Reset winding and clamp snubber techniques both serve to protect electronic circuits from voltage spikes, with reset windings primarily used in transformers to quickly dissipate stored energy, while clamp snubbers limit voltage by diverting excess energy through resistors and diodes. Understanding how each method impacts your circuit's performance can help you make an informed decision; explore the full article to dive deeper into their applications and benefits.
Table of Comparison
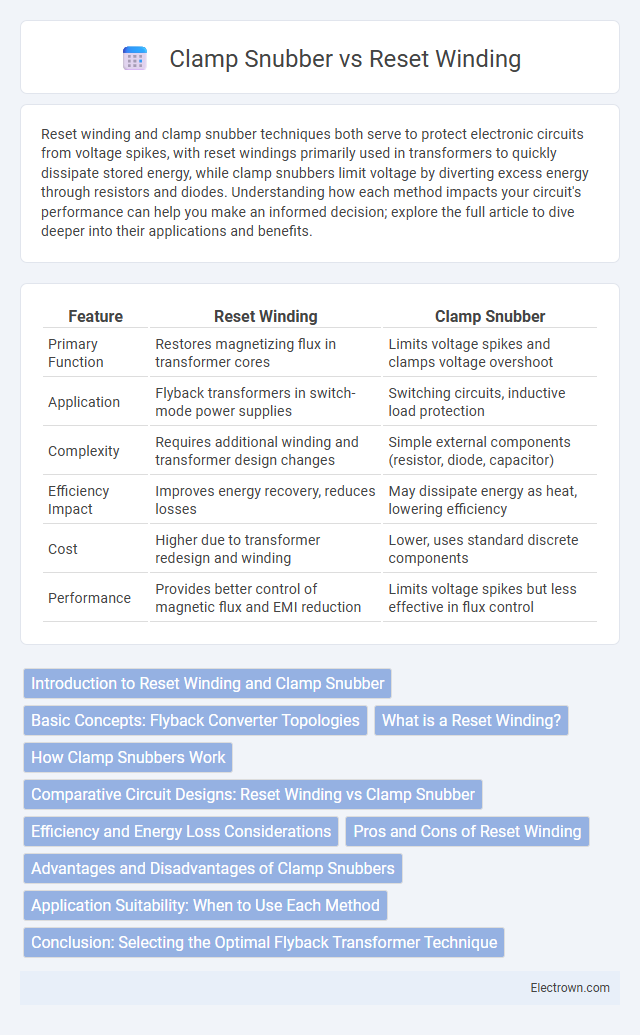
| Feature | Reset Winding | Clamp Snubber |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Restores magnetizing flux in transformer cores | Limits voltage spikes and clamps voltage overshoot |
| Application | Flyback transformers in switch-mode power supplies | Switching circuits, inductive load protection |
| Complexity | Requires additional winding and transformer design changes | Simple external components (resistor, diode, capacitor) |
| Efficiency Impact | Improves energy recovery, reduces losses | May dissipate energy as heat, lowering efficiency |
| Cost | Higher due to transformer redesign and winding | Lower, uses standard discrete components |
| Performance | Provides better control of magnetic flux and EMI reduction | Limits voltage spikes but less effective in flux control |
Introduction to Reset Winding and Clamp Snubber
Reset winding is a specialized coil in transformers or inductors designed to discharge magnetic energy and reset the core flux, improving efficiency and reducing core saturation. Clamp snubber circuits protect power electronics by absorbing voltage spikes generated during switching, thereby minimizing stress on components and enhancing reliability. Both techniques serve crucial roles in managing transient energy and maintaining stable operation in power electronic systems.
Basic Concepts: Flyback Converter Topologies
Reset winding in flyback converters functions to discharge the transformer's magnetic energy, ensuring core flux reset and preventing saturation during the off-cycle. Clamp snubber circuits absorb the voltage spike generated when the switch turns off, protecting components from overvoltage stress and improving reliability. Understanding these basic concepts helps optimize Your flyback converter topology for efficient energy transfer and enhanced circuit protection.
What is a Reset Winding?
A Reset winding is a specialized coil integrated into transformers or inductors to efficiently reset the magnetic core by providing a path for the magnetic flux to return to its initial state, preventing core saturation. It operates by generating a voltage that counteracts residual magnetization, improving energy recovery and system efficiency. Unlike clamp snubbers, which primarily limit voltage spikes by dissipating energy, reset windings manage the core's magnetic flux directly, minimizing power loss and enhancing reliability in switch-mode power supplies.
How Clamp Snubbers Work
Clamp snubbers work by dissipating the energy generated when an inductive load is suddenly switched off, preventing voltage spikes that could damage components. They consist of a resistor and capacitor arranged in a way to absorb transient voltages and smooth the voltage waveform across the switch or winding. Using a clamp snubber enhances the reliability of your circuit by protecting sensitive semiconductor devices from high-voltage transients.
Comparative Circuit Designs: Reset Winding vs Clamp Snubber
Reset winding and clamp snubber are two distinct circuit designs used to manage voltage spikes in inductive loads such as transformers and motors. Reset winding employs an additional coil to absorb and dissipate excess energy during switch-off, thereby reducing core saturation and improving efficiency, while a clamp snubber uses resistors and capacitors to divert and dissipate transient voltage spikes, protecting semiconductor devices. The reset winding design is more suitable for applications requiring high energy recovery and reduced losses, whereas clamp snubbers offer simpler implementation and effective voltage spike suppression in switching circuits.
Efficiency and Energy Loss Considerations
Reset winding enhances efficiency by providing a dedicated path for magnetic flux, reducing core losses and minimizing energy dissipation compared to Clamp snubbers. Clamp snubbers, while simpler, often result in higher energy loss due to continuous dissipation of voltage spikes through resistive components. Your choice impacts overall system performance, with reset winding preferred for low-loss and high-efficiency power conversion applications.
Pros and Cons of Reset Winding
Reset winding in power electronics offers efficient energy recovery by redirecting stored magnetic energy, reducing switching losses and improving overall converter performance. However, it complicates transformer design and can increase electromagnetic interference, demanding careful layout and insulation considerations. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize energy efficiency and size reduction over design complexity and EMI challenges.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Clamp Snubbers
Clamp snubbers offer advantages such as simplified design and effective suppression of voltage spikes in inductive circuits, enhancing overall circuit protection. They provide reliable energy dissipation and reduce electromagnetic interference, but may introduce increased power loss and heat generation compared to reset winding methods. Your choice depends on prioritizing ease of implementation and robust voltage control versus efficiency and thermal management.
Application Suitability: When to Use Each Method
Reset winding is ideal for high-frequency transformers in flyback converters where efficient energy recovery and minimal switching losses are crucial, especially in low-power applications. Clamp snubbers suit power supplies with higher voltage spikes and transient suppression needs, providing robust protection for switching devices in high-voltage, high-power environments. Selecting between reset winding and clamp snubber depends on converter topology, operating frequency, and the trade-off between efficiency and component stress management.
Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Flyback Transformer Technique
Choosing between reset winding and clamp snubber techniques for flyback transformers depends on efficiency and system complexity requirements. Reset windings offer improved energy recovery and reduced electromagnetic interference, making them suitable for high-performance designs. Clamp snubbers provide simpler implementation and cost-effectiveness but may incur higher power losses and lower overall efficiency.
Reset winding vs Clamp snubber Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com