Pinch-off voltage defines the voltage at which the current through a transistor channel ceases due to channel depletion, while threshold voltage is the minimum gate voltage needed to create a conductive channel; understanding their differences is crucial for optimizing transistor performance. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your knowledge of how these voltages impact electronic device operation.
Table of Comparison
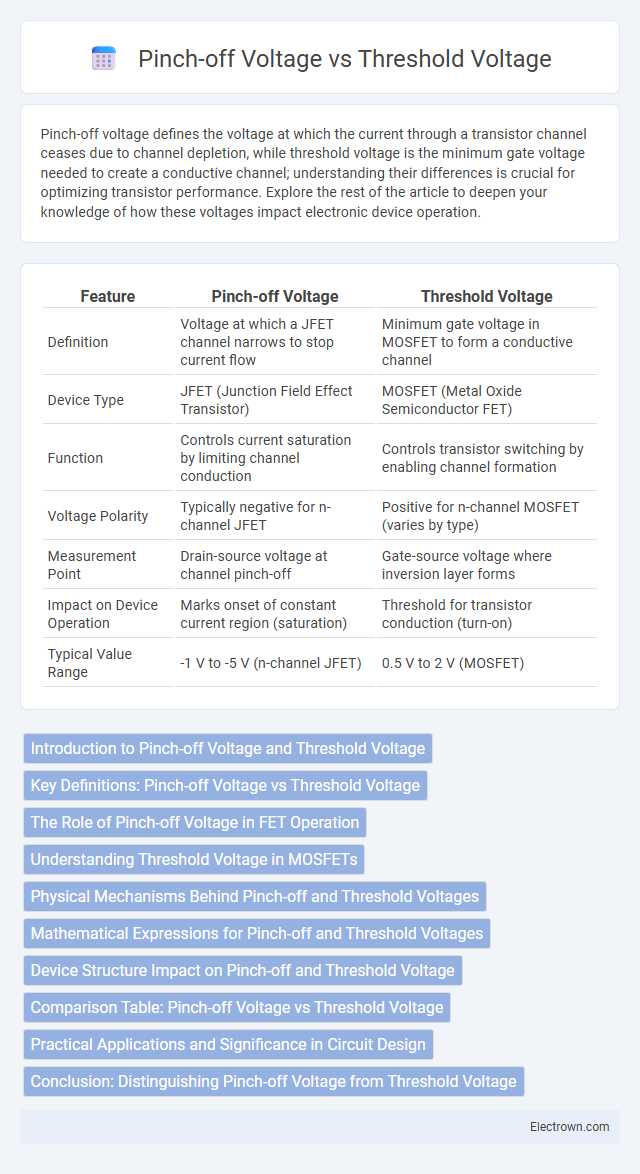
| Feature | Pinch-off Voltage | Threshold Voltage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voltage at which a JFET channel narrows to stop current flow | Minimum gate voltage in MOSFET to form a conductive channel |
| Device Type | JFET (Junction Field Effect Transistor) | MOSFET (Metal Oxide Semiconductor FET) |
| Function | Controls current saturation by limiting channel conduction | Controls transistor switching by enabling channel formation |
| Voltage Polarity | Typically negative for n-channel JFET | Positive for n-channel MOSFET (varies by type) |
| Measurement Point | Drain-source voltage at channel pinch-off | Gate-source voltage where inversion layer forms |
| Impact on Device Operation | Marks onset of constant current region (saturation) | Threshold for transistor conduction (turn-on) |
| Typical Value Range | -1 V to -5 V (n-channel JFET) | 0.5 V to 2 V (MOSFET) |
Introduction to Pinch-off Voltage and Threshold Voltage
Pinch-off voltage refers to the voltage at which a field-effect transistor (FET) channel closes, restricting current flow, whereas threshold voltage defines the minimum gate-to-source voltage required to create a conductive channel in a MOSFET. Both voltages are crucial parameters in transistor operation, influencing device switching and amplification behavior. Understanding the distinction between pinch-off and threshold voltages helps optimize transistor performance in analog and digital circuits.
Key Definitions: Pinch-off Voltage vs Threshold Voltage
Pinch-off voltage is the specific voltage at which a field-effect transistor (FET) channel becomes fully depleted, causing the current to saturate and no longer increase with higher drain voltage. Threshold voltage refers to the minimum gate-to-source voltage needed to create a conductive channel between the source and drain terminals, initiating current flow. Understanding the distinction between pinch-off voltage and threshold voltage is essential for optimizing your FET device performance in electronic circuits.
The Role of Pinch-off Voltage in FET Operation
Pinch-off voltage is a critical parameter in Field-Effect Transistors (FETs) that defines the voltage at which the conducting channel is effectively "pinched off," causing the current to saturate despite increases in drain-source voltage. This voltage differs from the threshold voltage, which is the minimum gate-source voltage required to create a conductive channel in the first place. Your understanding of pinch-off voltage is essential for analyzing the saturation region operation and ensuring optimal performance in analog and switching applications.
Understanding Threshold Voltage in MOSFETs
Threshold voltage in MOSFETs is the critical gate voltage at which a conductive channel forms between the source and drain, enabling current flow. Pinch-off voltage, often confused with threshold voltage, refers to the drain voltage at which the channel is "pinched off" near the drain end, causing current saturation. Understanding your MOSFET's threshold voltage helps optimize device switching and ensures accurate control of on/off states in electronic circuits.
Physical Mechanisms Behind Pinch-off and Threshold Voltages
Pinch-off voltage occurs when the depletion region in a JFET channel completely closes, halting current flow due to full channel constriction by the reverse-biased gate-source junction. Threshold voltage in MOSFETs arises from the voltage needed to invert the semiconductor surface under the gate oxide, forming a conductive channel for current. Your understanding of these voltages is crucial for optimizing transistor switching and amplification in electronic circuits.
Mathematical Expressions for Pinch-off and Threshold Voltages
Pinch-off voltage (V_P) in a JFET is mathematically expressed as V_P = -V_GS(off), where V_GS(off) is the gate-source cutoff voltage. Threshold voltage (V_TH) in MOSFETs is defined by V_TH = V_FB + 2ph_F + ((2e_si q N_A 2ph_F))/C_ox, where V_FB is the flat-band voltage, ph_F is the Fermi potential, e_si is silicon permittivity, q is the electronic charge, N_A is the substrate doping concentration, and C_ox is the oxide capacitance per unit area. The precise determination of these voltages is crucial for designing and analyzing transistor switching behavior and channel conduction.
Device Structure Impact on Pinch-off and Threshold Voltage
Device structure significantly influences pinch-off voltage and threshold voltage in field-effect transistors, with variations in channel length, oxide thickness, and doping concentration altering their values. Thinner oxide layers and higher doping levels typically lower the threshold voltage by enhancing the electric field control over the channel, while short-channel effects and channel geometry impact pinch-off voltage by modulating the depletion region formation. Understanding these structural impacts allows you to optimize device performance for specific electronic applications.
Comparison Table: Pinch-off Voltage vs Threshold Voltage
Pinch-off voltage is the voltage at which a field-effect transistor (FET) channel closes, causing current saturation, while threshold voltage is the minimum gate-to-source voltage needed to create a conductive channel in a MOSFET. Pinch-off voltage typically applies to junction FETs (JFETs) and indicates channel depletion, whereas threshold voltage relates to MOSFETs and signifies the onset of strong inversion. The key comparison includes: pinch-off voltage controls current saturation onset; threshold voltage dictates device turn-on; their values depend on device structure and doping concentrations.
Practical Applications and Significance in Circuit Design
Pinch-off voltage and threshold voltage are critical parameters in transistor operation, affecting device switching and amplification in circuits. Pinch-off voltage, essential in JFETs and MESFETs, determines when the channel is fully depleted, ensuring controlled current flow, while threshold voltage in MOSFETs sets the minimum gate voltage for channel conduction, influencing switching speed and power efficiency. Understanding these voltages helps optimize Your circuit design for stability, performance, and power consumption in analog and digital applications.
Conclusion: Distinguishing Pinch-off Voltage from Threshold Voltage
Pinch-off voltage is the specific voltage at which a JFET channel constricts, significantly reducing current flow, while threshold voltage refers to the gate voltage in MOSFETs that induces a conductive channel. Understanding this distinction is crucial for accurately designing and analyzing transistor behavior in analog and digital circuits. Your effective circuit performance depends on correctly identifying these voltages to predict and control device operation accurately.
Pinch-off voltage vs Threshold voltage Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com