Safety relays are specifically designed to meet stringent safety standards and provide reliable fault detection and fail-safe operation in critical applications, whereas standard relays primarily focus on general control tasks without the same level of risk mitigation. Understanding the differences in functionality and compliance can help you choose the right relay for your system's safety needs--continue reading to explore these key distinctions in detail.
Table of Comparison
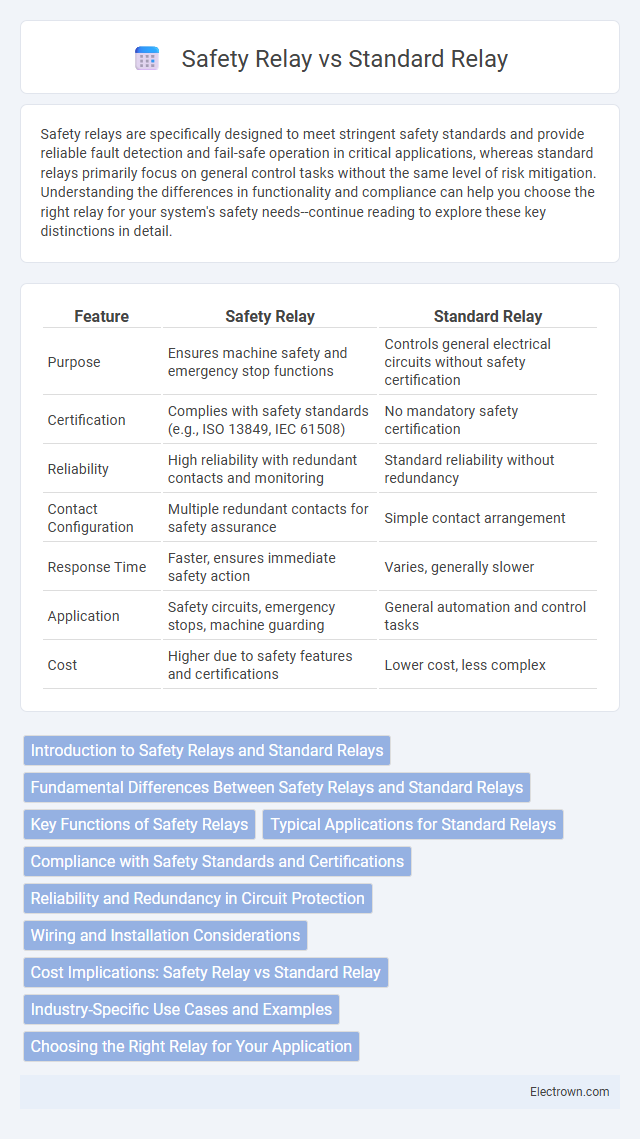
| Feature | Safety Relay | Standard Relay |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Ensures machine safety and emergency stop functions | Controls general electrical circuits without safety certification |
| Certification | Complies with safety standards (e.g., ISO 13849, IEC 61508) | No mandatory safety certification |
| Reliability | High reliability with redundant contacts and monitoring | Standard reliability without redundancy |
| Contact Configuration | Multiple redundant contacts for safety assurance | Simple contact arrangement |
| Response Time | Faster, ensures immediate safety action | Varies, generally slower |
| Application | Safety circuits, emergency stops, machine guarding | General automation and control tasks |
| Cost | Higher due to safety features and certifications | Lower cost, less complex |
Introduction to Safety Relays and Standard Relays
Safety relays are specialized devices designed to ensure machine safety by reliably monitoring safety functions and initiating controlled shutdowns during hazardous conditions. Standard relays serve general-purpose switching roles in electrical circuits but lack the redundancy and fail-safe features critical in safety applications. Your selection between safety relays and standard relays depends on the required compliance with safety standards and the necessity to protect operators and equipment from potential risks.
Fundamental Differences Between Safety Relays and Standard Relays
Safety relays are specifically designed with redundancy and self-monitoring features to ensure reliable operation in critical safety applications, whereas standard relays primarily focus on general switching functions without built-in safety validation. Safety relays comply with stringent international safety standards such as ISO 13849 and IEC 62061, providing predictable fault detection and fail-safe responses essential for protecting people and machinery. Your choice between these relays impacts system integrity, as safety relays prevent hazardous failures by actively monitoring contacts and circuits, unlike standard relays which lack such safety mechanisms.
Key Functions of Safety Relays
Safety relays are designed to monitor and ensure the reliable operation of safety functions by detecting faults and initiating safe shutdowns in hazardous situations, unlike standard relays that primarily control circuits without safety monitoring. Key functions of safety relays include redundant contact paths for fail-safe operation, self-monitoring for internal faults, and force-guided contacts to maintain safety integrity during relay failure. These features comply with international safety standards such as ISO 13849 and IEC 62061, making safety relays essential for critical applications in industrial automation and machinery safety.
Typical Applications for Standard Relays
Standard relays are commonly used in applications such as motor control, lighting systems, and HVAC controls where basic switching and isolation functions are required. These relays handle lower-risk tasks without stringent safety certifications, making them suitable for general-purpose industrial automation and household appliances. Your choice of a standard relay is ideal when reliable electrical load switching is needed without the necessity for integrated safety features.
Compliance with Safety Standards and Certifications
Safety relays are specifically designed to comply with stringent safety standards such as ISO 13849, IEC 62061, and IEC 61508, ensuring reliable operation in emergency stop circuits and safety applications. Standard relays lack these certifications and may not provide the necessary redundancy, self-monitoring, or fail-safe features required for critical safety functions. Using safety-certified relays helps manufacturers meet regulatory requirements and achieve SIL (Safety Integrity Level) or PL (Performance Level) ratings essential for industrial safety systems.
Reliability and Redundancy in Circuit Protection
Safety relays provide enhanced reliability through dual-channel monitoring and built-in redundancy, ensuring fault detection and fail-safe operation in critical circuit protection. Standard relays lack this dual-channel architecture, making them less reliable in safety-critical applications where circuit redundancy is essential. Incorporating safety relays minimizes risk of undetected failures, maintaining consistent performance under emergency shutdown or hazardous conditions.
Wiring and Installation Considerations
Safety relays require dedicated wiring with redundant contacts and self-monitoring circuits to ensure fail-safe operation and compliance with safety standards such as ISO 13849 and IEC 62061. Standard relays typically use simpler wiring schemes without redundancy, focusing on basic switching functions without safety self-checks. Installation of safety relays mandates careful adherence to manufacturer instructions and safety regulations to maintain integrity of safety functions, unlike standard relays which allow more flexible and less stringent wiring practices.
Cost Implications: Safety Relay vs Standard Relay
Safety relays typically involve higher initial costs compared to standard relays due to their advanced design and compliance with stringent safety standards like ISO 13849 and IEC 62061. While standard relays are more cost-effective for basic switching tasks, safety relays reduce long-term financial risks by preventing costly accidents and equipment damage through reliable fault detection. Your investment in safety relays can lead to significant savings by minimizing downtime and avoiding regulatory penalties associated with workplace hazards.
Industry-Specific Use Cases and Examples
Safety relays are critical in industries requiring stringent risk reduction, such as automotive manufacturing and chemical plants, where machinery must stop immediately upon fault detection to protect personnel. Standard relays are commonly used in less hazardous environments like HVAC systems or lighting control, where rapid shutdown isn't crucial. Your choice between safety and standard relays depends on the level of automation safety standards, such as ISO 13849 or IEC 62061, required for specific industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Relay for Your Application
Safety relays are specifically designed to meet stringent international safety standards such as ISO 13849 and IEC 62061, providing reliable fault detection and redundancy crucial for protecting operators and machinery. Standard relays serve general switching purposes without the specialized safety features, making them suitable for non-critical control circuits where safety compliance is not mandatory. When choosing the right relay for your application, prioritize safety relays in environments with high-risk machinery or regulatory safety requirements to ensure system integrity and personnel protection.
Safety Relay vs Standard Relay Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com