DC drives offer precise speed control and high starting torque, making them ideal for applications requiring smooth acceleration and deceleration, while AC drives provide greater efficiency, lower maintenance, and better performance in variable speed applications. Explore the following comparison to understand which drive best suits your industrial needs.
Table of Comparison
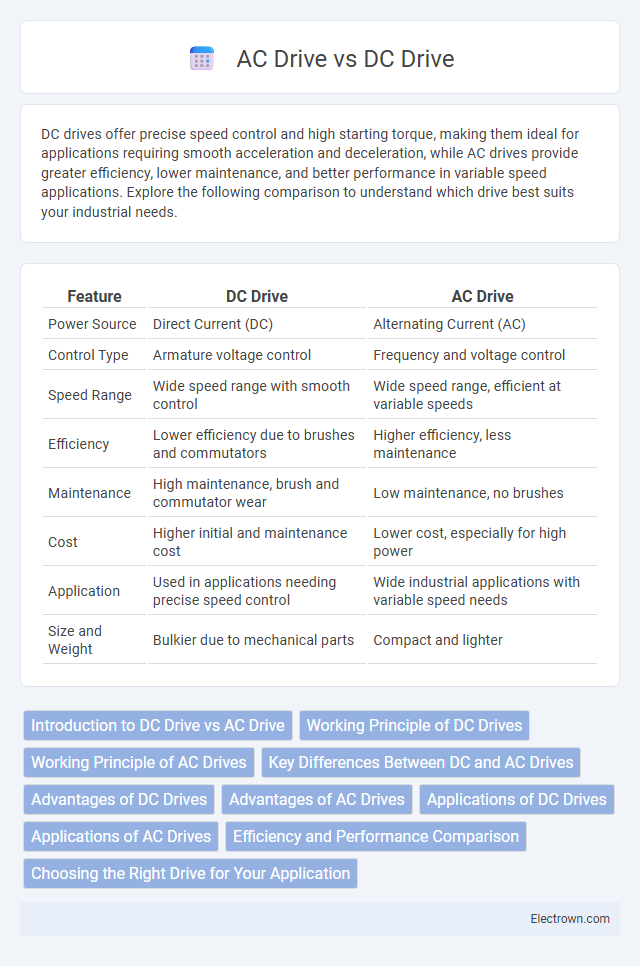
| Feature | DC Drive | AC Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Direct Current (DC) | Alternating Current (AC) |
| Control Type | Armature voltage control | Frequency and voltage control |
| Speed Range | Wide speed range with smooth control | Wide speed range, efficient at variable speeds |
| Efficiency | Lower efficiency due to brushes and commutators | Higher efficiency, less maintenance |
| Maintenance | High maintenance, brush and commutator wear | Low maintenance, no brushes |
| Cost | Higher initial and maintenance cost | Lower cost, especially for high power |
| Application | Used in applications needing precise speed control | Wide industrial applications with variable speed needs |
| Size and Weight | Bulkier due to mechanical parts | Compact and lighter |
Introduction to DC Drive vs AC Drive
DC drives control the speed and torque of direct current motors by adjusting voltage and current through a power electronic converter, offering precise speed regulation and high starting torque. AC drives, also known as variable frequency drives (VFDs), modulate the frequency and voltage supplied to alternating current motors, enhancing energy efficiency and reducing mechanical wear. Both drive types serve critical roles in industrial automation, with DC drives favored for applications requiring fine speed control and AC drives excelling in energy-efficient variable speed operations.
Working Principle of DC Drives
DC drives operate by controlling the voltage and current supplied to a DC motor, enabling precise regulation of speed and torque through variable armature voltage or field flux adjustments. The commutator and brushes in DC motors facilitate direct current flow, allowing for smooth and accurate motor control suitable for applications requiring fine speed variations. This working principle contrasts with AC drives, which utilize frequency modulation to control motor speed.
Working Principle of AC Drives
AC drives operate by varying the frequency and voltage supplied to an AC motor, using power electronic devices such as inverters and rectifiers to control motor speed and torque precisely. The drive converts incoming AC power to DC via a rectifier, then inverts this DC back to AC at the desired frequency and voltage using pulse-width modulation (PWM) techniques. This enables efficient speed control, energy savings, and improved motor performance in industrial applications.
Key Differences Between DC and AC Drives
DC drives use direct current to control motor speed with precise torque regulation, making them ideal for applications requiring smooth acceleration and variable speed. AC drives operate with alternating current, offering energy efficiency and low maintenance, suited for high-power industrial machinery and variable-frequency applications. Your choice depends on factors like torque accuracy, efficiency, and maintenance demands, with DC drives excelling in fine control and AC drives in durability and cost-effectiveness.
Advantages of DC Drives
DC drives offer precise speed control and high starting torque, making them ideal for applications requiring fine motor adjustments and heavy load handling. Their simple control circuitry and ability to provide smooth acceleration and deceleration enhance operational efficiency and reduce mechanical stress. Your choice of a DC drive can improve performance in systems where accurate speed regulation and quick response are critical.
Advantages of AC Drives
AC drives offer superior energy efficiency and reduced maintenance compared to DC drives due to their simpler design with fewer moving parts and no brushes. These drives provide precise speed and torque control, enhancing performance in industrial applications. Your equipment benefits from increased reliability and longer lifespan when using AC drives in variable-speed motor control systems.
Applications of DC Drives
DC drives are widely used in applications requiring precise speed control and high starting torque, such as electric traction systems, elevators, and conveyor belts. Their ability to provide smooth and adjustable torque makes them ideal for industrial machinery and robotics. You benefit from enhanced control and efficiency in processes demanding variable speed and quick response.
Applications of AC Drives
AC Drives are extensively used in industrial applications requiring precise speed and torque control, such as conveyor systems, pumps, and fans. They are ideal for energy-saving operations in HVAC systems and variable-speed compressors, enhancing overall efficiency. AC Drives also support automation processes in manufacturing, including robotics and CNC machines, due to their reliability and smooth motor control capabilities.
Efficiency and Performance Comparison
DC drives offer precise speed control and high starting torque, making them suitable for applications requiring variable speed and heavy load handling, but they typically have lower efficiency due to brush and commutator losses. AC drives, particularly with modern vector control or direct torque control technologies, deliver higher efficiency, reduced maintenance, and improved performance in terms of smooth speed regulation and energy savings. Overall, AC drives provide superior energy efficiency and longevity, while DC drives excel in dynamic response and torque characteristics.
Choosing the Right Drive for Your Application
Selecting the right drive depends on your application's torque, speed control, and efficiency requirements. DC drives offer precise speed control and high starting torque, ideal for applications needing smooth acceleration and frequent speed changes. AC drives provide better energy efficiency and lower maintenance, making them suitable for variable speed operations in industrial environments.
DC Drive vs AC Drive Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com