A float switch measures liquid levels by physically rising and falling with the fluid, offering simple and reliable mechanical detection, while capacitive level sensors detect changes in electrical capacitance caused by varying fluid levels, enabling non-contact and precise monitoring. Explore the rest of the article to understand which level sensor suits your application needs best.
Table of Comparison
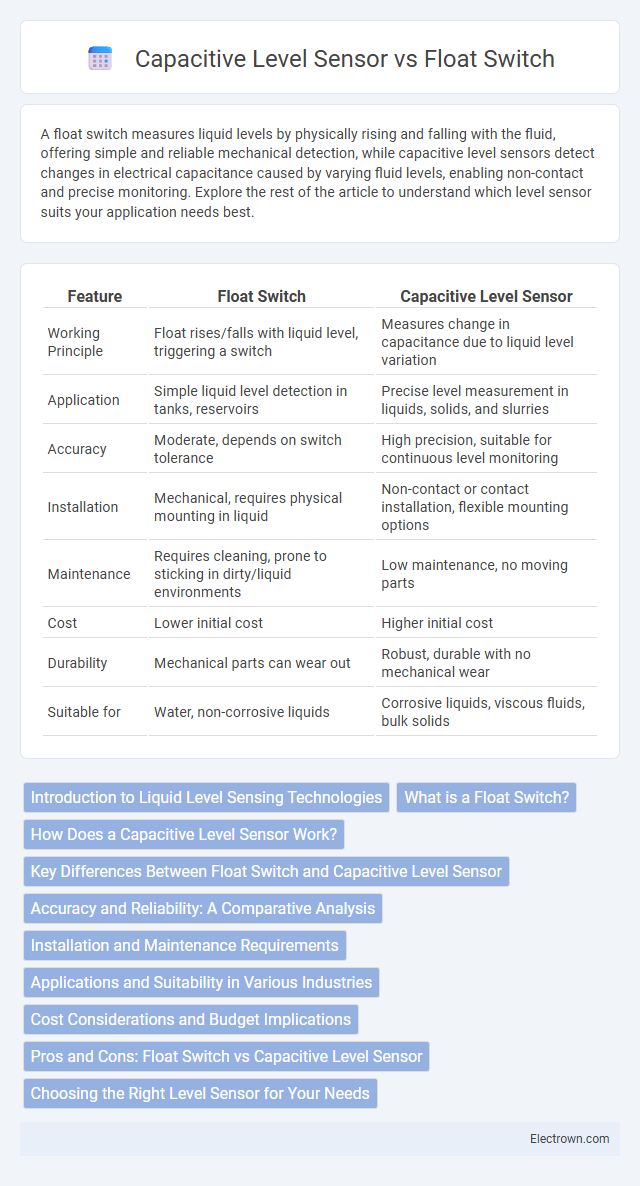
| Feature | Float Switch | Capacitive Level Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Working Principle | Float rises/falls with liquid level, triggering a switch | Measures change in capacitance due to liquid level variation |
| Application | Simple liquid level detection in tanks, reservoirs | Precise level measurement in liquids, solids, and slurries |
| Accuracy | Moderate, depends on switch tolerance | High precision, suitable for continuous level monitoring |
| Installation | Mechanical, requires physical mounting in liquid | Non-contact or contact installation, flexible mounting options |
| Maintenance | Requires cleaning, prone to sticking in dirty/liquid environments | Low maintenance, no moving parts |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Durability | Mechanical parts can wear out | Robust, durable with no mechanical wear |
| Suitable for | Water, non-corrosive liquids | Corrosive liquids, viscous fluids, bulk solids |
Introduction to Liquid Level Sensing Technologies
Float switches and capacitive level sensors are fundamental technologies used for liquid level detection in various industrial applications. Float switches operate through buoyancy, triggering an electrical contact when the liquid reaches a specific level, providing reliable and mechanical-based sensing. Capacitive sensors utilize changes in dielectric constant caused by the presence or absence of liquid, offering non-contact measurement with high sensitivity and accuracy.
What is a Float Switch?
A float switch is a mechanical device used to detect the level of liquid within a tank or container by floating on the surface and activating a switch when a certain level is reached. It is commonly employed in water tanks, sump pumps, and industrial fluid systems for simple, reliable liquid level control and monitoring. Your choice of a float switch ensures accurate liquid level detection through its buoyancy-driven mechanism, making it suitable for various applications involving water and other fluids.
How Does a Capacitive Level Sensor Work?
A capacitive level sensor detects liquid levels by measuring changes in capacitance caused by the dielectric constant variation between the sensor probe and the surrounding medium. When the liquid comes into contact with the sensor, the capacitance increases, triggering a signal that indicates the liquid level. Your system benefits from precise, non-contact measurement suitable for various fluids, unlike float switches that rely on mechanical movement.
Key Differences Between Float Switch and Capacitive Level Sensor
Float switches detect liquid level through a physical buoyant mechanism that triggers a switch, making them ideal for simple on/off level detection in water or other clean liquids. Capacitive level sensors measure changes in capacitance caused by the presence or absence of liquid, allowing for precise, continuous level measurement even in viscous or corrosive fluids. The key differences include the float switch's reliance on mechanical movement versus the capacitive sensor's electronic sensing, with capacitive sensors offering higher sensitivity and suitability for complex applications.
Accuracy and Reliability: A Comparative Analysis
Float switches offer high reliability in liquid level detection due to their mechanical simplicity but may encounter accuracy limitations in turbulent or viscous fluids. Capacitive level sensors provide superior accuracy by measuring dielectric constant changes, enabling precise detection even in challenging environments with varying fluid properties. Both technologies ensure dependable operation, yet capacitive sensors excel in applications demanding fine resolution and minimal maintenance.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Float switches require straightforward installation, typically involving mounting the float arm at the desired liquid level and connecting electrical wiring, making them suitable for tanks with accessible mounting points. Capacitive level sensors demand careful installation to ensure proper sensor placement and calibration, often needing non-metallic tanks or insulated probe segments to prevent false readings, which can increase complexity. Maintenance for float switches involves inspecting mechanical components for wear or obstructions, while capacitive sensors generally require less frequent upkeep but may need periodic recalibration and cleaning to maintain accuracy in varying liquid conditions.
Applications and Suitability in Various Industries
Float switches excel in applications requiring simple, cost-effective liquid level detection, commonly used in water treatment, HVAC systems, and sump pumps due to their reliability and ease of installation. Capacitive level sensors are preferred in industries like food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals where precise, non-contact measurement of various liquid types, including corrosive or viscous fluids, is critical. Each sensor type offers distinct advantages: float switches for straightforward, less sensitive detection, and capacitive sensors for continuous monitoring and compatibility with diverse industrial environments.
Cost Considerations and Budget Implications
Float switches generally offer a lower initial cost and simpler installation, making them suitable for budget-conscious projects with basic level detection needs. Capacitive level sensors, while more expensive upfront due to advanced technology and sensitivity, provide greater accuracy and reduced maintenance costs over time. Evaluating long-term operational expenses and application requirements is crucial when deciding between these two sensor types for efficient budget allocation.
Pros and Cons: Float Switch vs Capacitive Level Sensor
Float switches offer reliable mechanical operation with clear on/off signals and are cost-effective for simple liquid level detection but can suffer from wear, sticking, and limited sensitivity in viscous or turbulent fluids. Capacitive level sensors provide continuous, accurate level measurement and are suitable for a wide range of liquids, including corrosive and non-conductive fluids, though they tend to be more expensive and sensitive to changes in dielectric properties or buildup on sensor surfaces. Selection depends on application requirements such as measurement precision, fluid type, environmental conditions, and maintenance preferences.
Choosing the Right Level Sensor for Your Needs
Choosing the right level sensor depends on the specific application requirements such as fluid type, measurement accuracy, and environmental conditions. Float switches offer cost-effective, reliable detection for liquid presence and level, particularly in clean or non-corrosive fluids, while capacitive level sensors provide higher precision and versatility for a wide range of liquids, including those with varying dielectric constants. Your decision should consider factors like sensor durability, maintenance needs, and compatibility with the medium to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Float Switch vs Capacitive Level Sensor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com