Relays and contactors both control electrical circuits but differ significantly in size, power handling, and application; relays are typically used for low-power signals while contactors manage high-current loads like motors. Discover how to choose the right device for Your specific electrical control needs by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
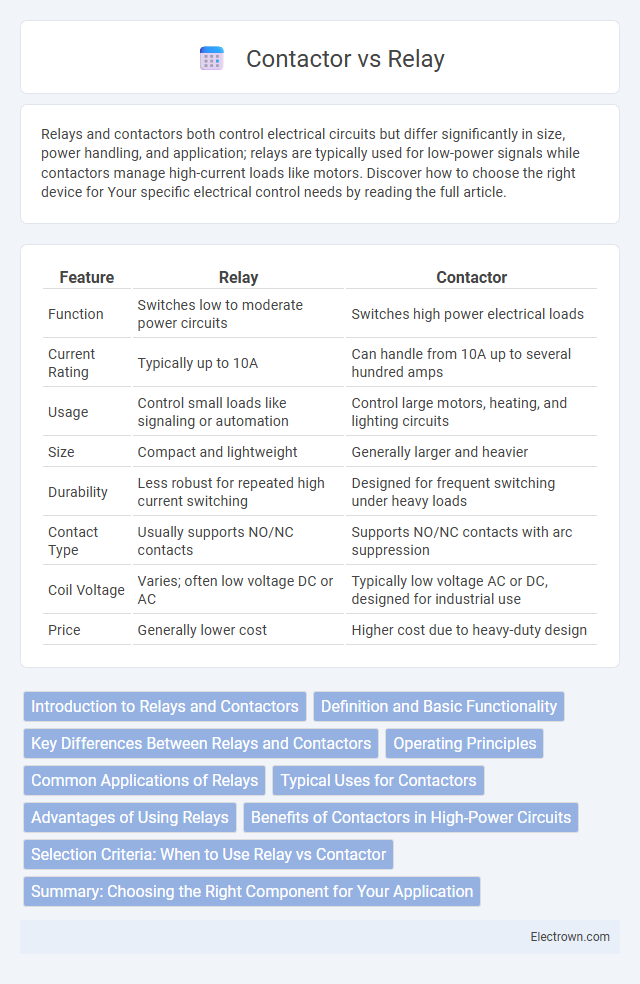
| Feature | Relay | Contactor |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Switches low to moderate power circuits | Switches high power electrical loads |
| Current Rating | Typically up to 10A | Can handle from 10A up to several hundred amps |
| Usage | Control small loads like signaling or automation | Control large motors, heating, and lighting circuits |
| Size | Compact and lightweight | Generally larger and heavier |
| Durability | Less robust for repeated high current switching | Designed for frequent switching under heavy loads |
| Contact Type | Usually supports NO/NC contacts | Supports NO/NC contacts with arc suppression |
| Coil Voltage | Varies; often low voltage DC or AC | Typically low voltage AC or DC, designed for industrial use |
| Price | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to heavy-duty design |
Introduction to Relays and Contactors
Relays and contactors are essential electromechanical devices used to control electrical circuits by opening or closing contacts. Relays are typically designed for low-current applications and provide precise switching capabilities, whereas contactors handle higher current loads in industrial settings. Understanding the differences between relays and contactors is crucial for selecting the right device to protect and manage your electrical system efficiently.
Definition and Basic Functionality
A relay is an electrically operated switch used to control a low-power circuit by opening and closing contacts in another circuit, often for signal or control purposes. A contactor, designed to handle higher currents, functions as a heavy-duty relay primarily used to switch electrical power circuits on and off, especially in motor control applications. Your choice between a relay and a contactor depends on the load requirements and the nature of the electrical control needed.
Key Differences Between Relays and Contactors
Relays and contactors differ primarily in their application and current capacity, with contactors designed for switching higher electrical loads typically above 10 amps, while relays handle lower currents below 10 amps. Contactors feature arc suppression mechanisms and robust construction to manage frequent switching in industrial environments, whereas relays are more suited for sensitive control and signal circuits. The coil voltage and control circuit design also vary, as contactors often utilize higher coil voltages for heavy-duty operations, contrasting with the lower voltage coils common in relays.
Operating Principles
Relays operate by energizing an electromagnetic coil that creates a magnetic field to pull a switch contact, enabling low-power circuits to control high-power loads with electrical isolation. Contactors function similarly but are specifically designed for switching high electrical currents in industrial applications, utilizing a robust electromagnetic core and armature mechanism for reliable heavy-duty performance. The coil activation in both devices causes mechanical movement to open or close contacts, but contactors often feature auxiliary contacts and arc suppression systems for enhanced durability.
Common Applications of Relays
Relays are commonly used in low-power switching applications such as control systems, automation devices, and signal switching circuits due to their ability to handle small currents and provide electrical isolation. They are ideal for automotive electronics, home appliances, and safety systems that require precise control without high voltage handling. Your control system benefits from relays when sensitive devices need protection from high-voltage spikes or when multiple circuits must be controlled simultaneously.
Typical Uses for Contactors
Contactors are primarily used in applications requiring frequent switching of high-power circuits such as electric motors, lighting systems, heating equipment, and industrial machinery. Their robust design enables them to handle large current loads and operate safely in demanding environments, making them ideal for HVAC systems and heavy-duty automation. You rely on contactors for reliable and efficient control of high-voltage electrical loads in commercial and industrial settings.
Advantages of Using Relays
Relays offer advantages such as lower cost, smaller size, and simpler control circuits compared to contactors, making them ideal for low-power applications and precise switching tasks. They provide electrical isolation between control and load circuits, enhancing safety and preventing damage to sensitive electronics. Your choice of relays can improve system reliability and efficiency in automation and control processes due to their fast response and easy integration.
Benefits of Contactors in High-Power Circuits
Contactors are designed to handle high-power circuits with superior durability and safety compared to relays, making them ideal for industrial applications where frequent switching of heavy loads occurs. Their enhanced arc suppression and robust construction ensure reliable operation under high voltage and current conditions, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. By using contactors in your high-power circuits, you benefit from improved control and long-term operational integrity.
Selection Criteria: When to Use Relay vs Contactor
Relays are best suited for low-power, control circuit applications where switching currents are typically under 10 amps, offering fast response times and compact size. Contactors are designed for high-power applications, handling large currents above 10 amps in motor control and heavy load switching with robust construction and enhanced durability. Selection depends on current rating, load type, duty cycle, and coil voltage requirements to ensure reliable operation in electrical control systems.
Summary: Choosing the Right Component for Your Application
Relays are ideal for low-current applications requiring electrical isolation and precise control, while contactors excel in high-current scenarios, managing heavy-duty loads like motors and industrial equipment. Your choice depends on current capacity, application complexity, and the need for durability under frequent switching. Selecting the right component ensures efficient operation, safety, and longevity in your electrical system.
Relay vs Contactor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com