Fiber optic communication offers significantly higher bandwidth and faster data transmission speeds compared to copper cables, making it ideal for modern high-demand networks. Discover how choosing the right medium can enhance your connectivity by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
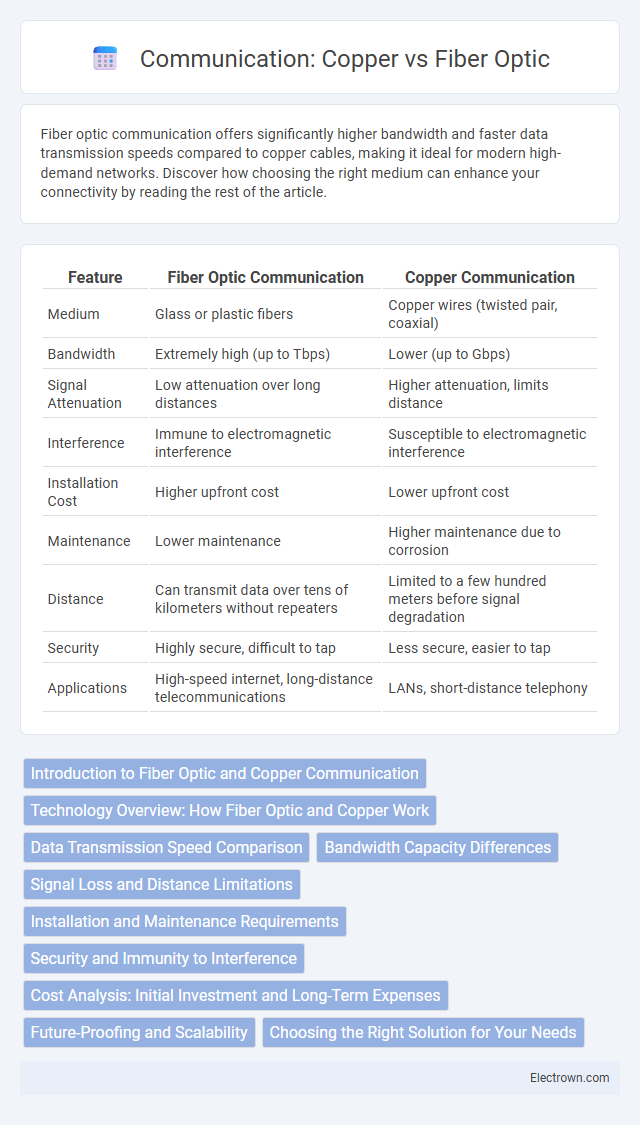
| Feature | Fiber Optic Communication | Copper Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Glass or plastic fibers | Copper wires (twisted pair, coaxial) |
| Bandwidth | Extremely high (up to Tbps) | Lower (up to Gbps) |
| Signal Attenuation | Low attenuation over long distances | Higher attenuation, limits distance |
| Interference | Immune to electromagnetic interference | Susceptible to electromagnetic interference |
| Installation Cost | Higher upfront cost | Lower upfront cost |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance | Higher maintenance due to corrosion |
| Distance | Can transmit data over tens of kilometers without repeaters | Limited to a few hundred meters before signal degradation |
| Security | Highly secure, difficult to tap | Less secure, easier to tap |
| Applications | High-speed internet, long-distance telecommunications | LANs, short-distance telephony |
Introduction to Fiber Optic and Copper Communication
Fiber optic communication uses light pulses transmitted through glass or plastic fibers, offering higher bandwidth and longer distance data transmission compared to copper cables. Copper communication relies on electrical signals transmitted via metal wires, typically used for shorter distances with susceptibility to electromagnetic interference. Understanding the differences helps optimize Your network infrastructure for speed, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
Technology Overview: How Fiber Optic and Copper Work
Fiber optic communication transmits data as pulses of light through strands of glass or plastic fibers, enabling high-speed and long-distance data transfer with minimal signal loss and interference. Copper communication utilizes electrical signals sent through copper wires, commonly twisted pairs or coaxial cables, suitable for shorter distances but prone to electromagnetic interference and signal degradation. Fiber optic technology supports higher bandwidth and faster data rates compared to copper, making it the preferred choice for modern telecommunications and high-performance networks.
Data Transmission Speed Comparison
Fiber optic communication offers significantly higher data transmission speeds compared to copper, reaching up to 100 Gbps over long distances without signal degradation. Copper cables typically support speeds up to 10 Gbps but are limited by interference and shorter maximum transmission lengths. Your network performance can be greatly enhanced by choosing fiber optic technology when prioritizing speed and reliability.
Bandwidth Capacity Differences
Fiber optic communication offers significantly higher bandwidth capacity compared to copper cables, supporting data transmission rates up to 100 Gbps and beyond, ideal for high-demand applications. Copper communication, typically limited to 1 Gbps or lower over longer distances due to electromagnetic interference and signal attenuation, is less suitable for modern high-speed networks. Fiber optics enable broader frequency ranges and longer transmission distances without signal degradation, making them superior for bandwidth-intensive environments.
Signal Loss and Distance Limitations
Fiber optic communication experiences significantly lower signal loss compared to copper cables, enabling data transmission over much longer distances without the need for signal boosters. Copper cables are limited by higher attenuation and electromagnetic interference, restricting effective communication typically to 100 meters for Ethernet connections. Your network's performance and reliability can be greatly enhanced by choosing fiber optics when minimizing signal degradation and covering extensive distances are critical factors.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Fiber optic cables demand precise installation techniques and specialized equipment, resulting in higher initial setup costs but offering greater durability and resistance to environmental interference. Copper cables are easier and quicker to install with standard tools, yet they require more frequent maintenance due to susceptibility to corrosion and electromagnetic interference. Your choice impacts long-term operational efficiency, where fiber optic systems reduce maintenance efforts despite complex installation procedures.
Security and Immunity to Interference
Fiber optic communication offers superior security due to its resistance to electromagnetic interference and signal tapping, making unauthorized access extremely difficult. Copper communication cables are highly susceptible to electromagnetic interference and can be tapped more easily, posing risks to data integrity and confidentiality. Fiber optic's immunity to radio frequency interference and noise ensures more stable and secure data transmission in environments with high electromagnetic activity.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Long-Term Expenses
Fiber optic communication typically requires a higher initial investment due to the cost of fiber cables, specialized installation, and advanced equipment compared to copper systems. Over time, fiber optics reduce long-term expenses with lower maintenance, higher durability, and enhanced bandwidth capabilities that support future upgrades. Your overall cost efficiency improves with fiber optic technology, especially for businesses demanding scalable and reliable high-speed data transmission.
Future-Proofing and Scalability
Fiber optic communication offers superior future-proofing and scalability compared to copper by supporting significantly higher bandwidths and transmission speeds over longer distances without signal degradation. Its ability to handle increasing data demands in sectors like 5G, cloud computing, and IoT ensures long-term infrastructure relevance and cost efficiency. Copper cables, limited in bandwidth and susceptible to electromagnetic interference, often require frequent upgrades to meet evolving network requirements.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Fiber optic communication offers superior bandwidth, faster data transmission, and longer-distance capabilities compared to copper, making it ideal for high-speed internet, data centers, and telecommunications. Copper cables remain cost-effective and easier to install for shorter distances and legacy systems, providing reliable performance for typical office or residential networks. Assess your data speed requirements, distance, budget, and environmental conditions to choose the right communication medium that aligns with your specific needs.
Fiber Optic vs Copper Communication Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com