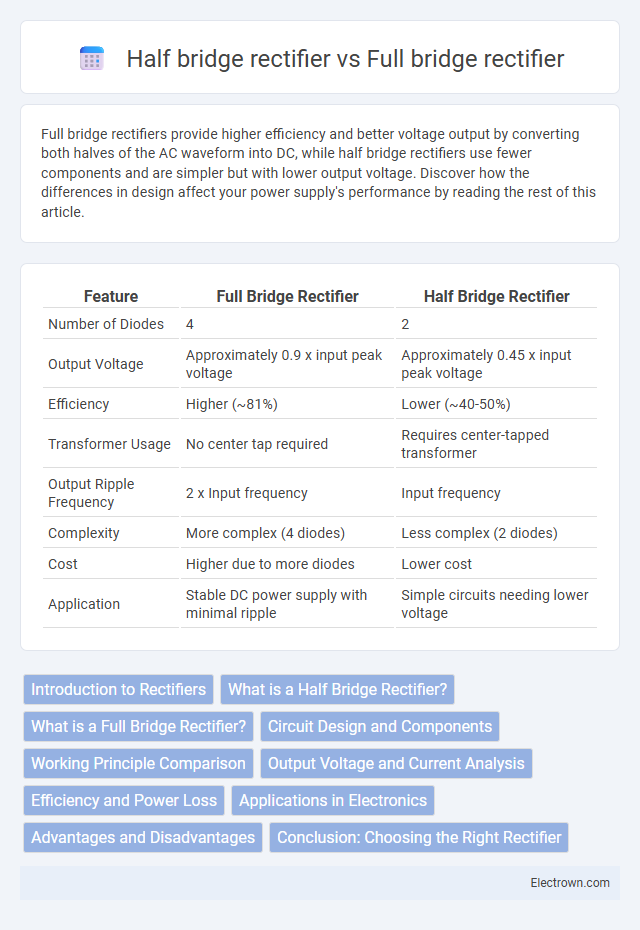
| Feature | Full Bridge Rectifier | Half Bridge Rectifier |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Diodes | 4 | 2 |
| Output Voltage | Approximately 0.9 x input peak voltage | Approximately 0.45 x input peak voltage |
| Efficiency | Higher (~81%) | Lower (~40-50%) |
| Transformer Usage | No center tap required | Requires center-tapped transformer |
| Output Ripple Frequency | 2 x Input frequency | Input frequency |
| Complexity | More complex (4 diodes) | Less complex (2 diodes) |
| Cost | Higher due to more diodes | Lower cost |
| Application | Stable DC power supply with minimal ripple | Simple circuits needing lower voltage |
Introduction to Rectifiers
Rectifiers convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) and are essential in power supplies for electronic devices. Full bridge rectifiers use four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration, enabling them to convert the entire AC waveform into DC, resulting in higher efficiency and lower ripple voltage compared to half bridge rectifiers. Half bridge rectifiers, employing only two diodes, rectify only one half of the AC waveform, producing a lower average output voltage with higher ripple, making them suitable for simpler, lower-power applications.
What is a Half Bridge Rectifier?
A Half Bridge Rectifier is an electronic circuit that converts alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) using two diodes arranged to conduct during opposite halves of the AC cycle. It is commonly used in power supply applications where moderate voltage levels and efficiency are required, offering a simpler and cost-effective design compared to a Full Bridge Rectifier. Your choice of a Half Bridge Rectifier suits applications needing reduced component count and lower voltage stress on diodes.
What is a Full Bridge Rectifier?
A Full Bridge Rectifier is an electronic circuit that converts alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) using four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration, enabling both halves of the AC waveform to be utilized efficiently. This design provides higher output voltage and improved power delivery compared to a Half Bridge Rectifier, which only uses two diodes and rectifies one half of the AC signal. Understanding this, you can optimize your power supply design for better efficiency and performance in electronic devices.
Circuit Design and Components
Full bridge rectifiers utilize four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration to convert AC to DC, enhancing output efficiency by allowing current flow during both halves of the AC cycle. Half bridge rectifiers employ only two diodes, resulting in simpler circuit design but lower efficiency and increased ripple voltage in the output. The full bridge topology demands more components and a slightly more complex design but offers better transformer utilization and smoother DC output compared to the half bridge rectifier.
Working Principle Comparison
A full bridge rectifier uses four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration to convert the entire input AC waveform into pulsating DC, allowing both halves of the AC signal to be utilized, resulting in higher efficiency and smoother output. In contrast, a half bridge rectifier employs two diodes, rectifying only one half of the AC waveform, which leads to lower output voltage and increased ripple. The full bridge design ensures continuous current flow through the load during both halves of the cycle, whereas the half bridge allows current flow during only one half, impacting overall performance and efficiency.
Output Voltage and Current Analysis
Full bridge rectifiers provide higher output voltage, nearly equal to the peak input voltage minus diode drops, offering full-wave rectification that delivers continuous current with less ripple compared to half bridge rectifiers. Half bridge rectifiers produce approximately half the output voltage of full bridge circuits due to their two-diode configuration and yield lower current capability and higher ripple. Your choice depends on the required voltage and current levels, with full bridge rectifiers preferred for maximum output efficiency and smoother DC delivery.
Efficiency and Power Loss
Full bridge rectifiers offer higher efficiency compared to half bridge rectifiers by utilizing four diodes to conduct during both half cycles of the AC input, resulting in reduced ripple and better transformer utilization. Power loss in full bridge rectifiers is moderately higher due to the voltage drop across two diodes per conduction path, whereas half bridge rectifiers have lower diode conduction losses with only one diode conducting per half cycle but suffer from decreased output voltage and increased ripple. Overall, the improved output waveform quality and voltage utilization of full bridge rectifiers often justify the slight increase in power loss for applications requiring higher efficiency.
Applications in Electronics
Full bridge rectifiers are widely used in power supply units for converting AC to DC in devices requiring higher efficiency and lower ripple voltage, such as computer power supplies and battery charging systems. Half bridge rectifiers are common in low-power applications and signal demodulation circuits where simplicity and cost-effectiveness are prioritized, like small adapters and audio equipment. Both rectifiers play crucial roles in electronics by enabling precise control of DC output for various industrial and consumer electronic devices.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Full bridge rectifiers offer higher efficiency and better transformer utilization due to using four diodes, providing full-wave rectification with reduced ripple voltage for smoother DC output. Half bridge rectifiers require fewer components and are simpler to design but deliver lower output voltage and higher ripple, which may affect your power supply quality. Choosing between them depends on your application's need for voltage stability versus component cost and circuit simplicity.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rectifier
Full bridge rectifiers provide higher efficiency and smoother DC output due to their utilization of four diodes, making them ideal for applications requiring stable voltage and low ripple. Half bridge rectifiers, using only two diodes, offer simpler design and lower cost but with increased ripple and less efficient conduction. Your choice depends on the specific power requirements, space constraints, and cost considerations of your electronic circuit.
Full bridge vs Half bridge rectifier Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com