Isolated power supplies provide electrical separation between input and output, enhancing safety and reducing noise interference, while non-isolated power supplies share a common ground, offering simpler design and higher efficiency. Understanding the differences between these two types can significantly impact Your choice for specific applications, so explore the rest of the article to make an informed decision.
Table of Comparison
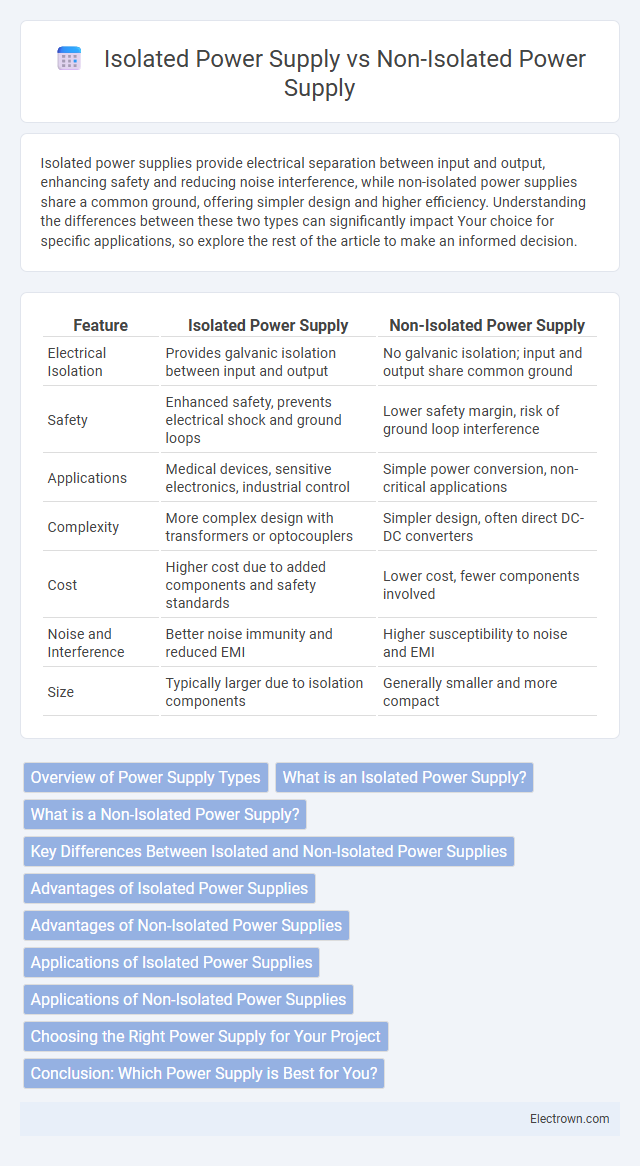
| Feature | Isolated Power Supply | Non-Isolated Power Supply |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Isolation | Provides galvanic isolation between input and output | No galvanic isolation; input and output share common ground |
| Safety | Enhanced safety, prevents electrical shock and ground loops | Lower safety margin, risk of ground loop interference |
| Applications | Medical devices, sensitive electronics, industrial control | Simple power conversion, non-critical applications |
| Complexity | More complex design with transformers or optocouplers | Simpler design, often direct DC-DC converters |
| Cost | Higher cost due to added components and safety standards | Lower cost, fewer components involved |
| Noise and Interference | Better noise immunity and reduced EMI | Higher susceptibility to noise and EMI |
| Size | Typically larger due to isolation components | Generally smaller and more compact |
Overview of Power Supply Types
Isolated power supplies provide electrical separation between input and output circuits, enhancing safety and reducing noise interference in sensitive applications like medical devices and industrial equipment. Non-isolated power supplies share a common ground between input and output, offering simpler design and higher efficiency suited for low-voltage, less critical environments such as battery chargers or LED drivers. Understanding the differences helps you select the right power supply type for your specific electrical isolation and performance requirements.
What is an Isolated Power Supply?
An isolated power supply separates its output from the input using a transformer, providing electrical isolation to enhance safety and reduce noise interference. This design prevents direct electrical connection, minimizing the risk of ground loops and protecting sensitive components from voltage spikes. Isolated power supplies are commonly used in medical equipment, industrial control systems, and communication devices where electrical safety and noise immunity are critical.
What is a Non-Isolated Power Supply?
A non-isolated power supply directly connects the input and output grounds, offering a simple and efficient design with minimal component count. This type of power supply is commonly found in applications where voltage isolation is not required, such as low-power DC-DC converters and internal electronic circuits. Its main advantage is higher efficiency and lower cost, but it lacks protection against electrical noise and ground loops that isolated power supplies provide.
Key Differences Between Isolated and Non-Isolated Power Supplies
Isolated power supplies provide electrical separation between input and output, enhancing safety and reducing noise interference in sensitive electronics. Non-isolated power supplies share a common ground between input and output, offering simpler design and higher efficiency but less protection against electrical faults. Key differences include isolation presence, safety levels, noise immunity, complexity, and typical application scenarios where isolated types are preferred for medical or industrial use, and non-isolated units suit low-cost, low-risk environments.
Advantages of Isolated Power Supplies
Isolated power supplies offer superior safety by electrically separating input and output, preventing ground loops and reducing the risk of electric shock in sensitive applications. They enhance noise immunity, ensuring more stable and cleaner power delivery critical for precision electronics and communication devices. Your systems benefit from improved protection against voltage spikes and interference, making isolated power supplies ideal for medical, industrial, and high-reliability environments.
Advantages of Non-Isolated Power Supplies
Non-isolated power supplies offer advantages such as higher efficiency and simpler circuit design due to the direct electrical connection between input and output. They typically have lower cost and smaller size, making them ideal for applications where galvanic isolation is not required. Your system benefits from reduced complexity and improved power density when using non-isolated power supplies in appropriate scenarios.
Applications of Isolated Power Supplies
Isolated power supplies are essential in medical devices, industrial automation, and communication systems where safety and noise reduction are critical. These power supplies prevent ground loops and electrical shocks by separating the input and output circuits, ensuring reliable operation in sensitive environments. Your equipment benefits from improved protection and signal integrity when using isolated power supplies in applications requiring strict isolation standards.
Applications of Non-Isolated Power Supplies
Non-isolated power supplies are commonly used in applications requiring efficient power conversion without galvanic isolation, such as DC-DC converters within electronic devices, battery-powered equipment, and embedded systems. These power supplies are ideal for scenarios where voltage translation or regulation is needed without isolation for safety, including telecommunications, industrial control circuits, and point-of-load regulation in computing hardware. Their compact design and higher efficiency make them suitable for cost-sensitive and space-constrained applications where isolation is not a critical requirement.
Choosing the Right Power Supply for Your Project
Choosing the right power supply for your project hinges on understanding the differences between isolated and non-isolated power supplies. Isolated power supplies provide galvanic isolation, reducing noise and protecting sensitive components, making them ideal for medical or industrial applications requiring high safety standards. Non-isolated power supplies offer higher efficiency and simpler design, suitable for projects where cost and footprint are priorities and isolation is not critical to your system's performance.
Conclusion: Which Power Supply is Best for You?
Choosing between an isolated power supply and a non-isolated power supply depends largely on your application's safety requirements and noise sensitivity. Isolated power supplies provide superior protection against electrical shock and noise interference, making them ideal for medical devices, industrial equipment, and sensitive electronics. Your best choice ensures optimal performance and safety tailored to your system's specific needs.
Isolated Power Supply vs Non-Isolated Power Supply Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com