Drive isolation transformers provide electrical isolation and reduce harmonics in industrial motor drives, enhancing system safety and equipment protection, while auto transformers offer voltage transformation with a common winding, making them more compact and cost-effective but without isolation benefits. Discover which transformer type best suits Your application by exploring their key differences and advantages in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
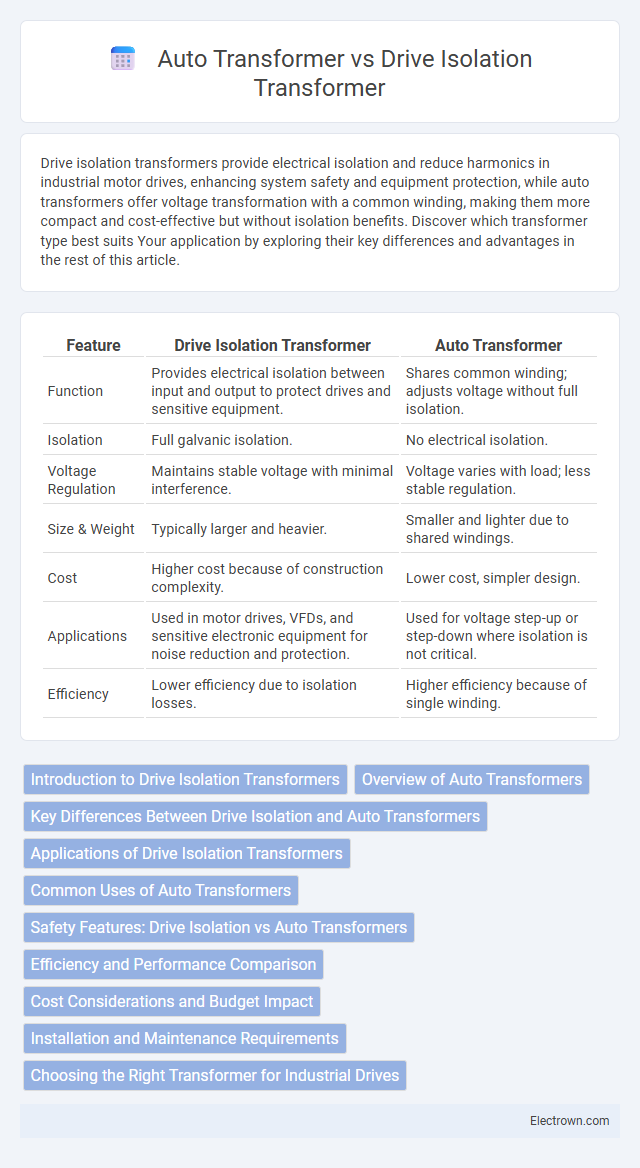
| Feature | Drive Isolation Transformer | Auto Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Provides electrical isolation between input and output to protect drives and sensitive equipment. | Shares common winding; adjusts voltage without full isolation. |
| Isolation | Full galvanic isolation. | No electrical isolation. |
| Voltage Regulation | Maintains stable voltage with minimal interference. | Voltage varies with load; less stable regulation. |
| Size & Weight | Typically larger and heavier. | Smaller and lighter due to shared windings. |
| Cost | Higher cost because of construction complexity. | Lower cost, simpler design. |
| Applications | Used in motor drives, VFDs, and sensitive electronic equipment for noise reduction and protection. | Used for voltage step-up or step-down where isolation is not critical. |
| Efficiency | Lower efficiency due to isolation losses. | Higher efficiency because of single winding. |
Introduction to Drive Isolation Transformers
Drive isolation transformers provide electrical isolation between the drive system and the power source, significantly reducing noise, harmonics, and transient voltages in motor control applications. These transformers enhance system reliability by minimizing electrical interference and protecting sensitive drive components from voltage spikes and ground loops. Your industrial drive system benefits from improved power quality and extended equipment lifespan when using a properly selected drive isolation transformer.
Overview of Auto Transformers
Auto transformers feature a single winding that acts as both the primary and secondary, sharing a common winding section, which results in a more compact and cost-effective design compared to isolation transformers. They provide voltage transformation with higher efficiency and lower copper losses, making them suitable for applications requiring voltage regulation without isolation. Auto transformers lack galvanic isolation, limiting their use where electrical isolation and safety are critical.
Key Differences Between Drive Isolation and Auto Transformers
Drive isolation transformers provide complete electrical isolation between input and output, enhancing safety and reducing electrical noise, while auto transformers share a common winding and offer voltage transformation without isolation. Their applications differ significantly: drive isolation transformers are ideal for sensitive electronics and motor drives, whereas auto transformers are preferred for lightweight step-up or step-down voltage tasks. Your choice depends on whether electrical isolation or compact, efficient voltage conversion is the priority.
Applications of Drive Isolation Transformers
Drive isolation transformers are specifically designed for sensitive industrial applications where electrical noise suppression, harmonic filtering, and equipment protection are critical, such as motor drives, automation systems, and variable frequency drives (VFDs). Unlike auto transformers, these transformers provide galvanic isolation, preventing ground loops and reducing electrical interference in drives and control circuits, enhancing system reliability. When ensuring the longevity and performance of your motor control systems, drive isolation transformers are essential for mitigating voltage spikes and enhancing power quality.
Common Uses of Auto Transformers
Auto transformers are commonly used in voltage regulation, starting of induction motors, and in power distribution systems to step up or step down voltages efficiently while saving space and cost. They are ideal for applications requiring variable voltage output, such as lighting systems, voltage stabilization in electrical panels, and motor control circuits. Unlike drive isolation transformers, auto transformers do not provide electrical isolation but offer better efficiency in scenarios with small voltage differences.
Safety Features: Drive Isolation vs Auto Transformers
Drive isolation transformers provide enhanced safety features by delivering galvanic isolation between the input power source and sensitive electronic drives, effectively reducing the risk of electrical shock, interference, and ground loop issues. In contrast, auto transformers lack galvanic isolation since they share a common winding, increasing the potential for electrical hazards and offering limited protection against transient voltage spikes. This fundamental difference makes drive isolation transformers preferable in applications requiring stringent safety standards and protection of delicate drive electronics.
Efficiency and Performance Comparison
Drive isolation transformers provide superior electrical isolation and noise reduction, enhancing motor drive performance by minimizing common-mode voltage and harmonic distortion. Auto transformers are more efficient due to lower copper losses and smaller size but lack galvanic isolation, which can affect sensitive drive systems. Your choice depends on whether efficiency or enhanced drive reliability and protection are prioritized in your application.
Cost Considerations and Budget Impact
Drive isolation transformers generally incur higher initial costs compared to auto transformers due to separate primary and secondary windings, which offer superior electrical isolation and safety. Auto transformers feature a simpler design with a single winding, leading to lower material expenses and reduced footprint, thus lowering upfront investment. Budget impact analysis favors auto transformers for cost-sensitive projects, while drive isolation transformers justify higher costs with enhanced protection and compliance in critical applications.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Drive isolation transformers require more complex installation due to their separate primary and secondary windings, ensuring electrical isolation that enhances safety and reduces noise interference in sensitive equipment. Auto transformers have simpler installation with a single winding and fewer components, leading to lower maintenance needs but less isolation protection. Your choice impacts long-term maintenance efforts, as isolation transformers typically demand routine checks for insulation integrity, while auto transformers benefit from straightforward servicing.
Choosing the Right Transformer for Industrial Drives
Selecting the right transformer for industrial drives hinges on understanding the key differences between drive isolation transformers and auto transformers. Drive isolation transformers provide superior electrical isolation and noise reduction, making them ideal for sensitive equipment and environments requiring enhanced safety and interference control. Auto transformers offer a more economical solution with efficient voltage regulation but lack the isolation benefits critical for protecting delicate drive components and ensuring operational reliability.
Drive Isolation Transformer vs Auto Transformer Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com