High-side switches control power delivery by connecting the load to the positive voltage supply, while low-side switches connect the load to ground, each offering distinct advantages in circuit protection and control. Discover which switching method best suits your application by exploring the detailed analysis in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
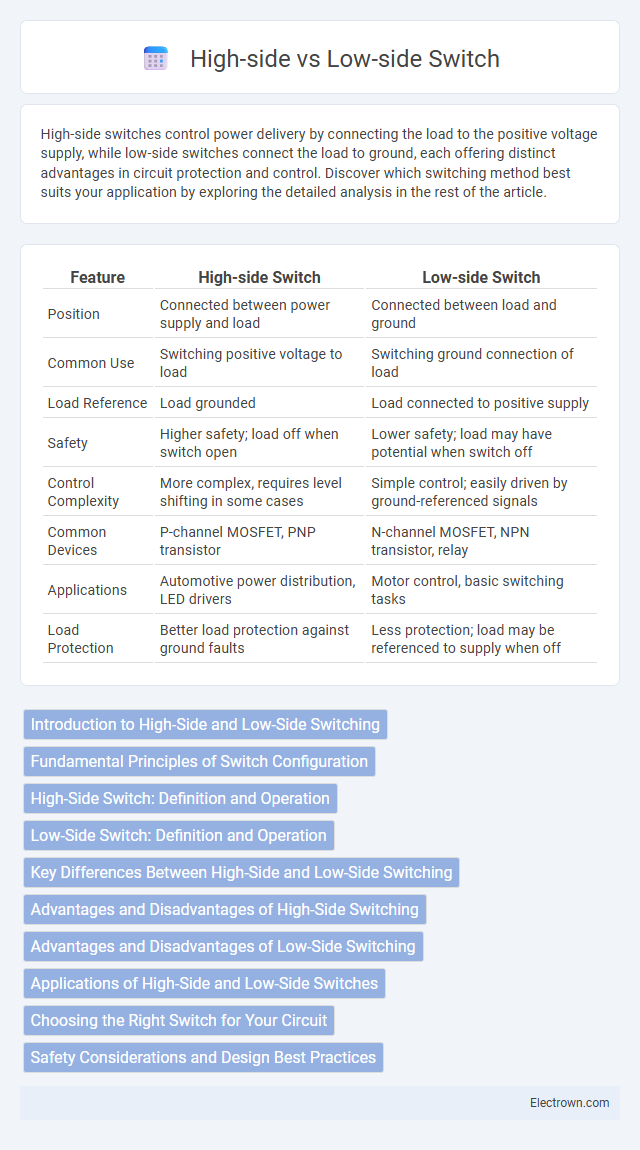
| Feature | High-side Switch | Low-side Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Position | Connected between power supply and load | Connected between load and ground |
| Common Use | Switching positive voltage to load | Switching ground connection of load |
| Load Reference | Load grounded | Load connected to positive supply |
| Safety | Higher safety; load off when switch open | Lower safety; load may have potential when switch off |
| Control Complexity | More complex, requires level shifting in some cases | Simple control; easily driven by ground-referenced signals |
| Common Devices | P-channel MOSFET, PNP transistor | N-channel MOSFET, NPN transistor, relay |
| Applications | Automotive power distribution, LED drivers | Motor control, basic switching tasks |
| Load Protection | Better load protection against ground faults | Less protection; load may be referenced to supply when off |
Introduction to High-Side and Low-Side Switching
High-side and low-side switches control the electrical load by placing the switch either between the power supply and the load (high-side) or between the load and ground (low-side). High-side switching is commonly used for positive voltage control, offering better protection and isolation for the load, while low-side switching is simpler and often cheaper, connecting the load directly to ground when activated. Selecting between high-side and low-side switch depends on circuit requirements, such as voltage levels, load type, and safety considerations.
Fundamental Principles of Switch Configuration
High-side switches connect the load to the positive voltage supply, enabling control by switching the supply line, which ensures the load is turned off when the switch is open. Low-side switches connect the load to ground, switching the connection to the ground line and providing simpler control but potential safety concerns regarding the load voltage. Fundamental principles dictate that high-side switching offers better load isolation and safety, while low-side switching provides easier implementation and cost-effectiveness.
High-Side Switch: Definition and Operation
A high-side switch controls power delivery by connecting the load to the positive voltage supply, allowing current to flow from the source through the load to ground. It operates by switching the positive voltage line, enabling better protection and easier control for devices requiring a common ground reference. Your circuit benefits from a high-side switch when maintaining a stable ground and isolating the load from the supply voltage is crucial for safety and performance.
Low-Side Switch: Definition and Operation
A low-side switch controls the load by connecting it to ground, completing the circuit on the negative side of the power supply. When activated, the switch allows current to flow from the power source, through the load, and into ground, effectively turning the load on or off. Understanding your low-side switch's operation is crucial for designing efficient circuits, especially in applications where ground referencing simplifies the switching mechanism.
Key Differences Between High-Side and Low-Side Switching
High-side switches connect the load to the positive supply voltage, allowing control by switching the positive side, while low-side switches connect the load to ground, controlling the negative side. High-side switching is preferred for safety and reducing noise in sensitive circuits, whereas low-side switching offers simpler design and cost-effectiveness. Your choice depends on the application's voltage requirements, load characteristics, and desired control complexity.
Advantages and Disadvantages of High-Side Switching
High-side switching offers the advantage of protecting the load from ground faults by connecting the load directly to ground, making it ideal for controlling devices requiring a stable reference voltage. It also allows easier integration with sensors and voltage monitoring since the switch isolates the power supply side, reducing interference. However, high-side switching circuits tend to be more complex and costly due to the need for specialized driver components and careful voltage threshold management.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Low-Side Switching
Low-side switching offers the advantage of simpler circuit design and easier implementation since the switch is placed between the load and ground, reducing cost and complexity. However, it has disadvantages including potential safety hazards as the load remains connected to the positive voltage, which can cause unexpected behavior or damage if the switch or load fails. Your choice of low-side switching should consider these trade-offs, especially in applications requiring precise load control or safety isolation.
Applications of High-Side and Low-Side Switches
High-side switches are commonly used in automotive and industrial applications where controlling the positive supply voltage is critical for safety and device protection. Low-side switches are preferred in applications involving load grounding, such as driving LEDs or relays, due to simpler wiring and cost-effectiveness. Both switches optimize circuit design by providing efficient control in power management, motor control, and lighting systems.
Choosing the Right Switch for Your Circuit
Selecting the right switch depends on the circuit voltage level and load type; high-side switches control the power supply line, isolating the load from the positive voltage, making them ideal for safety-critical applications and circuits requiring positive rail switching. Low-side switches connect the load to ground, offering simpler design and easier fault detection but with potential limitations in controlling devices sensitive to ground reference changes. Evaluate factors like load current, voltage rating, and switching speed to optimize circuit performance and reliability when choosing between high-side and low-side switches.
Safety Considerations and Design Best Practices
High-side switches connect the load to the positive supply, enhancing user safety by preventing accidental grounding and reducing the risk of short circuits, while low-side switches connect the load to ground and may expose control circuitry to higher voltages. Designing with high-side switches is preferred for safety-critical applications to isolate the load from the power source, while low-side switches can be implemented for simpler, cost-effective designs where safety risks are minimal. Ensure your design includes proper isolation, thermal management, and the use of appropriate MOSFETs or relays to optimize safety and performance.
High-side vs Low-side switch Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com