A Load Break Switch safely interrupts electrical current under load conditions, ensuring controlled disconnection of power, while an Isolator is primarily used to isolate equipment for maintenance without load interruption. Understand the key differences to optimize the safety and efficiency of Your electrical system by exploring the detailed comparison in this article.
Table of Comparison
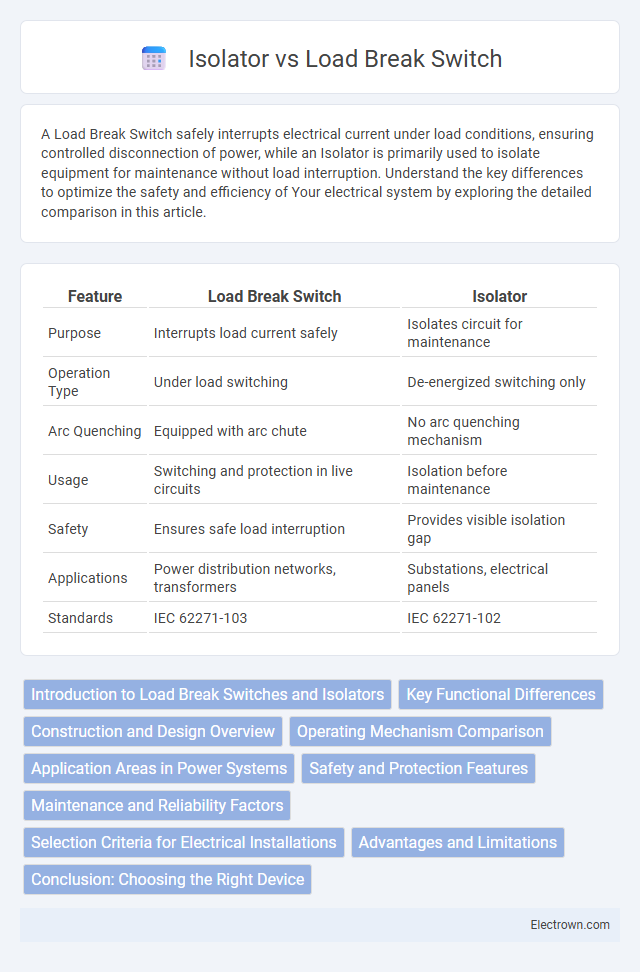
| Feature | Load Break Switch | Isolator |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Interrupts load current safely | Isolates circuit for maintenance |
| Operation Type | Under load switching | De-energized switching only |
| Arc Quenching | Equipped with arc chute | No arc quenching mechanism |
| Usage | Switching and protection in live circuits | Isolation before maintenance |
| Safety | Ensures safe load interruption | Provides visible isolation gap |
| Applications | Power distribution networks, transformers | Substations, electrical panels |
| Standards | IEC 62271-103 | IEC 62271-102 |
Introduction to Load Break Switches and Isolators
Load Break Switches enable safe interruption of electrical circuits under load, providing controlled switching capabilities essential for load management and system protection. Isolators, on the other hand, serve as safety devices that create visible breaks in the circuit, ensuring complete disconnection for maintenance but are not designed to interrupt load current. Understanding the functional differences between these devices enhances Your ability to design and maintain reliable electrical systems.
Key Functional Differences
Load Break Switches are designed to interrupt current flow under load conditions, providing safe switching and protection during power distribution. Isolators, on the other hand, are used primarily for ensuring a circuit is completely de-energized for maintenance, operating only when the load current is zero. Your choice should consider these key functional differences to ensure optimal safety and operational efficiency in electrical systems.
Construction and Design Overview
Load Break Switch features robust contacts designed to interrupt current flow under load conditions, incorporating arc extinction chambers and insulating materials to ensure safe operation, while its compact design allows for integration in electrical distribution systems. Isolators are primarily constructed for visible disconnection with simple mechanical linkages and large insulating barriers to provide clear isolation points without the capacity to break load current. The structural emphasis for Load Break Switches is on durability and operational safety during load interruption, whereas Isolators prioritize clear isolation for maintenance with minimal mechanical complexity.
Operating Mechanism Comparison
Load Break Switches use a motorized or manual mechanism designed to interrupt current flow under load conditions safely, employing arc quenching methods for protection. Isolators, on the other hand, operate with a simple mechanical link that physically disconnects the circuit only when there is no load current, relying on visible isolation for safety. Your choice between these devices should consider the operating mechanism's capability to handle live current interruption versus providing a clear circuit break for maintenance.
Application Areas in Power Systems
Load break switches are essential in power systems for safely interrupting current under load conditions, making them ideal for controlling distribution feeders, capacitor banks, and transformers. Isolators, designed solely for de-energized circuit isolation, play a crucial role in maintenance operations by providing visible separation points in transmission and distribution lines. Understanding the specific application areas of load break switches and isolators ensures your power system operates safely and efficiently during both normal and maintenance conditions.
Safety and Protection Features
Load Break Switches provide enhanced safety with their ability to interrupt current under load conditions, ensuring circuit protection during switching operations. Isolators, also known as disconnectors, are primarily designed for safe isolation of equipment and do not interrupt current; their main safety feature is providing visible isolation for maintenance purposes. Combining both devices in electrical systems maximizes protection by allowing safe load interruption and clear equipment isolation.
Maintenance and Reliability Factors
Load Break Switches offer superior reliability in maintenance due to their ability to interrupt current under load, reducing wear on contacts and minimizing downtime. Isolators require circuits to be de-energized before operation, which complicates maintenance and increases potential for human error. The design of Load Break Switches ensures safer and more efficient maintenance procedures, enhancing overall system reliability.
Selection Criteria for Electrical Installations
Load Break Switches are selected for electrical installations requiring safe interruption of load current under normal operating conditions, offering quick switching and fault isolation capabilities. Isolators, by contrast, are primarily chosen for ensuring a visible disconnecting gap for maintenance safety, not intended for breaking load current. Your decision should prioritize operational needs, load current ratings, and safety standards compliance to ensure appropriate functionality and protection.
Advantages and Limitations
Load Break Switches offer the advantage of safely interrupting current under load, allowing maintenance and operational flexibility without power shutdowns, which enhances system reliability and reduces downtime. However, their mechanical complexity and higher cost compared to isolators can increase maintenance requirements and initial investment. Isolators provide a simple, cost-effective solution for circuit isolation during de-energized conditions but lack the capability to interrupt current, making them unsuitable for load switching and requiring careful coordination to ensure safety.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Device
Selecting the right device between a Load Break Switch and an Isolator depends on the application's specific requirements for load interruption and safety isolation. A Load Break Switch is ideal for switching circuits under load, offering operational flexibility and enhanced safety during maintenance by safely interrupting current flow. In contrast, an Isolator provides a visible break for ensuring a safe isolation point but should only be operated when the circuit is de-energized, making it suitable primarily for safety isolation rather than load switching.
Load Break Switch vs Isolator Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com