Ground Fault Relays detect faults by sensing unintended current flow through the ground, providing essential protection against electric shock and equipment damage. Understanding the key differences between Ground Fault Relays and Earth Leakage Relays will help you choose the right protective device for your electrical system; explore the detailed comparison in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
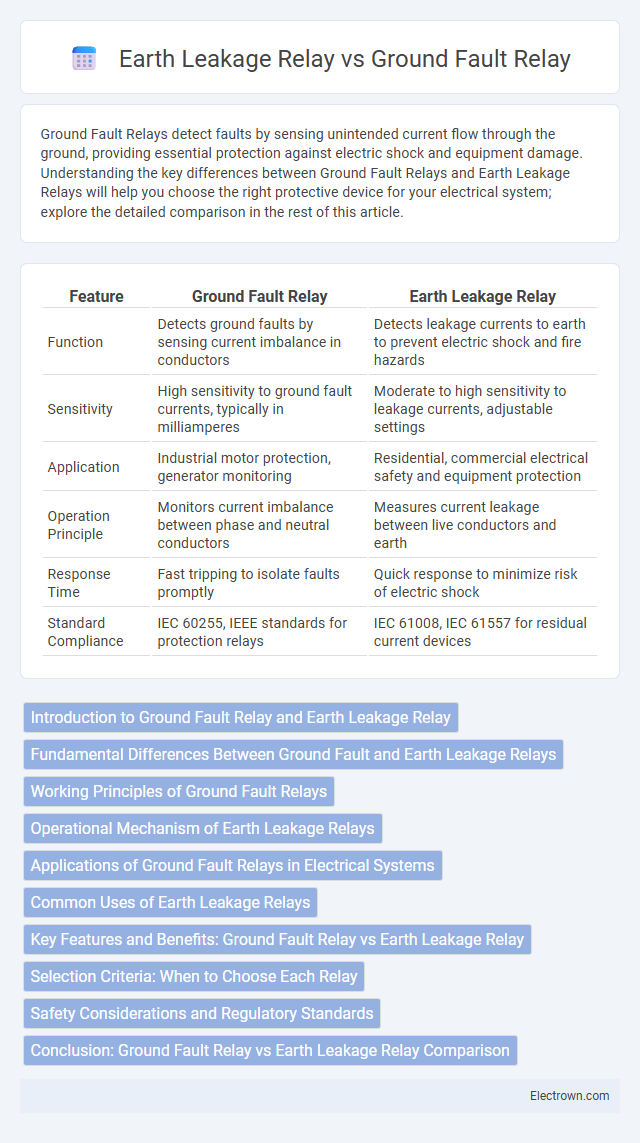
| Feature | Ground Fault Relay | Earth Leakage Relay |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Detects ground faults by sensing current imbalance in conductors | Detects leakage currents to earth to prevent electric shock and fire hazards |
| Sensitivity | High sensitivity to ground fault currents, typically in milliamperes | Moderate to high sensitivity to leakage currents, adjustable settings |
| Application | Industrial motor protection, generator monitoring | Residential, commercial electrical safety and equipment protection |
| Operation Principle | Monitors current imbalance between phase and neutral conductors | Measures current leakage between live conductors and earth |
| Response Time | Fast tripping to isolate faults promptly | Quick response to minimize risk of electric shock |
| Standard Compliance | IEC 60255, IEEE standards for protection relays | IEC 61008, IEC 61557 for residual current devices |
Introduction to Ground Fault Relay and Earth Leakage Relay
Ground Fault Relay detects abnormal current flow caused by unintended grounding, protecting electrical systems from faults and potential damage. Earth Leakage Relay monitors leakage currents to earth, ensuring safety by preventing electric shocks and fire hazards in residential and industrial environments. Your choice between these relays depends on the specific protection needs and system configuration.
Fundamental Differences Between Ground Fault and Earth Leakage Relays
Ground Fault Relays detect faults occurring when current flows through an unintended path to the ground, primarily identifying short circuits or insulation failures, whereas Earth Leakage Relays monitor leakage currents that may not cause immediate faults but indicate insulation degradation or potential safety hazards. Ground Fault Relays typically respond to higher fault currents for system protection, while Earth Leakage Relays are sensitive to low-level leakage currents to enhance personal safety by preventing electric shocks. The fundamental difference lies in their application focus: Ground Fault Relays protect equipment and systems, and Earth Leakage Relays safeguard human life by detecting hazardous leakage currents.
Working Principles of Ground Fault Relays
Ground Fault Relays operate by detecting unbalanced current in electrical systems, which occurs when current leaks to the ground, causing a deviation from the expected current flow. These relays continuously monitor the difference between the phase and neutral currents using current transformers to identify fault conditions. Upon sensing a ground fault, the relay triggers a protective circuit breaker to isolate the faulty section, preventing equipment damage and electrical hazards.
Operational Mechanism of Earth Leakage Relays
Earth leakage relays operate by detecting imbalance between the live and neutral conductors, indicating current leakage to the ground. This detection is achieved using a differential current transformer that senses any stray current flowing through the earth path. Your electrical system is protected as the relay trips the circuit when leakage current exceeds a preset threshold, preventing electric shock and fire hazards.
Applications of Ground Fault Relays in Electrical Systems
Ground Fault Relays are crucial in industrial and commercial electrical systems for detecting unbalanced current flow that indicates insulation failures or ground faults, preventing equipment damage and ensuring personnel safety. These relays are commonly applied in motor protection, transformer insulation monitoring, and distribution panels to quickly isolate faulty circuits, minimizing downtime. Your electrical system benefits from their precise ground fault detection which reduces fire hazards and maintains operational reliability.
Common Uses of Earth Leakage Relays
Earth leakage relays are primarily used in residential, commercial, and industrial electrical installations to detect leakage currents that pose a shock hazard or risk of fire due to insulation failure. These relays protect equipment and personnel by promptly disconnecting power when leakage currents exceed predefined thresholds, enhancing overall system safety. Their common applications include safeguarding household wiring, industrial motors, transformers, and distribution boards against earth faults.
Key Features and Benefits: Ground Fault Relay vs Earth Leakage Relay
Ground Fault Relays detect insulation failures by sensing imbalance in current between phase and neutral, providing fast disconnection to prevent electrical shock and equipment damage. Earth Leakage Relays are designed to identify leakage currents to the ground, offering comprehensive protection against earth faults and minimizing fire hazards in electrical installations. Understanding the key features and benefits of both relays helps you ensure optimal safety and system reliability in your electrical network.
Selection Criteria: When to Choose Each Relay
Ground Fault Relays are selected for applications requiring sensitive detection of ground faults in electrical systems with high fault current levels, typically in industrial environments where fast tripping is critical to protect equipment and personnel. Earth Leakage Relays are preferred in residential or commercial setups to detect low-level leakage currents that could pose shock hazards or fire risks, often integrated with Safety Switches (RCDs) for human protection. Choosing between these relays depends on system voltage, fault current magnitude, application environment, and the specific protection goals such as equipment safety versus human safety compliance.
Safety Considerations and Regulatory Standards
Ground Fault Relay and Earth Leakage Relay both serve crucial safety functions in electrical systems by detecting unintended current flow that could cause electric shock or fire hazards. Ground Fault Relays are often used in industrial applications to protect personnel and equipment by quickly isolating faulty circuits, while Earth Leakage Relays are commonly mandated by regulatory standards such as IEC 60364 and NEC to ensure residential and commercial safety. Your choice between these relays should align with specific regulatory requirements and the necessary sensitivity to prevent electrical hazards effectively.
Conclusion: Ground Fault Relay vs Earth Leakage Relay Comparison
Ground Fault Relays detect faults between phase conductors and ground by monitoring current imbalances, providing rapid protection in critical electrical systems. Earth Leakage Relays sense leakage currents to prevent electric shock hazards and equipment damage, primarily focusing on safety in residential and commercial installations. Your choice depends on the application requirements: Ground Fault Relays for industrial fault protection and Earth Leakage Relays for comprehensive safety against ground leakage currents.
Ground Fault Relay vs Earth Leakage Relay Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com