Mask ROM is a type of read-only memory programmed during the manufacturing process, offering high-density storage but no post-production modification, while PROM allows one-time programming by the user after manufacturing, providing greater flexibility for custom data storage. Explore the rest of the article to understand which option best suits your specific storage needs and applications.
Table of Comparison
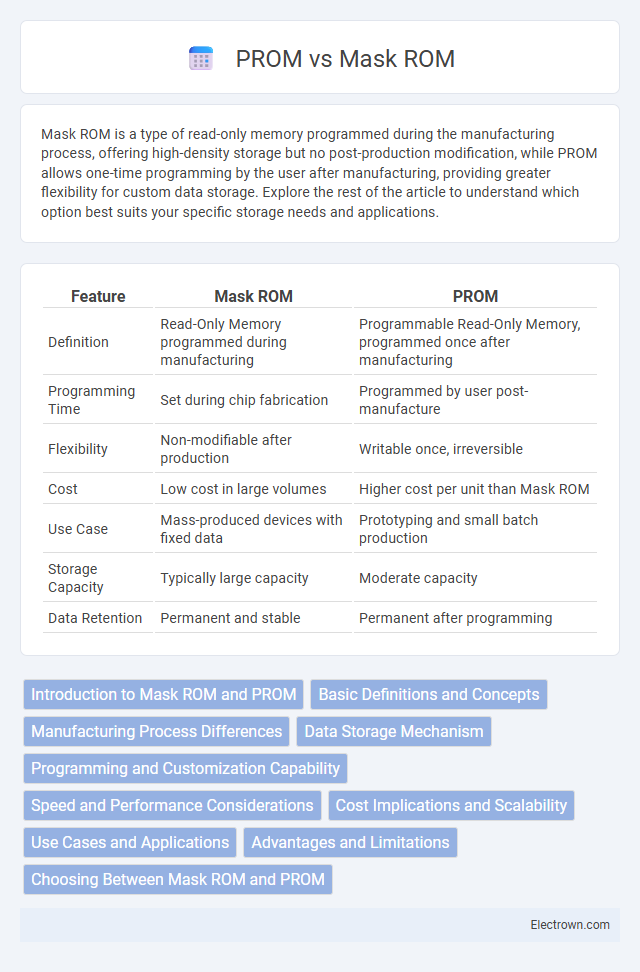
| Feature | Mask ROM | PROM |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Read-Only Memory programmed during manufacturing | Programmable Read-Only Memory, programmed once after manufacturing |
| Programming Time | Set during chip fabrication | Programmed by user post-manufacture |
| Flexibility | Non-modifiable after production | Writable once, irreversible |
| Cost | Low cost in large volumes | Higher cost per unit than Mask ROM |
| Use Case | Mass-produced devices with fixed data | Prototyping and small batch production |
| Storage Capacity | Typically large capacity | Moderate capacity |
| Data Retention | Permanent and stable | Permanent after programming |
Introduction to Mask ROM and PROM
Mask ROM (Read-Only Memory) is a type of non-volatile memory programmed during the manufacturing process, making it cost-effective for mass production with fixed data. PROM (Programmable Read-Only Memory) allows users to write data once after manufacturing using a special programmer, providing flexibility for customization before final deployment. Choosing between Mask ROM and PROM depends on your need for pre-programmed versus user-defined data storage.
Basic Definitions and Concepts
Mask ROM (Read-Only Memory) is a type of non-volatile memory programmed during the manufacturing process, making its data permanent and unchangeable. PROM (Programmable Read-Only Memory) allows you to program the data once after manufacturing using a special device, enabling customization before final use. Understanding these basic concepts helps determine which memory type best suits applications requiring fixed or customizable data storage.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Mask ROM and PROM differ significantly in their manufacturing processes; Mask ROM is mass-produced using photolithography where the data is permanently encoded during the wafer fabrication stage, resulting in lower unit costs and high-volume efficiency. PROM, or Programmable Read-Only Memory, undergoes a generic manufacturing process and receives its data encoding post-fabrication through a one-time electrical programming step, allowing for customization but at higher per-unit costs. The inherent rigidity of Mask ROM's pre-set data contrasts with PROM's flexibility, affecting lead times and production scalability.
Data Storage Mechanism
Mask ROM stores data permanently through a custom photolithographic process during manufacturing, embedding the information in silicon via predefined transistor patterns. PROM allows data to be written once after fabrication by physically altering fuse links or anti-fuse elements using a programming device. The fundamental difference lies in Mask ROM's fixed data stored at the chip creation, while PROM's storage is user-programmable post-manufacture.
Programming and Customization Capability
Mask ROM is programmed during the manufacturing process with fixed data, offering no post-production customization, making it ideal for high-volume, cost-sensitive applications. PROM allows one-time programming after manufacturing through a user-applied process, providing limited flexibility for customized data storage. Your choice depends on whether you need pre-defined permanent data or the flexibility to program the memory once after production.
Speed and Performance Considerations
Mask ROM offers faster read speeds and higher performance as its data is permanently embedded during manufacturing, reducing access latency compared to PROM. PROM requires programming after production, which can introduce slight delays and less optimized access times. For applications demanding consistent high-speed read operations, your choice should favor Mask ROM for superior performance efficiency.
Cost Implications and Scalability
Mask ROM offers lower per-unit costs for large production volumes due to its fixed data pattern programmed during manufacturing, making it cost-effective for mass production but inflexible for updates. PROM allows customization after manufacturing, providing greater scalability for smaller batches or evolving designs, though it incurs higher per-unit costs and longer production times. Your choice between Mask ROM and PROM should consider initial setup costs against the need for scalability and post-production flexibility.
Use Cases and Applications
Mask ROM is widely used in high-volume consumer electronics like embedded systems, gaming consoles, and network devices due to its low per-unit cost and high reliability. PROM suits prototyping, firmware development, and small production runs where flexibility to program after manufacturing is essential. Both memory types find applications in firmware storage, with Mask ROM favored for fixed data and PROM for customizable or upgradable code.
Advantages and Limitations
Mask ROM offers the advantage of high density and low unit cost for large production volumes due to its pre-manufactured data pattern, making it ideal for mass-produced consumer electronics. PROM provides flexibility by allowing data to be written once post-fabrication, which is beneficial for prototype development and small batch production but lacks the reprogrammability of EEPROM or Flash memory. Limitations of Mask ROM include inflexibility and high initial tooling costs, while PROM's constraints involve a one-time programmable nature and higher per-unit cost compared to Mask ROM.
Choosing Between Mask ROM and PROM
Choosing between Mask ROM and PROM depends on the volume and flexibility requirements of your project. Mask ROM offers lower unit costs and faster access speeds for high-volume production but lacks post-manufacturing programmability. PROM provides the advantage of programming after fabrication, making it ideal for prototyping or low to medium production quantities where design changes are anticipated.
Mask ROM vs PROM Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com