A constant current source maintains a fixed current regardless of load changes, ideal for applications like LED driving and battery charging, while a constant voltage source keeps voltage steady, commonly used to power electronic circuits. Understanding the differences between these sources will help you choose the right power supply for your specific needs; continue reading to explore their characteristics and applications.
Table of Comparison
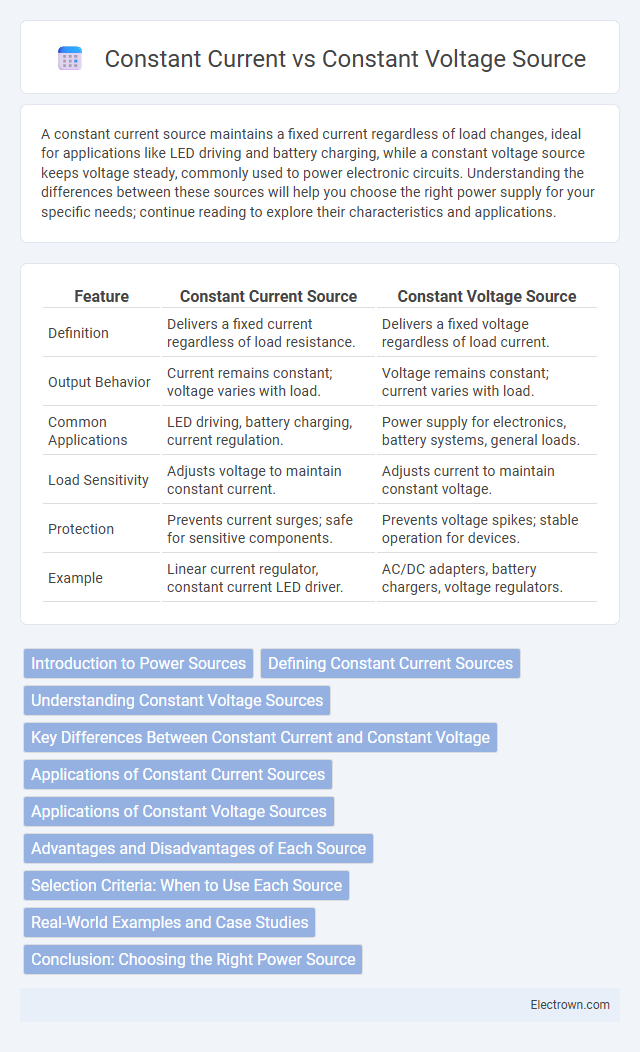
| Feature | Constant Current Source | Constant Voltage Source |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Delivers a fixed current regardless of load resistance. | Delivers a fixed voltage regardless of load current. |
| Output Behavior | Current remains constant; voltage varies with load. | Voltage remains constant; current varies with load. |
| Common Applications | LED driving, battery charging, current regulation. | Power supply for electronics, battery systems, general loads. |
| Load Sensitivity | Adjusts voltage to maintain constant current. | Adjusts current to maintain constant voltage. |
| Protection | Prevents current surges; safe for sensitive components. | Prevents voltage spikes; stable operation for devices. |
| Example | Linear current regulator, constant current LED driver. | AC/DC adapters, battery chargers, voltage regulators. |
Introduction to Power Sources
Constant current sources maintain a fixed current output regardless of changes in load resistance, making them ideal for applications like LED driving and battery charging. Constant voltage sources deliver a fixed voltage output, adapting current flow based on load demands, commonly used in power supplies for electronic devices. Understanding the fundamental differences between constant current and constant voltage sources is crucial for selecting the right power supply in circuits requiring precise control of voltage or current.
Defining Constant Current Sources
Constant current sources provide a stable and precise current regardless of voltage fluctuations or load changes, making them essential for applications requiring consistent current flow. They regulate current by adjusting the voltage to maintain the desired amperage, critical in LED driving, battery charging, and electronic testing. Your devices benefit from constant current sources by preventing damage and ensuring optimal performance in circuits needing uniform current delivery.
Understanding Constant Voltage Sources
Constant voltage sources maintain a fixed voltage output regardless of the current drawn by the load, making them ideal for powering devices like LEDs, sensors, and battery chargers that require stable voltage levels. These sources are designed to minimize voltage fluctuations, ensuring consistent performance and preventing damage to sensitive electronic components. Proper understanding of constant voltage sources is essential in designing circuits that require reliable voltage regulation for optimal functionality and safety.
Key Differences Between Constant Current and Constant Voltage
Constant current sources maintain a fixed current output regardless of load variations, making them ideal for LED drivers and battery charging applications where precise current control is critical. Constant voltage sources provide a stable voltage output despite changes in load, commonly used in power supplies for electronic circuits requiring consistent voltage levels. The key difference lies in their regulation focus: constant current sources prioritize current stability, while constant voltage sources ensure voltage stability.
Applications of Constant Current Sources
Constant current sources are essential in applications requiring stable current despite voltage fluctuations, such as LED driving, battery charging, and precision measurement instruments. Your electronic devices benefit from consistent current supply to prevent damage and ensure optimal performance, especially in circuits with varying load conditions. These sources are crucial in laser diode operation, electroplating, and medical equipment, where maintaining exact current levels is critical.
Applications of Constant Voltage Sources
Constant voltage sources are essential in applications requiring stable voltage supply regardless of load changes, such as powering LED lighting systems, battery chargers, and electronic circuits. Your devices benefit from consistent voltage to ensure proper operation and prevent damage caused by voltage fluctuations. These sources are widely used in consumer electronics, telecommunications equipment, and industrial automation systems where voltage stability is critical.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Source
Constant current sources provide stable current regardless of load variations, making them ideal for driving LEDs and battery charging, but can be less efficient and generate heat under varying voltage demands. Constant voltage sources maintain a fixed voltage, offering simplicity and compatibility with most electronic devices, but risk current fluctuations that may damage sensitive components. Choosing between them depends on application requirements such as load characteristics, efficiency, and protection needs.
Selection Criteria: When to Use Each Source
Choose a constant current source when precise control of current is essential, such as in LED driving or battery charging applications, ensuring stable current despite voltage variations. Opt for a constant voltage source when maintaining a fixed voltage is critical, typical in powering electronic circuits or devices requiring steady voltage regardless of load changes. Evaluating load characteristics, device requirements, and safety considerations guides the selection between constant current and constant voltage sources.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
LED lighting systems often use constant current sources to maintain consistent brightness and prevent damage caused by current fluctuations, ensuring longer lifespan and energy efficiency. Solar power inverters typically operate as constant voltage sources to match grid requirements, stabilizing output to protect connected equipment and optimize energy transfer. Battery charging circuits employ both methods, using constant current during initial charging phases and switching to constant voltage as the battery reaches full capacity to maximize safety and battery health.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Power Source
Selecting the appropriate power source depends on the specific application requirements, where constant current sources excel in driving LEDs and laser diodes ensuring stable current flow, while constant voltage sources are ideal for powering resistive loads and electronic circuits requiring fixed voltage. Understanding device tolerance and load characteristics is crucial for optimizing performance and preventing damage. Prioritizing either constant current or constant voltage ensures system reliability, efficiency, and longevity tailored to the electrical component's needs.
Constant current vs constant voltage source Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com