Schottky diodes offer faster switching speeds and lower forward voltage drops compared to conventional PN junction diodes, making them ideal for high-frequency and low-voltage applications. Explore the rest of the article to understand how these differences impact your electronic circuit designs.
Table of Comparison
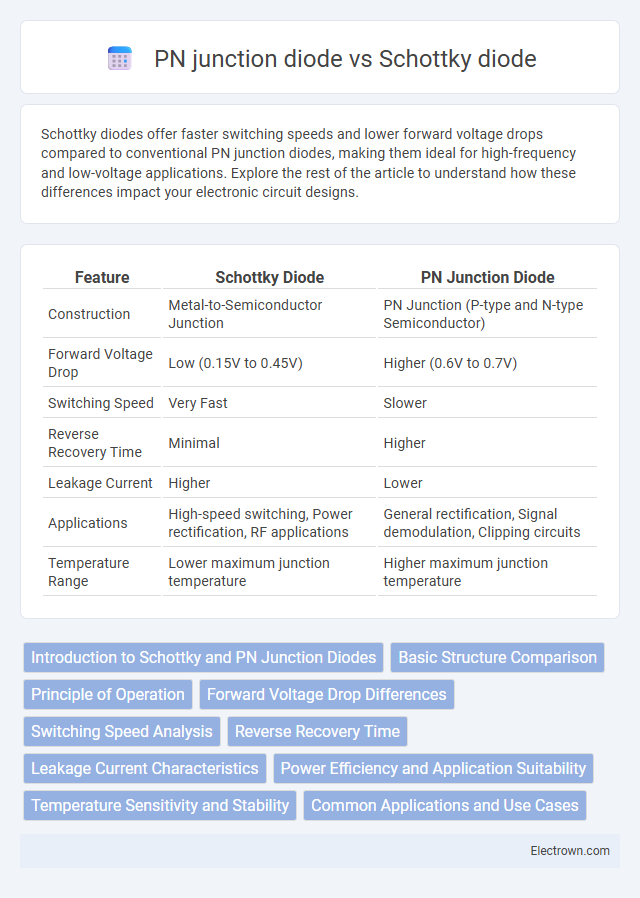
| Feature | Schottky Diode | PN Junction Diode |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | Metal-to-Semiconductor Junction | PN Junction (P-type and N-type Semiconductor) |
| Forward Voltage Drop | Low (0.15V to 0.45V) | Higher (0.6V to 0.7V) |
| Switching Speed | Very Fast | Slower |
| Reverse Recovery Time | Minimal | Higher |
| Leakage Current | Higher | Lower |
| Applications | High-speed switching, Power rectification, RF applications | General rectification, Signal demodulation, Clipping circuits |
| Temperature Range | Lower maximum junction temperature | Higher maximum junction temperature |
Introduction to Schottky and PN Junction Diodes
Schottky diodes feature a metal-semiconductor junction offering low forward voltage drop and fast switching, making them ideal for high-frequency applications and power rectification. PN junction diodes consist of p-type and n-type semiconductor materials forming a depletion region, used widely for rectification, voltage regulation, and signal demodulation. Understanding the differences in structure and electrical characteristics helps you select the right diode for efficiency and speed in your electronic circuits.
Basic Structure Comparison
The Schottky diode features a metal-semiconductor junction, typically formed by contacting a metal directly with an n-type semiconductor, resulting in a low forward voltage drop and fast switching speed. In contrast, the PN junction diode is composed of p-type and n-type semiconductor layers joined together, creating a depletion region responsible for its rectifying behavior. Your choice between the two depends on the required switching speed and voltage characteristics, with Schottky diodes excelling in high-speed and low-voltage applications.
Principle of Operation
A Schottky diode operates based on the metal-semiconductor junction, allowing current to flow primarily through majority carriers and resulting in faster switching speeds and lower forward voltage drops. In contrast, a PN junction diode relies on the recombination of electrons and holes at the p-n interface, which involves minority carrier injection and leads to slower response times. Your choice between these diodes depends on the required switching speed and efficiency for your electronic circuit.
Forward Voltage Drop Differences
Schottky diodes typically exhibit a forward voltage drop between 0.15 to 0.45 volts, significantly lower than the 0.6 to 0.7 volts common in PN junction diodes. This reduced voltage drop in Schottky diodes results from the metal-semiconductor junction, allowing faster switching and increased efficiency in low-voltage applications. The lower forward voltage also contributes to reduced power dissipation, making Schottky diodes ideal for power-sensitive circuits.
Switching Speed Analysis
Schottky diodes exhibit significantly faster switching speeds compared to PN junction diodes due to their metal-semiconductor junction, which reduces charge storage and eliminates minority carrier recombination delays. This characteristic enables Schottky diodes to operate efficiently in high-frequency applications and switching circuits, minimizing power loss and heat generation. Your choice between these diodes should consider the required switching speed and application frequency to maximize performance and efficiency.
Reverse Recovery Time
Schottky diodes exhibit significantly lower reverse recovery time compared to PN junction diodes due to their metal-semiconductor junction, which lacks minority carrier charge storage. This characteristic enables faster switching speeds and reduces power loss in high-frequency applications such as power supplies and RF circuits. In contrast, PN junction diodes experience longer reverse recovery times caused by the recombination of stored charge carriers, leading to slower response and higher switching losses.
Leakage Current Characteristics
Schottky diodes exhibit significantly lower leakage current compared to PN junction diodes due to their metal-semiconductor junction, which reduces minority carrier injection and recombination. This characteristic enables Schottky diodes to perform better in high-frequency and low-voltage applications where minimizing leakage current is crucial. Your choice of diode for sensitive electronic circuits can benefit from this reduced leakage, improving efficiency and thermal stability.
Power Efficiency and Application Suitability
Schottky diodes exhibit lower forward voltage drop (typically 0.2-0.3V) compared to PN junction diodes (0.6-0.7V), resulting in higher power efficiency and reduced heat dissipation in high-speed switching applications. Their fast switching capabilities and low reverse recovery time make Schottky diodes ideal for power rectification in switching power supplies and RF applications, whereas PN junction diodes are better suited for general-purpose rectification and high voltage environments due to their higher reverse breakdown voltage. The enhanced efficiency and switching speed of Schottky diodes drive their preference in energy-sensitive and high-frequency circuits, optimizing overall system performance.
Temperature Sensitivity and Stability
Schottky diodes exhibit lower temperature sensitivity compared to PN junction diodes due to their metal-semiconductor junction, which results in a more stable forward voltage drop across varying temperatures. PN junction diodes experience a significant increase in forward voltage drop and leakage current as temperature rises, affecting overall stability and performance. Managing your device's thermal environment is crucial when choosing between these diodes to ensure consistent operation under different temperature conditions.
Common Applications and Use Cases
Schottky diodes are commonly used in high-speed switching applications, power rectification, and RF circuits due to their low forward voltage drop and fast recovery time. PN junction diodes find widespread use in general-purpose rectification, signal demodulation, and voltage regulation, where slower switching speeds are acceptable. Your choice between the two depends on the need for efficiency and speed versus cost-effectiveness and durability in specific electronic designs.
Schottky diode vs PN junction diode Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com