Inverter drives offer precise motor speed control and energy efficiency, while converter drives primarily focus on basic voltage transformation with limited speed regulation. Explore the rest of the article to understand which drive best suits your application needs.
Table of Comparison
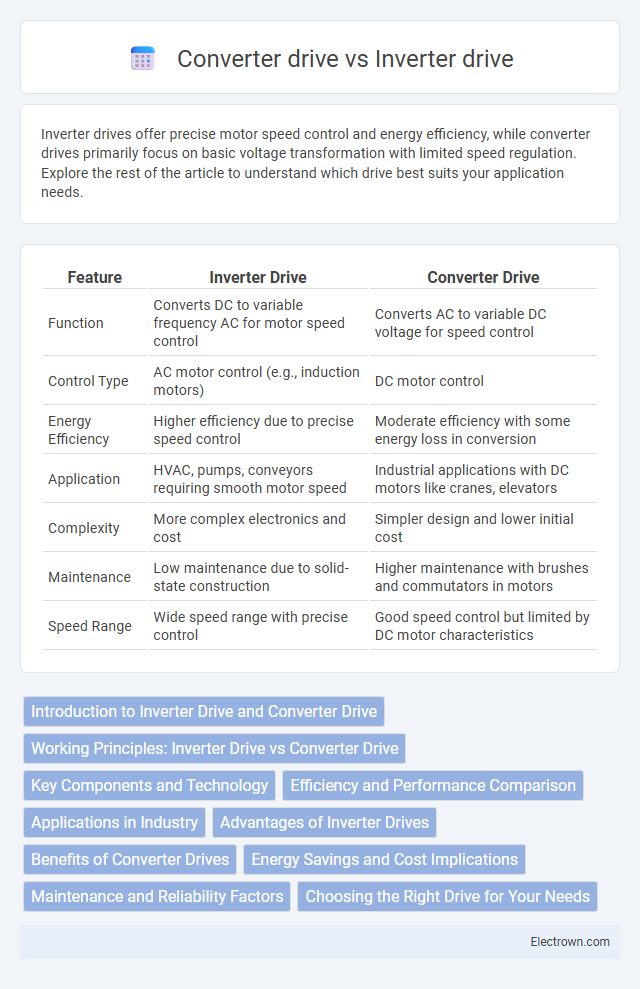
| Feature | Inverter Drive | Converter Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Converts DC to variable frequency AC for motor speed control | Converts AC to variable DC voltage for speed control |
| Control Type | AC motor control (e.g., induction motors) | DC motor control |
| Energy Efficiency | Higher efficiency due to precise speed control | Moderate efficiency with some energy loss in conversion |
| Application | HVAC, pumps, conveyors requiring smooth motor speed | Industrial applications with DC motors like cranes, elevators |
| Complexity | More complex electronics and cost | Simpler design and lower initial cost |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to solid-state construction | Higher maintenance with brushes and commutators in motors |
| Speed Range | Wide speed range with precise control | Good speed control but limited by DC motor characteristics |
Introduction to Inverter Drive and Converter Drive
Inverter drives utilize pulse width modulation (PWM) to convert DC power to variable-frequency AC, enabling precise motor speed control and energy efficiency across applications such as HVAC and industrial automation. Converter drives, often referred to as rectifier drives, convert AC to DC to manage motor torque and speed, commonly used in DC motor operations or where controlled DC output is essential. Both technologies optimize motor performance but differ in power conversion methods and application suitability based on load characteristics and control requirements.
Working Principles: Inverter Drive vs Converter Drive
Inverter drives operate by converting DC power into variable-frequency AC power to control motor speed and torque precisely, utilizing pulse-width modulation (PWM) techniques. Converter drives, on the other hand, primarily convert AC to DC and regulate motor torque and speed by controlling voltage and current supplied to the motor through rectification and chopper circuits. The inverter drive's ability to vary frequency offers more efficient and smooth motor control compared to the fixed-frequency output characteristic of traditional converter drives.
Key Components and Technology
Inverter drives use power semiconductor devices like IGBTs or MOSFETs to convert DC into variable-frequency AC, enabling precise motor speed control. Converter drives primarily convert AC to DC using rectifiers and control motor torque and speed through different DC voltage levels. Your choice depends on the application requirements for efficiency, motor type, and control complexity.
Efficiency and Performance Comparison
Inverter drives typically offer higher efficiency and superior performance by providing precise motor speed control and reducing energy consumption through variable frequency operation. Converter drives, while effective for basic speed control, generally exhibit lower efficiency due to fixed frequency outputs and less refined voltage regulation. Your choice impacts energy savings and operational accuracy, with inverter drives being optimal for applications demanding enhanced efficiency and dynamic performance.
Applications in Industry
Inverter drives are widely used in industries requiring precise speed control and energy-efficient operation, such as HVAC systems, conveyors, and pumping applications. Converter drives are typically employed in applications demanding constant torque and high starting torque, including heavy machinery, hoists, and steel mills. Both technologies enhance industrial automation but are selected based on specific operational needs and load characteristics.
Advantages of Inverter Drives
Inverter drives offer superior energy efficiency by precisely controlling motor speed and torque, leading to reduced power consumption compared to converter drives. They provide smoother acceleration and deceleration, minimizing mechanical stress and extending equipment lifespan. Inverter drives also support a wide range of motor types and enable advanced features such as regenerative braking and programmable control, enhancing overall system performance and flexibility.
Benefits of Converter Drives
Converter drives offer superior control over motor speed and torque by converting AC to DC and back to variable frequency AC, ensuring precise and smooth operation. They enhance energy efficiency in industrial applications by optimizing power usage and reducing harmonic distortion compared to inverter drives. Maintenance costs are lower due to robust components designed for high power capacity and improved system reliability.
Energy Savings and Cost Implications
Inverter drives offer significant energy savings by precisely controlling motor speed and reducing power consumption, leading to lower electricity bills compared to converter drives that typically operate at fixed speeds. Your operational costs decrease over time with inverter drives due to enhanced efficiency and reduced wear on mechanical components, minimizing maintenance expenses. Although inverter drives might require a higher initial investment, the long-term cost benefits through energy savings and improved system reliability make them a more economical choice.
Maintenance and Reliability Factors
Inverter drives typically require less maintenance due to their solid-state components and advanced diagnostic features, which enhance reliability and reduce downtime. Converter drives often involve more mechanical parts, such as brushes and commutators, leading to higher wear and increased maintenance demands. The increased thermal management and electronic protection in inverter drives contribute to longer equipment lifespan and more consistent performance under varying load conditions.
Choosing the Right Drive for Your Needs
Inverter drives offer precise speed control and energy efficiency by converting DC power back to variable frequency AC, ideal for applications requiring adjustable speed and torque. Converter drives excel in applications needing fixed frequency DC power, providing robust performance for processes like electroplating or DC motor control. Understanding your specific load characteristics and control requirements ensures you select the optimal drive for maximum operational efficiency and cost savings.
Inverter drive vs Converter drive Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com