Twisted pair cables consist of pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together to reduce electromagnetic interference, making them ideal for standard networking and telecommunication applications. Shielded cables include an additional protective layer that shields against external electromagnetic noise, offering enhanced performance in environments with high interference; discover the key differences and which option suits your needs by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
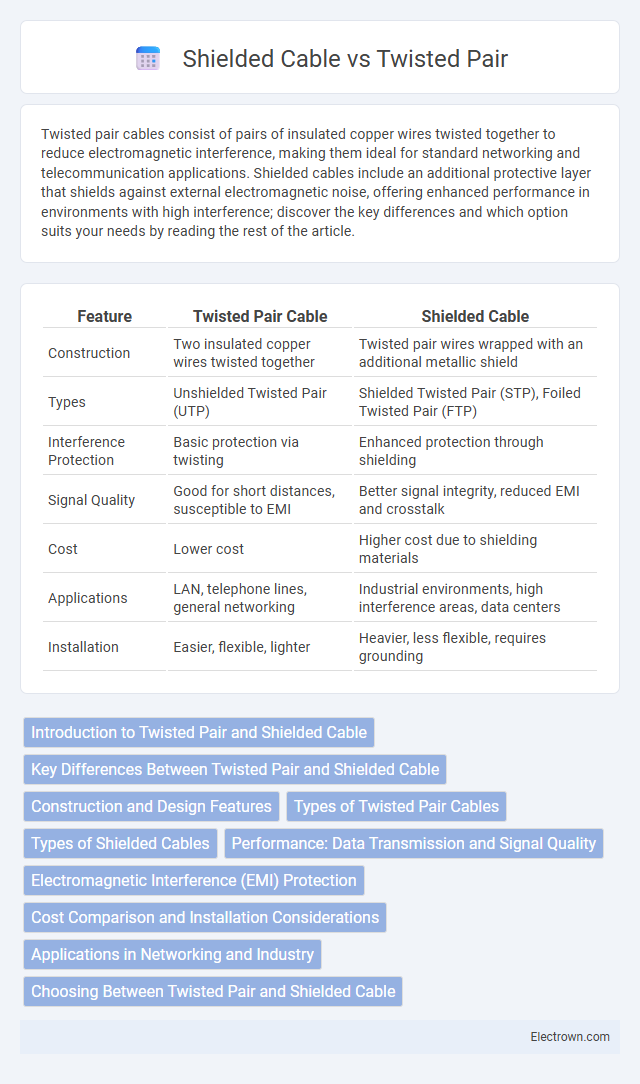
| Feature | Twisted Pair Cable | Shielded Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | Two insulated copper wires twisted together | Twisted pair wires wrapped with an additional metallic shield |
| Types | Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) | Shielded Twisted Pair (STP), Foiled Twisted Pair (FTP) |
| Interference Protection | Basic protection via twisting | Enhanced protection through shielding |
| Signal Quality | Good for short distances, susceptible to EMI | Better signal integrity, reduced EMI and crosstalk |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to shielding materials |
| Applications | LAN, telephone lines, general networking | Industrial environments, high interference areas, data centers |
| Installation | Easier, flexible, lighter | Heavier, less flexible, requires grounding |
Introduction to Twisted Pair and Shielded Cable
Twisted Pair cables consist of pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together to reduce electromagnetic interference, commonly used in Ethernet and telephone networks. Shielded Cables incorporate an additional metallic shield around the twisted pairs, providing enhanced protection against external noise and crosstalk, ideal for environments with high interference. Choosing the right cable depends on your network's susceptibility to interference and required signal integrity.
Key Differences Between Twisted Pair and Shielded Cable
Twisted pair cables consist of pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together to reduce electromagnetic interference, making them ideal for telecommunication and networking applications. Shielded cables, such as Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) or coaxial cables, include an additional conductive layer that encases the wire pairs or individual wires, providing enhanced protection against external electrical noise and crosstalk. Understanding the key differences in construction and shielding helps you choose the right cable for environments requiring higher resistance to signal degradation and interference.
Construction and Design Features
Twisted pair cables feature pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together to reduce electromagnetic interference and crosstalk, making them ideal for voice and data transmission. Shielded cables incorporate an additional conductive shield, such as a foil or braided mesh, surrounding the twisted pairs to provide enhanced protection against external electromagnetic interference. The construction of shielded cables results in higher durability and better signal integrity in environments with significant electrical noise compared to unshielded twisted pair cables.
Types of Twisted Pair Cables
Twisted pair cables come mainly in two types: Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) and Shielded Twisted Pair (STP). UTP cables are widely used in Ethernet networks due to their cost-effectiveness and simplicity, featuring pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together to reduce electromagnetic interference. STP cables include an additional shielding layer to protect against external noise, making them ideal for environments with high interference, thus enhancing your network's reliability and performance.
Types of Shielded Cables
Shielded cables include foil shield, braided shield, and spiral shield types, each designed to protect twisted pair wires from electromagnetic interference (EMI). Foil shields provide 100% coverage with a thin metal layer, ideal for high-frequency signals, while braided shields offer greater mechanical strength and flexibility due to their woven wire mesh. Spiral shields combine flexibility and partial coverage, making them suitable for dynamic or moving applications requiring moderate EMI protection.
Performance: Data Transmission and Signal Quality
Twisted pair cables offer reliable data transmission with reduced electromagnetic interference through their twisted design, making them ideal for standard networking environments. Shielded cables enhance signal quality by incorporating a protective layer that minimizes external noise and crosstalk, ensuring superior performance in high-interference settings like industrial or dense data centers. Your choice should depend on the required transmission speed and environmental factors influencing signal integrity.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Protection
Twisted pair cables reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) by pairing two conductors with opposite currents, which cancels out external noise. Shielded cables provide an extra layer of metal shielding, offering superior EMI protection in environments with strong interference sources. Your choice depends on the level of EMI exposure and the required data transmission quality for your network.
Cost Comparison and Installation Considerations
Twisted pair cables generally offer a lower cost compared to shielded cables, making them a budget-friendly option for many networking installations. Installation of twisted pair cables is simpler and more flexible due to their lighter weight and unshielded design, which allows for easier bending and routing through walls and conduits. Shielded cables require careful grounding and more precise handling to maintain electromagnetic interference protection, often resulting in higher labor costs and more complex installation procedures.
Applications in Networking and Industry
Twisted pair cables are widely used in Ethernet networks for their cost-effectiveness and ease of installation, especially in office environments and residential setups. Shielded cables, due to their superior protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI), are preferred in industrial settings where machinery and heavy electrical equipment can disrupt signal integrity. Choosing the right cable for your networking needs ensures optimal performance and reliability in both commercial and industrial applications.
Choosing Between Twisted Pair and Shielded Cable
Choosing between twisted pair and shielded cable depends on the specific interference environment and data transmission requirements. Twisted pair cables, such as unshielded twisted pair (UTP), offer cost-effective solutions suited for environments with minimal electromagnetic interference (EMI) and are commonly used in Ethernet networks. Shielded cables, including shielded twisted pair (STP) and foil shielded cables, provide better protection against EMI and crosstalk, making them ideal for industrial settings or high-frequency data transmission where signal integrity is critical.
Twisted Pair vs Shielded Cable Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com