VCOs (Voltage-Controlled Oscillators) offer frequency tuning by voltage input, making them ideal for applications requiring variable frequencies, while crystal oscillators provide highly stable and precise fixed frequencies due to their quartz crystal resonance. Explore the detailed comparison of VCO and crystal oscillators to understand which one suits Your project needs best.
Table of Comparison
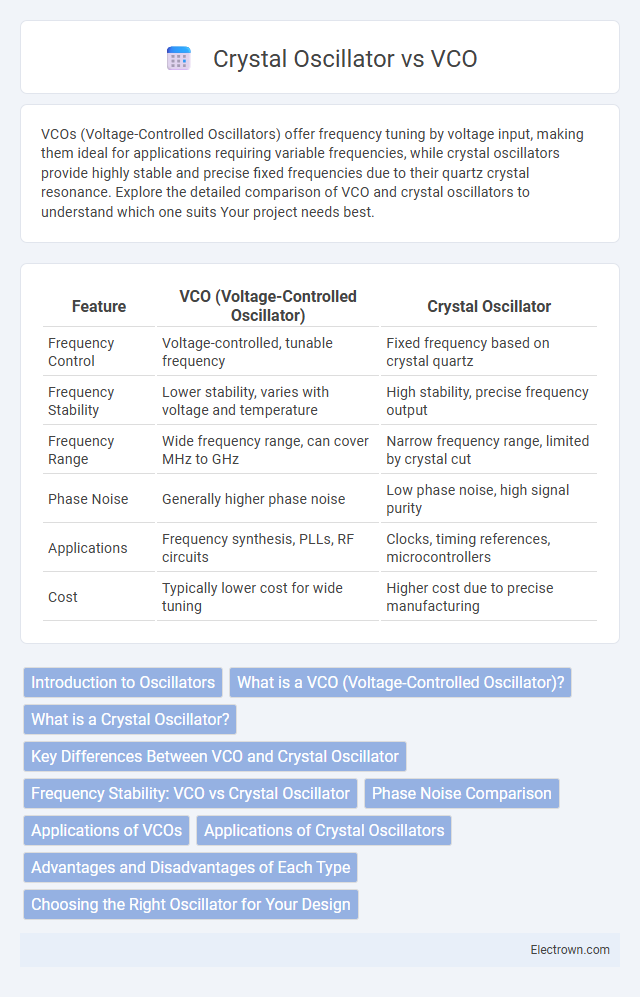
| Feature | VCO (Voltage-Controlled Oscillator) | Crystal Oscillator |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Control | Voltage-controlled, tunable frequency | Fixed frequency based on crystal quartz |
| Frequency Stability | Lower stability, varies with voltage and temperature | High stability, precise frequency output |
| Frequency Range | Wide frequency range, can cover MHz to GHz | Narrow frequency range, limited by crystal cut |
| Phase Noise | Generally higher phase noise | Low phase noise, high signal purity |
| Applications | Frequency synthesis, PLLs, RF circuits | Clocks, timing references, microcontrollers |
| Cost | Typically lower cost for wide tuning | Higher cost due to precise manufacturing |
Introduction to Oscillators
Oscillators are essential components in electronic circuits, generating repetitive signals needed for timing and frequency control. Voltage-Controlled Oscillators (VCOs) allow frequency adjustment based on input voltage, enabling flexible tuning in communication systems. Crystal Oscillators provide highly stable and precise frequencies due to the piezoelectric properties of quartz crystals, making them ideal for applications requiring accuracy and low phase noise.
What is a VCO (Voltage-Controlled Oscillator)?
A Voltage-Controlled Oscillator (VCO) is an electronic oscillator whose oscillation frequency is controlled by an input voltage, enabling precise frequency modulation in communication and signal processing systems. VCOs are integral components in phase-locked loops (PLLs), frequency synthesizers, and modulator circuits, offering tunable frequency ranges that vary proportionally with the applied control voltage. Unlike crystal oscillators that produce a fixed, highly stable frequency, VCOs provide adjustable frequency outputs essential for dynamic frequency control applications in RF and microwave technologies.
What is a Crystal Oscillator?
A crystal oscillator is an electronic oscillator circuit that uses the mechanical resonance of a vibrating crystal, usually quartz, to generate a precise frequency signal. It offers high stability, low phase noise, and consistent frequency accuracy, making it ideal for timing applications in communication systems, microcontrollers, and digital watches. Unlike voltage-controlled oscillators (VCOs), crystal oscillators maintain a fixed frequency determined by the crystal's physical properties, ensuring minimal frequency drift over time and temperature variations.
Key Differences Between VCO and Crystal Oscillator
VCOs (Voltage-Controlled Oscillators) offer frequency tunability controlled by an input voltage, making them ideal for modulated signals and frequency synthesis applications. Crystal oscillators provide highly stable and precise frequency outputs due to the quartz crystal's consistent resonant frequency but lack tunability. Understanding your project's need for frequency stability versus tunability will help you choose between the fixed-frequency precision of crystal oscillators and the adaptable frequency range of VCOs.
Frequency Stability: VCO vs Crystal Oscillator
Crystal oscillators exhibit superior frequency stability due to their reliance on quartz crystal resonance, maintaining precise frequencies with minimal drift over temperature and time. Voltage-Controlled Oscillators (VCOs) offer variable frequency output but suffer from higher phase noise and greater susceptibility to temperature variations, resulting in less stable frequencies. Applications requiring high precision, such as clocks and communication systems, typically favor crystal oscillators for their consistent frequency stability.
Phase Noise Comparison
Voltage-Controlled Oscillators (VCOs) typically exhibit higher phase noise compared to crystal oscillators due to their reliance on active semiconductor components and LC tank circuits, which are more susceptible to thermal and flicker noise. Crystal oscillators leverage the high Q-factor of quartz resonators, resulting in significantly lower phase noise and superior frequency stability, making them preferable for applications requiring precision timing. In RF systems, the choice between VCOs and crystal oscillators depends on the trade-off between tunability and phase noise performance.
Applications of VCOs
Voltage-Controlled Oscillators (VCOs) are essential in communication systems, including phase-locked loops (PLLs) for frequency synthesis and modulation. Their ability to vary output frequency based on input voltage makes them ideal for tuning radio transmitters, frequency modulation (FM) receivers, and signal generators. You can find VCOs extensively used in radar systems, clock generators, and wireless communication devices where agile frequency control is crucial.
Applications of Crystal Oscillators
Crystal oscillators are widely used in applications requiring high frequency stability and precision, such as in wristwatches, communication systems, and microcontrollers. Their ability to maintain a consistent oscillation frequency under varying environmental conditions makes them ideal for timing circuits and frequency references. Your electronic devices benefit from crystal oscillators' accuracy, ensuring reliable synchronization in data transmission and signal processing.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Type
Voltage-Controlled Oscillators (VCOs) offer wide frequency tuning range and fast frequency modulation, making them ideal for phase-locked loops and frequency synthesis, but they suffer from phase noise sensitivity and non-linear tuning characteristics. Crystal Oscillators provide superior frequency stability, low phase noise, and precise frequency control due to the quartz resonator, though they are limited in frequency tuning flexibility and generally have higher power consumption. Choosing between VCOs and Crystal Oscillators depends on the application requirements for frequency agility versus accuracy and spectral purity.
Choosing the Right Oscillator for Your Design
Choosing the right oscillator for your design depends on factors such as frequency stability, phase noise, and tuning range. VCOs (Voltage-Controlled Oscillators) offer wide frequency tuning and are ideal for applications requiring frequency modulation and agile signal generation. Crystal oscillators provide superior frequency stability and low phase noise, making them suitable for precision timing and communication systems where accuracy is critical.
VCO vs Crystal Oscillator Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com