Line reactors and load reactors are essential components in electrical systems designed to reduce harmonics, limit inrush current, and protect sensitive equipment; line reactors are installed on the supply side to mitigate supply fluctuations, while load reactors are placed on the output side to protect motors and drives from voltage spikes and harmonics. To understand which reactor best suits Your system and enhance equipment performance, read on to explore their key differences and applications.
Table of Comparison
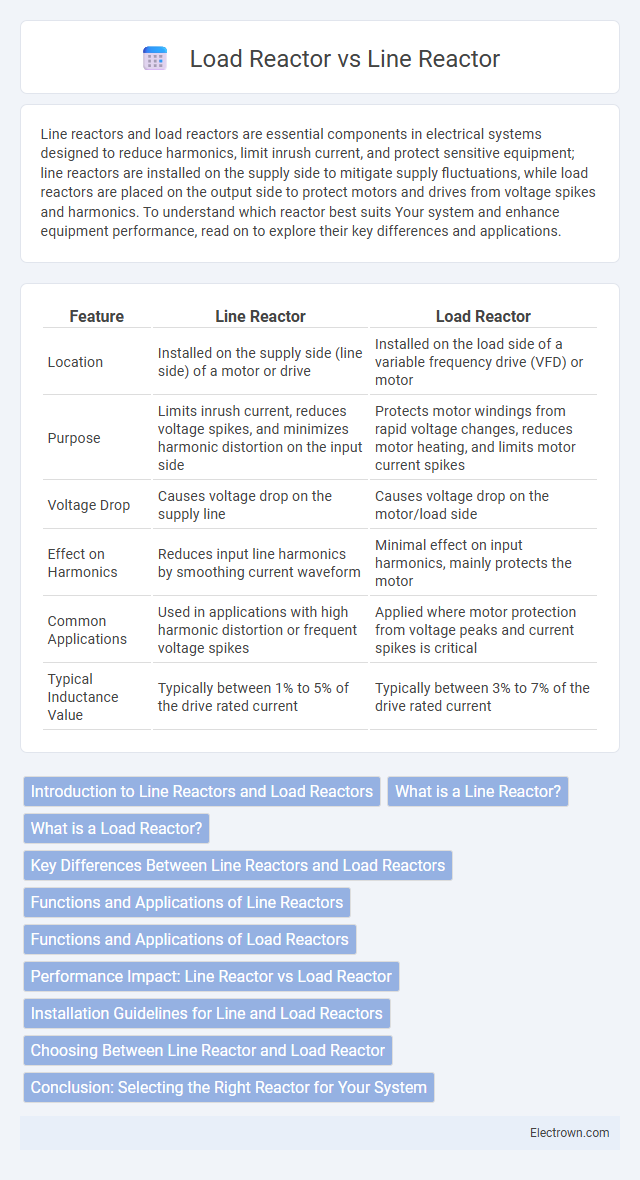
| Feature | Line Reactor | Load Reactor |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Installed on the supply side (line side) of a motor or drive | Installed on the load side of a variable frequency drive (VFD) or motor |
| Purpose | Limits inrush current, reduces voltage spikes, and minimizes harmonic distortion on the input side | Protects motor windings from rapid voltage changes, reduces motor heating, and limits motor current spikes |
| Voltage Drop | Causes voltage drop on the supply line | Causes voltage drop on the motor/load side |
| Effect on Harmonics | Reduces input line harmonics by smoothing current waveform | Minimal effect on input harmonics, mainly protects the motor |
| Common Applications | Used in applications with high harmonic distortion or frequent voltage spikes | Applied where motor protection from voltage peaks and current spikes is critical |
| Typical Inductance Value | Typically between 1% to 5% of the drive rated current | Typically between 3% to 7% of the drive rated current |
Introduction to Line Reactors and Load Reactors
Line reactors are inductive components installed on the supply side of variable frequency drives (VFDs) to reduce harmonics, voltage spikes, and motor current distortion, enhancing overall system reliability. Load reactors, positioned on the motor side, primarily protect the drive and motor from reflected wave effects and high dv/dt voltages generated by the VFD output. Both reactors improve power quality and extend equipment lifespan by mitigating electrical noise and transient disturbances.
What is a Line Reactor?
A Line Reactor is an electrical component installed on the supply side of a motor drive or variable frequency drive (VFD) to reduce harmonic distortion, limit inrush current, and protect equipment from voltage spikes by adding inductive impedance. It improves power quality by smoothing current flow and reducing electrical noise in semiconductor devices. Unlike load reactors, which are placed on the output side to protect the motor, line reactors primarily safeguard the drive and upstream power source.
What is a Load Reactor?
A Load Reactor is an inductive coil connected in series with a motor or load to reduce voltage spikes and harmonics caused by sudden changes in current, thereby protecting the equipment and improving power quality. It helps minimize motor overheating and extends the lifespan by smoothing current flow and reducing electromagnetic interference. Unlike Line Reactors, which are placed at the input side of variable frequency drives, Load Reactors are installed on the output side, closer to the motor or load.
Key Differences Between Line Reactors and Load Reactors
Line reactors are installed on the supply side to limit inrush current and reduce harmonic distortion, improving overall power quality and protecting upstream equipment. Load reactors are placed on the motor side to reduce motor heating, torque pulsations, and voltage spikes, enhancing motor protection and performance. Your choice depends on whether you need to safeguard the power source or improve motor operation under specific electrical conditions.
Functions and Applications of Line Reactors
Line reactors serve as inductive components that limit inrush current, reduce harmonic distortion, and protect variable frequency drives (VFDs) from voltage spikes in industrial motor control systems. They are commonly installed on the input side of VFDs to improve power quality and enhance the lifespan of electrical equipment in manufacturing plants. Applications include reducing motor stress in conveyor systems, HVAC controls, and pumping stations, where maintaining stable voltage and minimizing electrical noise is critical.
Functions and Applications of Load Reactors
Load reactors primarily serve to reduce motor current spikes and protect variable frequency drives (VFDs) from overvoltage by smoothing out rapid voltage changes caused by motor winding inductance. They are commonly applied in motor-driven systems where load harmonics and voltage spikes can cause operational issues or damage sensitive equipment, such as conveyors, pumps, and fans. You benefit from improved system reliability and extended VFD lifespan by incorporating load reactors tailored to your motor's specific electrical characteristics.
Performance Impact: Line Reactor vs Load Reactor
Line reactors primarily reduce harmonics and protect equipment from voltage spikes by being installed on the input side of variable frequency drives, enhancing overall system stability. Load reactors, placed on the output side, mitigate motor winding stress and cable voltage spikes, thus improving motor lifespan and performance under varying load conditions. Your choice between line and load reactors directly impacts the efficiency and reliability of power systems based on whether you prioritize input-side conditioning or output-side protection.
Installation Guidelines for Line and Load Reactors
Installation guidelines for line reactors emphasize placing them upstream of the variable frequency drive (VFD) to limit voltage spikes and reduce harmonic distortion, ensuring proper grounding and secure connections to prevent electrical noise. Load reactors are installed downstream of the VFD, close to the motor terminals, to protect motor windings from high di/dt stresses and to minimize insulation damage, requiring careful sizing based on motor load characteristics. Proper installation for both types involves adhering to manufacturer specifications, maintaining adequate spacing for heat dissipation, and verifying correct reactor ratings according to voltage and current levels.
Choosing Between Line Reactor and Load Reactor
Choosing between a line reactor and a load reactor depends on your specific application needs, such as mitigating harmonics, reducing voltage spikes, or improving motor protection. Line reactors are typically installed on the supply side to safeguard drives from supply disturbances, while load reactors are positioned on the motor side to protect the motor from voltage transients and to reduce motor heating. Evaluating factors like ambient conditions, system impedance, and motor characteristics will help you select the optimal reactor type for enhanced electrical system performance and reliability.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Reactor for Your System
Selecting the right reactor for your system depends on the specific application requirements, where line reactors are ideal for reducing harmonics and protecting equipment from voltage spikes, while load reactors provide tailored inductive reactance to control motor currents and minimize torque pulsations. Understanding the electrical characteristics, such as current ratings, impedance values, and operational environment, is crucial to optimize system performance and enhance equipment longevity. Properly matching the reactor type ensures improved power quality, minimized system downtime, and efficient energy utilization.
Line Reactor vs Load Reactor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com