String inverters consolidate the energy from multiple solar panels into a single output, offering cost-effective and efficient performance for uniform panel conditions but can suffer from reduced output if one panel underperforms. Microinverters, installed on each panel, maximize energy production by optimizing individual panel output and provide better monitoring and flexibility for your solar system; explore the rest of the article to understand which option suits your energy needs best.
Table of Comparison
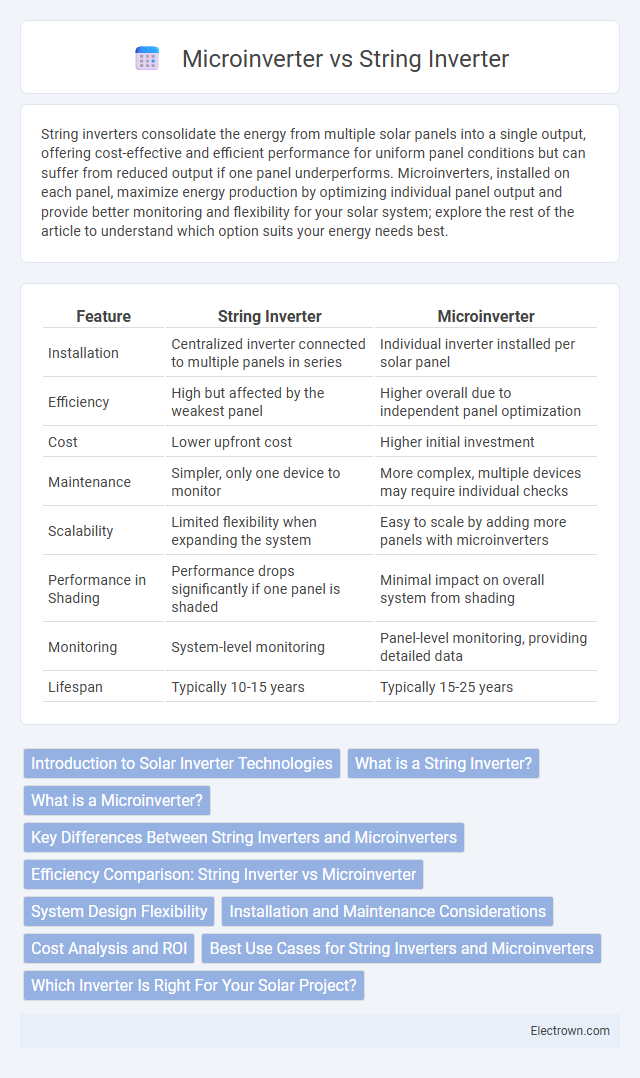
| Feature | String Inverter | Microinverter |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Centralized inverter connected to multiple panels in series | Individual inverter installed per solar panel |
| Efficiency | High but affected by the weakest panel | Higher overall due to independent panel optimization |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost | Higher initial investment |
| Maintenance | Simpler, only one device to monitor | More complex, multiple devices may require individual checks |
| Scalability | Limited flexibility when expanding the system | Easy to scale by adding more panels with microinverters |
| Performance in Shading | Performance drops significantly if one panel is shaded | Minimal impact on overall system from shading |
| Monitoring | System-level monitoring | Panel-level monitoring, providing detailed data |
| Lifespan | Typically 10-15 years | Typically 15-25 years |
Introduction to Solar Inverter Technologies
String inverters and microinverters represent two primary solar inverter technologies used in converting DC solar power to usable AC electricity. String inverters connect panels in series, optimizing cost and efficiency for uniform sunlight conditions, while microinverters are installed on each panel independently, enhancing performance in shaded or complex roof layouts. Understanding these technologies helps you choose the best solution for maximizing your solar energy system's output and reliability.
What is a String Inverter?
A string inverter is a central device that converts direct current (DC) generated by multiple solar panels connected in series into alternating current (AC) for household or grid use. It optimizes the energy output of the entire solar string, but its efficiency can be affected if one panel underperforms due to shading or damage. String inverters are commonly used in residential and commercial solar systems for their cost-effectiveness and ease of installation.
What is a Microinverter?
A microinverter is a compact device attached to each solar panel that independently converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) right at the panel level. This technology maximizes energy harvest from individual panels by optimizing performance and minimizing losses caused by shading or panel mismatch. You benefit from increased system reliability and easier monitoring compared to traditional string inverters.
Key Differences Between String Inverters and Microinverters
String inverters consolidate the DC power from multiple solar panels into a single inverter, optimizing cost and simplicity but are susceptible to performance drops if one panel underperforms. Microinverters attach to individual panels, maximizing energy harvest by reducing shading or mismatch losses, enhancing overall system efficiency and reliability. The choice depends on system size, shading conditions, and budget, with microinverters offering superior monitoring and panel-level control.
Efficiency Comparison: String Inverter vs Microinverter
String inverters typically offer higher efficiency rates ranging from 95% to 98%, making them well-suited for installations with uniform sunlight exposure. Microinverters excel in maximizing overall energy harvest by optimizing each solar panel individually, especially in shaded or complex roof layouts, with efficiencies around 96% per panel. Your choice between string inverter and microinverter depends on your property's shading conditions and the need for panel-level performance monitoring.
System Design Flexibility
Microinverters offer superior system design flexibility by allowing each solar panel to operate independently, optimizing energy production even in shaded or complex roof layouts. String inverters require panels to be connected in series, limiting design options and making the system more susceptible to performance drops due to shading or panel mismatch. Your choice impacts overall energy yield and ease of system expansion or troubleshooting.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
String inverters typically offer simpler installation with fewer components, reducing initial labor costs and complexity compared to microinverters, which require individual units on each solar panel. Maintenance for string inverters involves monitoring a centralized system, making fault detection more straightforward, whereas microinverters provide panel-level diagnostics but may require more frequent inspection and replacement. Your choice depends on the balance between ease of installation and granular maintenance preferences for optimal solar system performance.
Cost Analysis and ROI
String inverters generally have lower upfront costs compared to microinverters, making them a more budget-friendly option for large-scale solar installations. Microinverters offer higher energy efficiency and system monitoring at the panel level, which can lead to increased energy yield and faster return on investment (ROI) despite the higher initial price. Evaluating cost per watt and projected energy savings is crucial for determining the most economical choice based on specific site conditions and financial goals.
Best Use Cases for String Inverters and Microinverters
String inverters are best used in residential or commercial solar systems with uniform shading and consistent panel orientation, offering cost-effective energy conversion for large, contiguous arrays. Microinverters excel in installations with shading issues, varied roof angles, or complex layouts, enabling individual panel optimization and maximizing overall system output. Your choice depends on site conditions: string inverters suit simpler setups, while microinverters handle diverse panel performance challenges efficiently.
Which Inverter Is Right For Your Solar Project?
String inverters are ideal for solar projects with uniform sunlight exposure, offering cost-effective efficiency for larger systems and simpler installation. Microinverters excel in setups with shading issues or complex roof layouts by optimizing each panel individually and enhancing overall energy harvest. Choosing the right inverter depends on your system size, shading challenges, and budget considerations to maximize solar energy production and return on investment.
String inverter vs microinverter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com