Server-Side Rendering (SSR) improves website performance by generating HTML on the server, enhancing SEO and providing faster initial load times compared to client-side approaches. Understanding the differences between SSR and Electron Microscopy Resources (EMR) can help you choose the right solution for your project's needs--explore the full article for a detailed comparison.
Table of Comparison
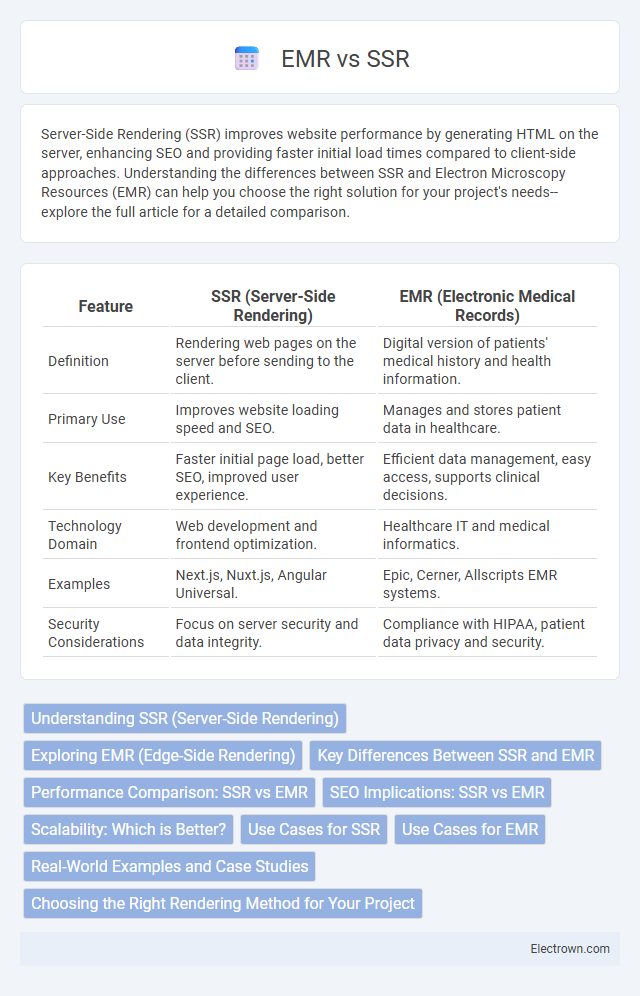
| Feature | SSR (Server-Side Rendering) | EMR (Electronic Medical Records) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rendering web pages on the server before sending to the client. | Digital version of patients' medical history and health information. |
| Primary Use | Improves website loading speed and SEO. | Manages and stores patient data in healthcare. |
| Key Benefits | Faster initial page load, better SEO, improved user experience. | Efficient data management, easy access, supports clinical decisions. |
| Technology Domain | Web development and frontend optimization. | Healthcare IT and medical informatics. |
| Examples | Next.js, Nuxt.js, Angular Universal. | Epic, Cerner, Allscripts EMR systems. |
| Security Considerations | Focus on server security and data integrity. | Compliance with HIPAA, patient data privacy and security. |
Understanding SSR (Server-Side Rendering)
Server-Side Rendering (SSR) involves generating the full HTML content of a webpage on the server before sending it to the client, ensuring faster initial load times and improved SEO performance. SSR allows browsers to receive fully rendered pages, enhancing user experience, especially on slower devices or networks. Popular frameworks like Next.js and Nuxt.js leverage SSR to optimize web application performance by reducing client-side JavaScript execution.
Exploring EMR (Edge-Side Rendering)
Edge-Side Rendering (EMR) enhances web performance by processing content on edge servers located closer to users, reducing latency compared to traditional Server-Side Rendering (SSR). EMR enables dynamic content delivery with faster load times, improving user experience and SEO rankings by minimizing the distance data travels. This method leverages CDN edge nodes to balance the workload between client and server, optimizing resources and enabling real-time updates without full page reloads.
Key Differences Between SSR and EMR
SSR (Shared Save Record) and EMR (Electronic Medical Record) differ primarily in scope and functionality; SSR involves shared patient data accessible across multiple providers, enhancing care coordination, while EMR typically refers to digital records maintained within a single healthcare organization. SSR systems emphasize interoperability and patient data exchange across different platforms, whereas EMRs focus on internal documentation and clinical workflows. Understanding these distinctions can help you choose the right system for seamless data management and improved healthcare delivery.
Performance Comparison: SSR vs EMR
Server-Side Rendering (SSR) delivers faster initial page loads by rendering content on the server, which improves SEO and reduces Time to First Byte (TTFB) compared to client-side rendering used in Electron Microscopy Reconstruction (EMR). EMR leverages advanced local hardware acceleration and GPU resources to render complex 3D reconstructions swiftly but may experience latency due to client-side processing overhead. SSR typically outperforms EMR in web-based applications by minimizing rendering time and optimizing server resource allocation, whereas EMR excels in high-fidelity, computation-intensive microscopy image rendering tasks.
SEO Implications: SSR vs EMR
Server-Side Rendering (SSR) significantly enhances SEO by delivering fully rendered HTML pages to search engine crawlers, improving indexability and page load speed. Client-Side Rendering (CSR), including frameworks like EMR (Ember.js), often results in delayed content visibility for crawlers, potentially hindering SEO performance. Websites leveraging SSR tend to achieve higher search rankings and better user engagement due to optimized metadata and faster time-to-content.
Scalability: Which is Better?
Server-Side Rendering (SSR) offers better scalability for dynamic content and personalized user experiences, as it generates HTML on the server for each request, reducing client load but increasing server demand. Edge-Managed Rendering (EMR) leverages distributed edge servers, enhancing scalability by reducing latency and offloading processing closer to the user, making it ideal for high-traffic applications with global audiences. Scalability depends on application needs; SSR suits centralized control and dynamic content, while EMR excels in performance and resilience for distributed user bases.
Use Cases for SSR
Solid State Relays (SSR) excel in applications requiring fast switching with no mechanical wear, such as industrial automation, temperature control systems, and motor drives. Their ability to operate silently and handle high-frequency switching makes them ideal for audio equipment, medical devices, and semiconductor manufacturing. SSRs also offer enhanced reliability in harsh environments where vibration and dust would deteriorate Electromechanical Relays (EMR).
Use Cases for EMR
EMR (Electronic Medical Records) are essential for managing patient data in outpatient settings, small clinics, and specialty practices due to their streamlined documentation and easy access to medical history. They improve clinical workflows by enabling efficient scheduling, billing, and lab integration, enhancing overall patient care coordination. Your healthcare facility can benefit from EMR systems to optimize routine care management and support decision-making with real-time patient information.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
In real-world scenarios, SSR (Server-Side Rendering) is exemplified by companies like Netflix and Airbnb, which leverage SSR to improve initial load times and SEO performance by pre-rendering content on the server. EMR (Elastic MapReduce), prominently used by organizations such as Yelp and Expedia, enables efficient large-scale data processing and analytics through distributed computing on AWS cloud infrastructure. Case studies show SSR enhances user engagement by delivering faster page loads, while EMR streamlines complex data workflows and reduces operational costs in big data environments.
Choosing the Right Rendering Method for Your Project
Choosing the right rendering method for your project depends on factors like performance, SEO needs, and user experience. Server-Side Rendering (SSR) delivers fully rendered pages from the server, improving load times and SEO for dynamic content. In contrast, Client-Side Rendering (CSR) or Emulated Rendering (EMR) relies on the browser to generate content, suitable for highly interactive applications but less optimal for initial load speed and SEO.
SSR vs EMR Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com