Plastic packages offer lightweight, cost-effective solutions with good electrical insulation but can be prone to thermal expansion and lower heat resistance compared to ceramic packages, which provide superior thermal conductivity and mechanical strength for high-performance applications. Explore this article to understand how choosing between plastic and ceramic packages can impact your device's durability and efficiency.
Table of Comparison
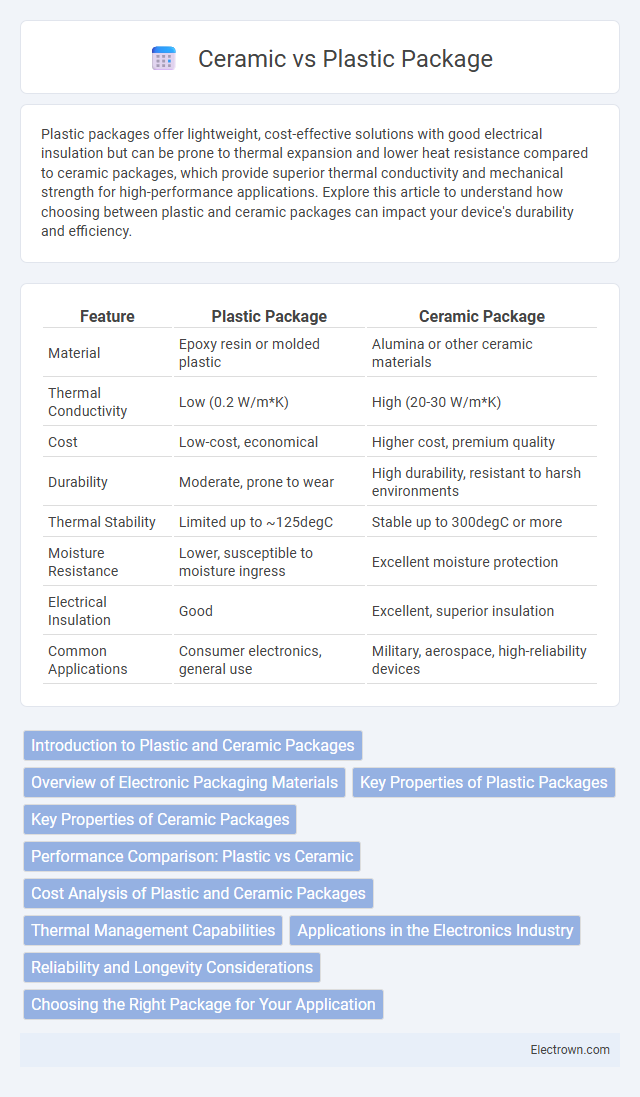
| Feature | Plastic Package | Ceramic Package |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Epoxy resin or molded plastic | Alumina or other ceramic materials |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (0.2 W/m*K) | High (20-30 W/m*K) |
| Cost | Low-cost, economical | Higher cost, premium quality |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to wear | High durability, resistant to harsh environments |
| Thermal Stability | Limited up to ~125degC | Stable up to 300degC or more |
| Moisture Resistance | Lower, susceptible to moisture ingress | Excellent moisture protection |
| Electrical Insulation | Good | Excellent, superior insulation |
| Common Applications | Consumer electronics, general use | Military, aerospace, high-reliability devices |
Introduction to Plastic and Ceramic Packages
Plastic and ceramic packages serve as fundamental enclosures in semiconductor manufacturing, with plastic packages being widely utilized for cost-efficiency and versatility in consumer electronics. Ceramic packages offer superior thermal conductivity and enhanced protection against environmental stresses, making them preferred for high-reliability applications such as aerospace and medical devices. Your choice between plastic and ceramic depends on balancing budget constraints with performance requirements, especially in demanding operational environments.
Overview of Electronic Packaging Materials
Electronic packaging materials significantly impact device performance and reliability, with plastic and ceramic being the most common options. Plastic packages offer cost-effective, lightweight, and flexible solutions suitable for mass production but typically provide lower thermal conductivity and moisture resistance. Ceramic packages excel in high-performance applications due to superior thermal management, mechanical strength, and hermetic sealing, making them ideal for aerospace, military, and high-frequency electronics.
Key Properties of Plastic Packages
Plastic packages offer excellent electrical insulation, lightweight construction, and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for various electronic components. Their thermal conductivity is lower than ceramic packages, which can affect heat dissipation but provides sufficient protection in many standard applications. Plastic packaging materials also exhibit good mechanical strength and moisture resistance, enhancing device reliability in everyday environments.
Key Properties of Ceramic Packages
Ceramic packages offer superior thermal conductivity, enhancing heat dissipation crucial for high-performance electronic components. They exhibit excellent moisture resistance and mechanical strength, ensuring durability in harsh operating environments. The material's inherent electrical insulation and stability at elevated temperatures make ceramic packages ideal for aerospace, medical, and high-frequency applications.
Performance Comparison: Plastic vs Ceramic
Ceramic packages exhibit superior thermal conductivity and mechanical stability compared to plastic packages, making them ideal for high-performance applications requiring efficient heat dissipation and durability. Plastic packages, while more cost-effective and lightweight, typically have lower thermal resistance, which can limit performance in high-power or high-frequency electronic components. The choice between plastic and ceramic packaging heavily depends on the application's thermal, mechanical, and economic requirements.
Cost Analysis of Plastic and Ceramic Packages
Plastic packages offer a cost-effective solution with lower manufacturing expenses and material costs compared to ceramic packages, making them ideal for high-volume production and budget-sensitive applications. Ceramic packages provide superior thermal conductivity and durability but come with higher costs due to complex fabrication processes and expensive raw materials. You can optimize your design budget by selecting plastic packages for cost efficiency or ceramic packages when performance and reliability justify the investment.
Thermal Management Capabilities
Ceramic packages excel in thermal management due to their superior thermal conductivity and ability to withstand high temperatures, making them ideal for high-power electronic components. Plastic packages offer lower thermal performance but provide cost-effective solutions for less demanding applications. Your choice between plastic and ceramic packaging should consider the thermal requirements of your device to ensure efficient heat dissipation and reliability.
Applications in the Electronics Industry
Plastic packages dominate the electronics industry due to their cost-effectiveness, lightweight nature, and excellent insulation properties, making them ideal for consumer electronics, automotive components, and mobile devices. Ceramic packages offer superior thermal stability, high-frequency performance, and enhanced protection against moisture and mechanical stress, which are critical for aerospace, military, and high-reliability medical applications. Your choice between plastic and ceramic packaging depends on the specific performance requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints of the electronic device.
Reliability and Longevity Considerations
Ceramic packages offer superior reliability and longevity due to their excellent thermal stability, resistance to moisture, and mechanical strength, making them ideal for high-performance and harsh environment applications. Plastic packages, while cost-effective and suitable for mass production, are more prone to degradation from moisture absorption and thermal cycling, which can lead to reduced lifespan and reliability under stress. Selecting ceramic packages enhances device durability and performance consistency in demanding conditions, ensuring longer operational life compared to plastic alternatives.
Choosing the Right Package for Your Application
Selecting the appropriate package--plastic or ceramic--depends on factors such as thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and environmental exposure specific to your application. Ceramic packages excel in high-temperature stability and superior heat dissipation, making them ideal for power devices and harsh environments. Plastic packages offer cost-effectiveness and flexibility for mass-produced consumer electronics but may underperform in extreme conditions where ceramics are preferred.
Plastic vs Ceramic package Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com