The ESP32 excels in wireless connectivity with integrated Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, making it ideal for IoT applications, while the STM32 offers a wide range of powerful MCUs with superior real-time performance and extensive peripheral options for industrial and embedded systems. Explore the rest of the article to determine which microcontroller fits your specific project needs.
Table of Comparison
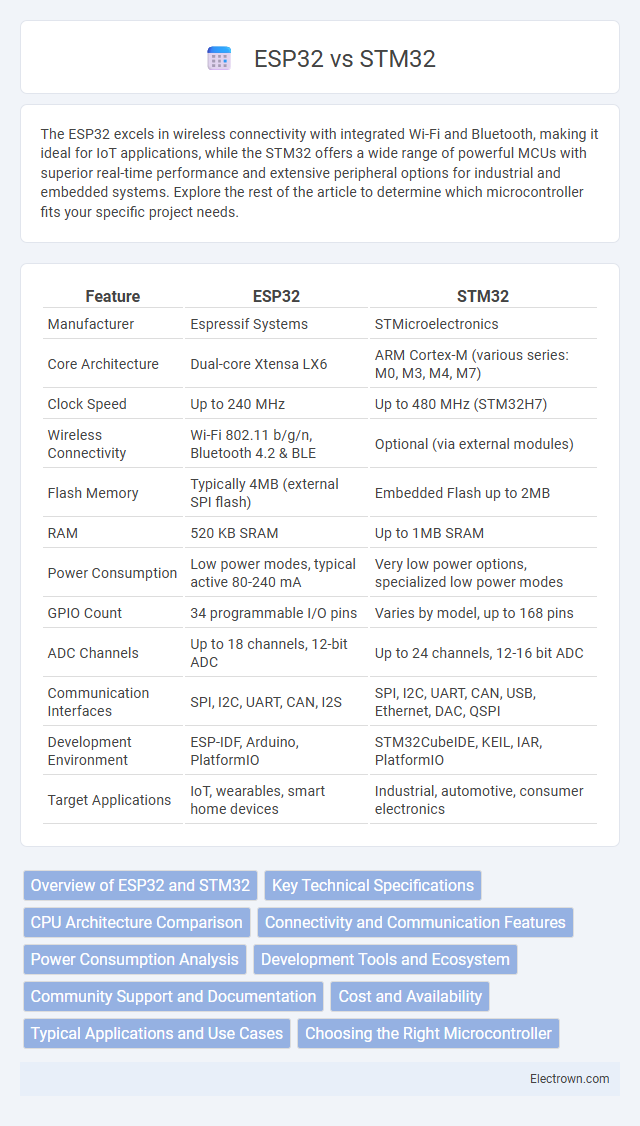
| Feature | ESP32 | STM32 |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Espressif Systems | STMicroelectronics |
| Core Architecture | Dual-core Xtensa LX6 | ARM Cortex-M (various series: M0, M3, M4, M7) |
| Clock Speed | Up to 240 MHz | Up to 480 MHz (STM32H7) |
| Wireless Connectivity | Wi-Fi 802.11 b/g/n, Bluetooth 4.2 & BLE | Optional (via external modules) |
| Flash Memory | Typically 4MB (external SPI flash) | Embedded Flash up to 2MB |
| RAM | 520 KB SRAM | Up to 1MB SRAM |
| Power Consumption | Low power modes, typical active 80-240 mA | Very low power options, specialized low power modes |
| GPIO Count | 34 programmable I/O pins | Varies by model, up to 168 pins |
| ADC Channels | Up to 18 channels, 12-bit ADC | Up to 24 channels, 12-16 bit ADC |
| Communication Interfaces | SPI, I2C, UART, CAN, I2S | SPI, I2C, UART, CAN, USB, Ethernet, DAC, QSPI |
| Development Environment | ESP-IDF, Arduino, PlatformIO | STM32CubeIDE, KEIL, IAR, PlatformIO |
| Target Applications | IoT, wearables, smart home devices | Industrial, automotive, consumer electronics |
Overview of ESP32 and STM32
ESP32 is a powerful dual-core microcontroller with integrated Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, making it ideal for IoT applications requiring wireless connectivity, while STM32 offers a broad range of ARM Cortex-M based microcontrollers known for high performance, low power consumption, and extensive peripheral support. The ESP32 excels in rapid prototyping and embedded projects needing seamless network integration, whereas STM32 provides scalable options from entry-level to high-end devices suitable for industrial and real-time applications. Your choice depends on whether wireless features or processing power and peripheral versatility are the priority for your project.
Key Technical Specifications
The ESP32 features a dual-core Xtensa LX6 processor running up to 240 MHz, integrated Wi-Fi 802.11 b/g/n, and Bluetooth 4.2, with up to 520 KB SRAM and 4 MB flash memory. The STM32 family, based on ARM Cortex-M cores ranging from M0 to M7, offers a broader variety of clock speeds (up to 480 MHz), larger RAM options, and extensive peripheral support but lacks built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. Your choice depends on whether wireless connectivity (ESP32) or processing power and peripheral flexibility (STM32) align better with your project requirements.
CPU Architecture Comparison
ESP32 features a dual-core Tensilica Xtensa LX6 CPU with clock speeds up to 240 MHz, optimized for wireless communication and real-time control, while STM32 microcontrollers utilize ARM Cortex-M cores ranging from M0 to M7, offering diverse performance levels and power efficiency for embedded applications. The ESP32's architecture excels in integrated Wi-Fi and Bluetooth connectivity, making it suitable for IoT projects requiring robust wireless protocols. STM32's Cortex-M architecture supports extensive peripheral options and low-power modes, providing flexibility for industrial and automotive embedded systems.
Connectivity and Communication Features
The ESP32 excels in wireless connectivity with integrated dual-mode Bluetooth (BLE and Classic) and Wi-Fi 802.11 b/g/n support, making it ideal for IoT applications requiring robust wireless communication. In contrast, the STM32 family offers extensive wired communication protocols such as CAN, USB, UART, SPI, and I2C, catering to industrial and automotive environments where reliable, low-latency data transfer is critical. Your choice depends on whether wireless connectivity or diverse wired interfaces are essential for your project's communication needs.
Power Consumption Analysis
ESP32 features a dual-core processor with integrated Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, consuming approximately 80-260 mA during active operation but can drop to as low as 5 uA in deep sleep mode, enabling efficient power management for IoT applications. STM32 microcontrollers offer diverse power modes, typically drawing around 20-30 mA in active mode and as low as 100 nA in standby, making them highly suitable for ultra-low-power embedded solutions. Your choice depends on balancing wireless connectivity needs against ultra-low power consumption priorities.
Development Tools and Ecosystem
ESP32 development thrives with the ESP-IDF framework and extensive support from Arduino IDE, offering abundant libraries and community resources that accelerate prototyping. STM32 benefits from a robust ecosystem including STM32CubeMX for peripheral configuration and the widely-used Keil and STM32CubeIDE, providing professional-grade debugging and optimization tools. Your choice between ESP32 and STM32 depends on whether you prioritize rapid, flexible Wi-Fi/Bluetooth integration or deep control with comprehensive firmware customization.
Community Support and Documentation
The ESP32 benefits from a large and active community with extensive forums, GitHub repositories, and user-contributed tutorials, providing rich documentation for rapid development. STM32, supported by STMicroelectronics, offers comprehensive official documentation, including detailed datasheets, reference manuals, and a robust ecosystem with professional tools like STM32CubeMX and HAL libraries. Both platforms have thriving communities, but ESP32 excels in ease of community-driven support while STM32 stands out in official technical resources.
Cost and Availability
ESP32 microcontrollers generally offer a lower-cost solution compared to STM32, making them ideal for budget-sensitive projects and hobbyist applications. ESP32 chips are widely available through multiple distributors and feature integrated Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, enhancing their value proposition. STM32 devices, while sometimes pricier, provide extensive scalability and availability across various performance tiers, supported by a robust ecosystem for industrial and professional use.
Typical Applications and Use Cases
The ESP32 excels in IoT applications requiring built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth connectivity, such as smart home devices, wearable electronics, and wireless sensor networks. STM32 microcontrollers are favored in industrial automation, automotive systems, and medical devices due to their robust performance, real-time capabilities, and extensive peripheral support. Both platforms serve embedded systems but target different use cases based on connectivity needs and processing power.
Choosing the Right Microcontroller
Choosing the right microcontroller depends on project requirements such as processing power, connectivity, and power efficiency. The ESP32 excels in wireless communication with built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, making it ideal for IoT applications requiring network connectivity. In contrast, the STM32 offers a wide range of performance options and extensive peripheral support, suited for applications needing high computational capabilities and real-time control.
ESP32 vs STM32 Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com