Mesh topology offers robust network reliability through direct connections between all devices, ensuring efficient data transfer even if one link fails, while star topology centralizes communication with a hub, simplifying troubleshooting but creating a single point of failure. Explore the rest of the article to discover which topology suits your network needs best.
Table of Comparison
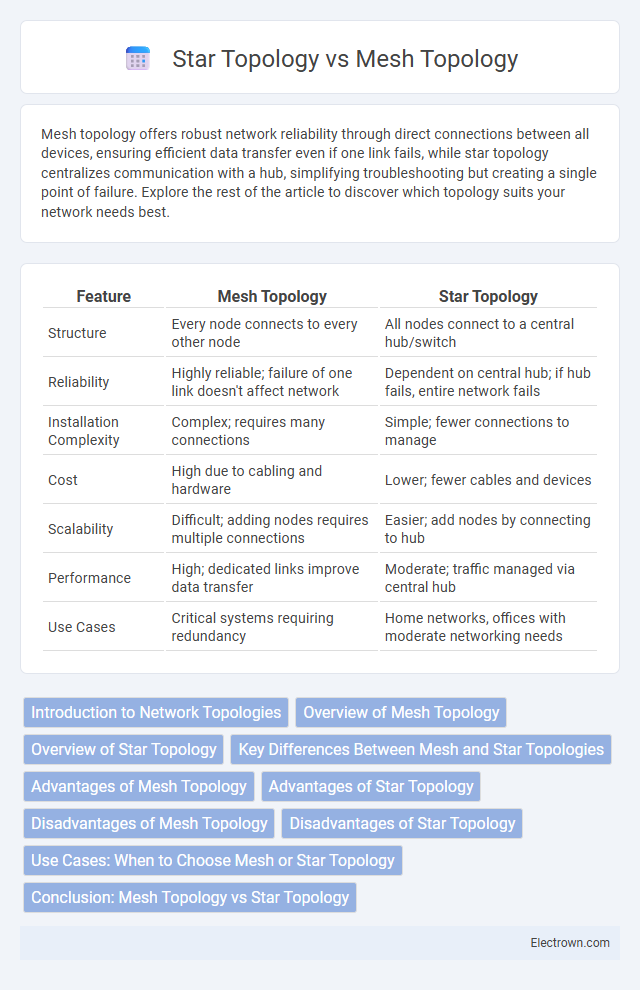
| Feature | Mesh Topology | Star Topology |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Every node connects to every other node | All nodes connect to a central hub/switch |
| Reliability | Highly reliable; failure of one link doesn't affect network | Dependent on central hub; if hub fails, entire network fails |
| Installation Complexity | Complex; requires many connections | Simple; fewer connections to manage |
| Cost | High due to cabling and hardware | Lower; fewer cables and devices |
| Scalability | Difficult; adding nodes requires multiple connections | Easier; add nodes by connecting to hub |
| Performance | High; dedicated links improve data transfer | Moderate; traffic managed via central hub |
| Use Cases | Critical systems requiring redundancy | Home networks, offices with moderate networking needs |
Introduction to Network Topologies
Mesh topology features direct connections between all devices, ensuring high redundancy and fault tolerance, ideal for critical network environments. Star topology connects all devices to a central hub, simplifying management and troubleshooting while limiting the impact of individual device failures. Understanding these topologies helps you choose the best network structure based on scalability, reliability, and maintenance needs.
Overview of Mesh Topology
Mesh topology features a network structure where each device connects directly to every other device, ensuring high redundancy and fault tolerance. It enables efficient data routing through multiple paths, minimizing the risk of network failures and enhancing overall reliability. This topology is commonly used in mission-critical environments requiring uninterrupted data flow.
Overview of Star Topology
Star topology features a central hub or switch to which all network devices are individually connected, allowing efficient data management and fault isolation. It offers high performance with minimal collision domains and easier troubleshooting due to its centralized structure. This topology is commonly used in modern LANs for its scalability and reliability.
Key Differences Between Mesh and Star Topologies
Mesh topology features direct connections between all devices, ensuring high redundancy and fault tolerance by allowing multiple data paths. Star topology centralizes connections through a single hub or switch, simplifying network management but creating a single point of failure. When deciding Your network design, consider mesh topology for robust, high-availability environments and star topology for easier maintenance and scalability.
Advantages of Mesh Topology
Mesh topology offers superior fault tolerance due to its multiple redundant connections, ensuring network reliability even if one link fails. It enables high data privacy and security since data can travel along dedicated paths, reducing the risk of interception. The scalability of mesh networks supports dynamic device addition without disrupting existing nodes, making it ideal for complex, large-scale environments.
Advantages of Star Topology
Star topology offers centralized management, making network troubleshooting and maintenance more efficient compared to mesh topology. It provides enhanced scalability, allowing easy addition or removal of devices without disrupting the entire network. The topology's design minimizes the risk of network failure since a single device or cable failure does not affect the overall network connectivity.
Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
Mesh topology suffers from high implementation costs due to the extensive cabling and hardware required to connect every device to each other. Maintenance becomes complex and time-consuming as troubleshooting involves multiple paths and connections, increasing downtime risks. Your network scalability is limited because adding new devices requires additional connections for each existing node, complicating expansion efforts.
Disadvantages of Star Topology
Star topology disadvantages include a single point of failure since the central hub or switch controls the entire network; if it fails, all connected devices lose communication. This topology also requires more cable length compared to other designs, increasing installation costs and complexity. Your network performance can be compromised by hub congestion, leading to slower data transfer rates and potential bottlenecks.
Use Cases: When to Choose Mesh or Star Topology
Mesh topology is ideal for environments requiring high fault tolerance and continuous connectivity, such as data centers and critical network infrastructures, because each device connects directly to multiple nodes. Star topology suits small to medium-sized networks like office setups or home networks where centralized management and easier troubleshooting are priorities. Your choice depends on balancing redundancy needs and simplicity; opt for mesh when reliability is critical and star when cost efficiency and straightforward maintenance matter most.
Conclusion: Mesh Topology vs Star Topology
Mesh topology offers superior redundancy and fault tolerance by connecting each device directly to multiple others, ensuring continuous network operation despite individual link failures. Star topology simplifies management and installation by centralizing connections through a single hub or switch, making it cost-effective and easy to scale for smaller networks. Your choice between mesh and star topology depends on whether network reliability or simplicity and budget are the primary priorities.
Mesh Topology vs Star Topology Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com