Soft start reduces the initial electrical surge by gradually ramping up power, protecting your appliances and extending their lifespan, while hard start delivers full power immediately, which can cause mechanical stress and potential damage over time. Explore the rest of the article to understand which starting method best suits your equipment and energy needs.
Table of Comparison
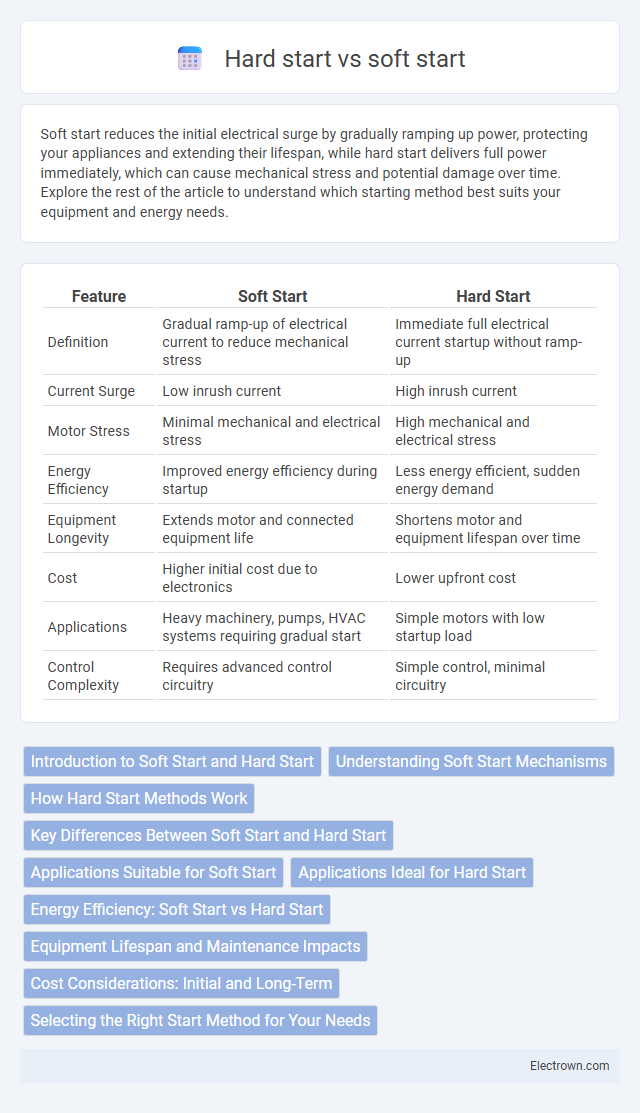
| Feature | Soft Start | Hard Start |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Gradual ramp-up of electrical current to reduce mechanical stress | Immediate full electrical current startup without ramp-up |
| Current Surge | Low inrush current | High inrush current |
| Motor Stress | Minimal mechanical and electrical stress | High mechanical and electrical stress |
| Energy Efficiency | Improved energy efficiency during startup | Less energy efficient, sudden energy demand |
| Equipment Longevity | Extends motor and connected equipment life | Shortens motor and equipment lifespan over time |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to electronics | Lower upfront cost |
| Applications | Heavy machinery, pumps, HVAC systems requiring gradual start | Simple motors with low startup load |
| Control Complexity | Requires advanced control circuitry | Simple control, minimal circuitry |
Introduction to Soft Start and Hard Start
Soft start and hard start refer to methods of controlling the initial power surge in electrical motors. Soft start gradually increases voltage to reduce mechanical stress and electrical peak currents, enhancing motor longevity and energy efficiency. Hard start applies full voltage instantly, causing higher inrush current that can lead to increased wear and potential electrical issues.
Understanding Soft Start Mechanisms
Soft start mechanisms gradually increase voltage or current to electrical motors, reducing inrush currents and mechanical stress during startup. This controlled ramp-up minimizes electrical disturbances and extends the lifespan of motor components by preventing sudden torque spikes. Soft starters use semiconductor devices like thyristors or triacs to modulate power delivery, optimizing energy efficiency and enhancing operational reliability in industrial applications.
How Hard Start Methods Work
Hard start methods kick-start electric motors by momentarily applying a high voltage or current to overcome initial inertia and mechanical resistance. This sudden surge rapidly increases motor torque, enabling quick acceleration from a standstill but often causing electrical and mechanical stress. Circuit components like capacitors or autotransformers are commonly used to handle these peak loads during the start phase.
Key Differences Between Soft Start and Hard Start
Soft start motors limit inrush current by gradually increasing voltage, reducing mechanical stress and extending equipment lifespan. Hard start motors apply full voltage immediately, causing higher current spikes and potential wear on electrical components. The choice between soft start and hard start impacts energy efficiency, motor protection, and overall system reliability.
Applications Suitable for Soft Start
Soft start motors are ideal for applications requiring gradual acceleration to reduce mechanical stress and electrical surges, such as conveyor belts, pumps, fans, and compressors. These devices benefit from smooth torque ramp-up, minimizing wear and extending equipment lifespan. Soft start technology is particularly suited for HVAC systems, industrial mixers, and elevators, where controlled start-up enhances operational stability and efficiency.
Applications Ideal for Hard Start
Hard start motors deliver high starting torque essential for heavy-duty applications such as compressors, pumps, and large HVAC systems. You benefit from their ability to handle frequent starts and stops without performance loss, making them ideal for industrial machinery and equipment with high inertia loads. Their robust design ensures reliable operation under demanding conditions where smooth acceleration is less critical than power.
Energy Efficiency: Soft Start vs Hard Start
Soft start motor controllers improve energy efficiency by gradually increasing voltage, reducing inrush current and mechanical stress, which lowers power consumption during startup. Hard start methods draw full power instantly, leading to higher energy spikes and increased strain on electrical components. Implementing soft start systems can result in significant energy savings and extended equipment lifespan compared to hard start techniques.
Equipment Lifespan and Maintenance Impacts
Soft start reduces mechanical stress on motors by gradually increasing voltage, significantly extending equipment lifespan and decreasing maintenance frequency. Hard start applies full voltage immediately, causing higher inrush currents that accelerate wear and increase the risk of mechanical failure. Implementing soft start technology leads to lower downtime and reduced replacement costs compared to traditional hard start methods.
Cost Considerations: Initial and Long-Term
Soft start systems typically incur higher initial costs due to sophisticated control electronics and components designed to limit inrush current, reducing mechanical stress and electrical spikes during motor startup. Over the long term, soft starters can lower maintenance expenses and extend equipment lifespan by minimizing wear and tear on electrical and mechanical parts. In contrast, hard start methods have lower upfront costs but may lead to increased long-term expenses from frequent motor repairs and energy inefficiency caused by high starting currents.
Selecting the Right Start Method for Your Needs
Choosing between a soft start and hard start depends on your specific application requirements and equipment sensitivity. Soft start methods gradually increase voltage to reduce inrush current and mechanical stress, ideal for prolonging motor life in applications like HVAC systems or conveyors. Hard start techniques provide immediate full voltage, suitable for equipment requiring quick, full torque startup despite higher wear risk, so assess your operational needs to select the best option for your system's reliability and efficiency.
Soft start vs hard start Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com