Fused disconnect switches offer reliable circuit isolation with built-in overcurrent protection through replaceable fuses, while circuit breakers provide automatic trip mechanisms for resetting after faults without fuse replacement. Understanding the key differences between these devices helps you select the best option for your electrical system's safety and maintenance needs--explore the detailed comparison in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
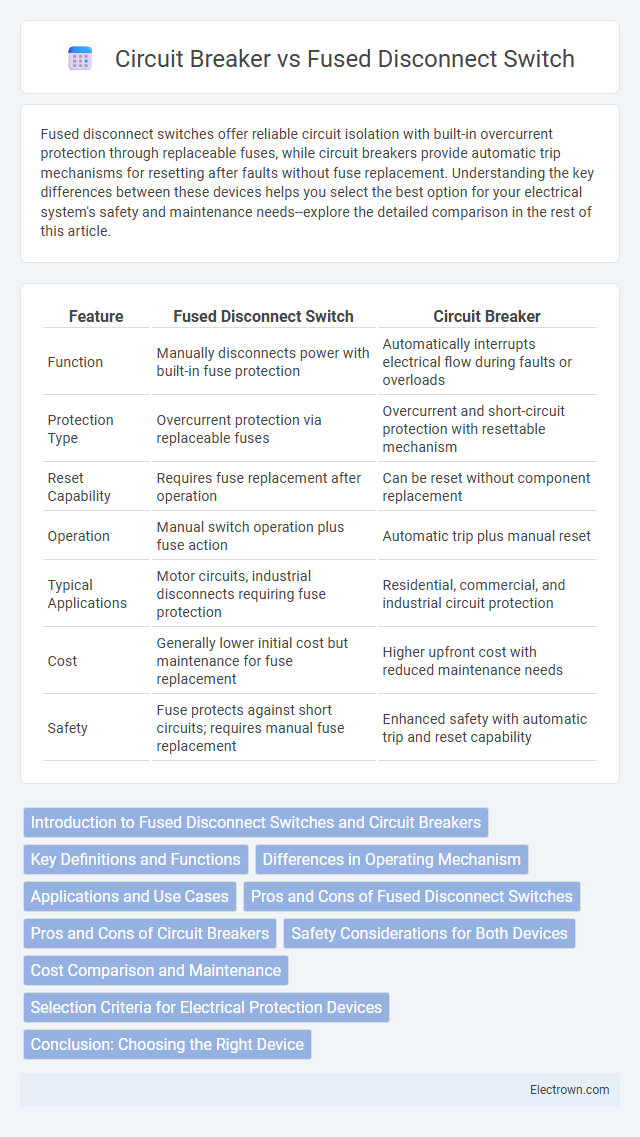
| Feature | Fused Disconnect Switch | Circuit Breaker |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Manually disconnects power with built-in fuse protection | Automatically interrupts electrical flow during faults or overloads |
| Protection Type | Overcurrent protection via replaceable fuses | Overcurrent and short-circuit protection with resettable mechanism |
| Reset Capability | Requires fuse replacement after operation | Can be reset without component replacement |
| Operation | Manual switch operation plus fuse action | Automatic trip plus manual reset |
| Typical Applications | Motor circuits, industrial disconnects requiring fuse protection | Residential, commercial, and industrial circuit protection |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost but maintenance for fuse replacement | Higher upfront cost with reduced maintenance needs |
| Safety | Fuse protects against short circuits; requires manual fuse replacement | Enhanced safety with automatic trip and reset capability |
Introduction to Fused Disconnect Switches and Circuit Breakers
Fused disconnect switches combine a manual switch with a protective fuse, providing overload and short-circuit protection by isolating electrical circuits safely. Circuit breakers serve as automatic switches that interrupt current flow upon detecting faults, enabling quick restoration without replacing components. Your choice between these devices impacts maintenance, safety protocols, and system reliability in electrical installations.
Key Definitions and Functions
A fused disconnect switch combines a manual switch with a fuse to provide overcurrent protection and safe disconnection of electrical circuits, primarily used for isolating equipment during maintenance. Circuit breakers are automatic protective devices that interrupt current flow when overcurrent or short circuits are detected, offering reusability without replacement after tripping. Both devices serve critical roles in electrical safety, with fused disconnect switches providing a simpler, cost-effective solution for fixed overcurrent protection, while circuit breakers offer quick reset capabilities and advanced protection features.
Differences in Operating Mechanism
Fused disconnect switches use a built-in fuse to interrupt current flow by melting when excessive current passes through, providing overcurrent protection through a physical element. Circuit breakers employ an internal switching mechanism that trips automatically upon detecting an overload or short circuit, allowing for manual reset without replacement parts. Understanding these operating mechanisms helps you choose the right device based on maintenance preferences and protection needs.
Applications and Use Cases
Fused disconnect switches are ideal for protecting electrical equipment in industrial settings where short-circuit protection and manual isolation are critical, such as motor control centers and distribution panels. Circuit breakers offer versatile applications with automatic trip features for overload and short-circuit protection, commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial electrical systems to safeguard circuits and ensure continuous power management. Understanding your specific requirements helps determine whether a fused disconnect switch or circuit breaker provides the best balance of protection, safety, and operational control.
Pros and Cons of Fused Disconnect Switches
Fused disconnect switches offer enhanced protection by combining switching and overcurrent interruption in a single device, minimizing equipment damage and improving operational safety. Their simplicity and compact design allow for easy installation and maintenance, but they have limited reset capability since the fuse must be replaced after a fault. While fused switches provide reliable protection, your system may require more flexibility and reset options, in which case circuit breakers might be preferable.
Pros and Cons of Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers offer reliable protection by automatically interrupting current flow during overloads or short circuits, ensuring safety and minimizing equipment damage. They can be reset quickly after tripping, reducing downtime compared to fused disconnect switches that require fuse replacement. However, circuit breakers are typically more expensive and may require periodic maintenance to ensure proper function.
Safety Considerations for Both Devices
Fused disconnect switches provide reliable overcurrent protection by melting the fuse element under fault conditions, preventing equipment damage and enhancing safety through clear isolation. Circuit breakers offer a resettable solution with instant trip capabilities, quickly interrupting fault currents to protect circuits and personnel from electrical hazards. Your choice should consider maintenance ease, fault current levels, and the necessary level of protection to ensure optimal safety in your electrical system.
Cost Comparison and Maintenance
Fused disconnect switches generally offer a lower initial cost compared to circuit breakers, making them a cost-effective option for basic overcurrent protection in industrial and commercial applications. Maintenance for fused disconnect switches involves periodic fuse replacement and inspection, which is straightforward but requires keeping spare fuses on hand, while circuit breakers demand regular testing and potential recalibration to ensure reliable trip performance. You should consider the total cost of ownership, including replacement parts and maintenance labor, to determine the most economical solution for your specific electrical system.
Selection Criteria for Electrical Protection Devices
Selecting between a fused disconnect switch and a circuit breaker depends on factors like fault current rating, response time, and maintenance preferences. Fused disconnect switches offer superior short-circuit protection and are often preferred in high fault current applications, whereas circuit breakers provide ease of reset and adjustable trip settings for varied load conditions. Your choice should balance system safety requirements, operational convenience, and compliance with relevant electrical codes.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Device
Selecting between a fused disconnect switch and a circuit breaker depends on your specific safety, protection, and maintenance needs. A fused disconnect switch offers reliable overcurrent protection with clear fuse status indication, making it ideal for simple, cost-effective solutions. Your choice should align with the required interruption capacity, ease of replacement, and the application environment to ensure optimal electrical system performance.
Fused Disconnect Switch vs Circuit Breaker Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com