Zigbee offers low-power, short-range communication ideal for home automation, while LoRa provides long-range connectivity with low energy consumption perfect for wide-area IoT deployments. Explore the rest of the article to discover which technology best suits Your specific needs and applications.
Table of Comparison
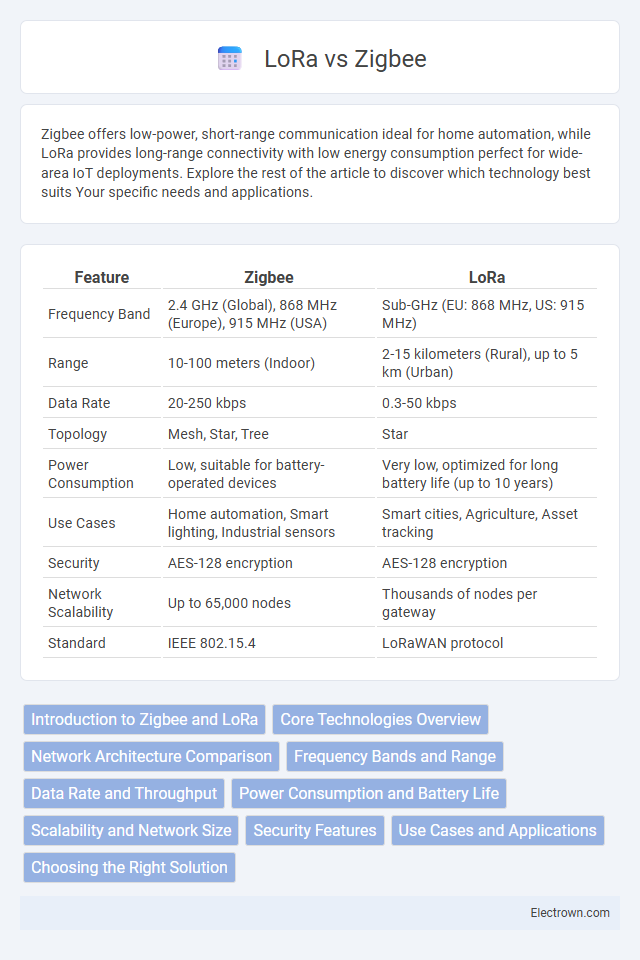
| Feature | Zigbee | LoRa |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Band | 2.4 GHz (Global), 868 MHz (Europe), 915 MHz (USA) | Sub-GHz (EU: 868 MHz, US: 915 MHz) |
| Range | 10-100 meters (Indoor) | 2-15 kilometers (Rural), up to 5 km (Urban) |
| Data Rate | 20-250 kbps | 0.3-50 kbps |
| Topology | Mesh, Star, Tree | Star |
| Power Consumption | Low, suitable for battery-operated devices | Very low, optimized for long battery life (up to 10 years) |
| Use Cases | Home automation, Smart lighting, Industrial sensors | Smart cities, Agriculture, Asset tracking |
| Security | AES-128 encryption | AES-128 encryption |
| Network Scalability | Up to 65,000 nodes | Thousands of nodes per gateway |
| Standard | IEEE 802.15.4 | LoRaWAN protocol |
Introduction to Zigbee and LoRa
Zigbee is a wireless communication protocol designed for short-range, low-power, mesh networking, widely used in home automation and smart lighting systems. LoRa (Long Range) technology specializes in long-range, low-power wide-area networks (LPWAN), ideal for IoT applications requiring extensive coverage and minimal energy consumption. Understanding the differences in range, power efficiency, and network topology can help you choose the best solution for your specific IoT deployment needs.
Core Technologies Overview
Zigbee operates on IEEE 802.15.4 standard, utilizing low-power, short-range mesh networking ideal for home automation and smart lighting systems. LoRa employs Chirp Spread Spectrum modulation in sub-GHz frequencies, enabling long-range, low-data-rate communication suited for IoT applications like smart agriculture and asset tracking. Zigbee's mesh topology enhances network reliability within 10-100 meters, while LoRa's star topology supports communication over several kilometers with minimal power consumption.
Network Architecture Comparison
Zigbee operates on a mesh network architecture, enabling devices to communicate directly or through intermediary nodes, which enhances network reliability and range within a localized environment. LoRa utilizes a star-of-stars topology, where end devices connect to gateways that relay information to a central network server, optimized for long-range, low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) applications. The decentralized mesh of Zigbee provides high device density and fault tolerance, while LoRa's centralized star topology supports scalable coverage over kilometers with minimal power consumption.
Frequency Bands and Range
Zigbee operates primarily in the 2.4 GHz frequency band, offering a range of approximately 10 to 100 meters, making it ideal for short-range, low-power applications in home automation and sensor networks. LoRa utilizes sub-GHz frequency bands such as 868 MHz in Europe and 915 MHz in North America, enabling long-range communication up to 15 kilometers in rural areas and several kilometers in urban environments with minimal power consumption. The lower frequency bands of LoRa provide superior penetration through obstacles and extended coverage compared to the higher frequency, shorter range capabilities of Zigbee.
Data Rate and Throughput
Zigbee offers data rates up to 250 kbps, suitable for short-range, low-power wireless communication in home automation and sensor networks. LoRa provides significantly lower data rates, ranging from 0.3 kbps to 50 kbps, optimized for long-range, low-power wide area networks (LPWAN) with extended battery life. Throughput in Zigbee is higher due to its faster data rate, while LoRa sacrifices throughput for maximum range and energy efficiency, making it ideal for IoT applications requiring sparse data transmission over large distances.
Power Consumption and Battery Life
Zigbee operates on low power with typical consumption around 30-60mA during transmission, enabling battery life of 1-2 years for devices using AA batteries under typical usage. LoRa technology drastically reduces power consumption by employing low duty cycle transmissions, allowing devices to run on a single battery for 5-10 years, particularly in applications with infrequent data sending. For ultra-low power IoT deployments, LoRa offers superior battery longevity compared to Zigbee, especially in wide-area networks with sparse communication.
Scalability and Network Size
Zigbee networks support up to 65,000 devices in a mesh topology, ideal for dense, short-range applications requiring low power consumption and moderate data rates. LoRa excels in wide-area network scalability, enabling thousands of nodes across kilometers with star or star-of-stars topologies, optimized for low power, low bandwidth IoT deployments. While Zigbee suits local networks within buildings or campuses, LoRa's long-range capabilities make it preferable for rural or city-wide sensor networks.
Security Features
Zigbee employs AES-128 encryption with secure key establishment and network-level security to protect data integrity and confidentiality in smart home and IoT applications. LoRa uses AES-128 encryption alongside unique network and application keys to ensure end-to-end security for long-range, low-power wide-area network communications. Both protocols offer robust security features but cater to different network topologies and use cases, with Zigbee optimized for mesh networks and LoRa designed for extensive geographic coverage.
Use Cases and Applications
Zigbee excels in short-range, low-power applications such as smart home automation, industrial control, and sensor networks, where devices require frequent communication within a confined area. LoRa is designed for long-range, low-bandwidth use cases like agricultural monitoring, asset tracking, and smart city infrastructure, enabling connectivity across several kilometers with minimal energy consumption. Your choice depends on the required communication range and data throughput, with Zigbee suited to dense device environments and LoRa ideal for wide-area IoT deployments.
Choosing the Right Solution
Choosing the right solution between Zigbee and LoRa depends on your specific connectivity needs and environment. Zigbee excels in short-range, low-power mesh networks ideal for home automation and smart lighting, while LoRa offers long-range communication with low energy consumption, perfect for wide-area IoT deployments like agriculture and smart cities. Assess your coverage requirements, data transmission frequency, and device density to determine which technology best supports your IoT project's efficiency and scalability.
Zigbee vs LoRa Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com