Glass temperature sensors offer excellent chemical resistance and high accuracy in extreme environments, making them ideal for delicate applications where contamination must be minimized. Metal temperature sensors provide durability and faster response times in rugged conditions, ensuring reliable performance in industrial settings; explore the benefits and limitations of each type to determine which sensor best suits your temperature monitoring needs.
Table of Comparison
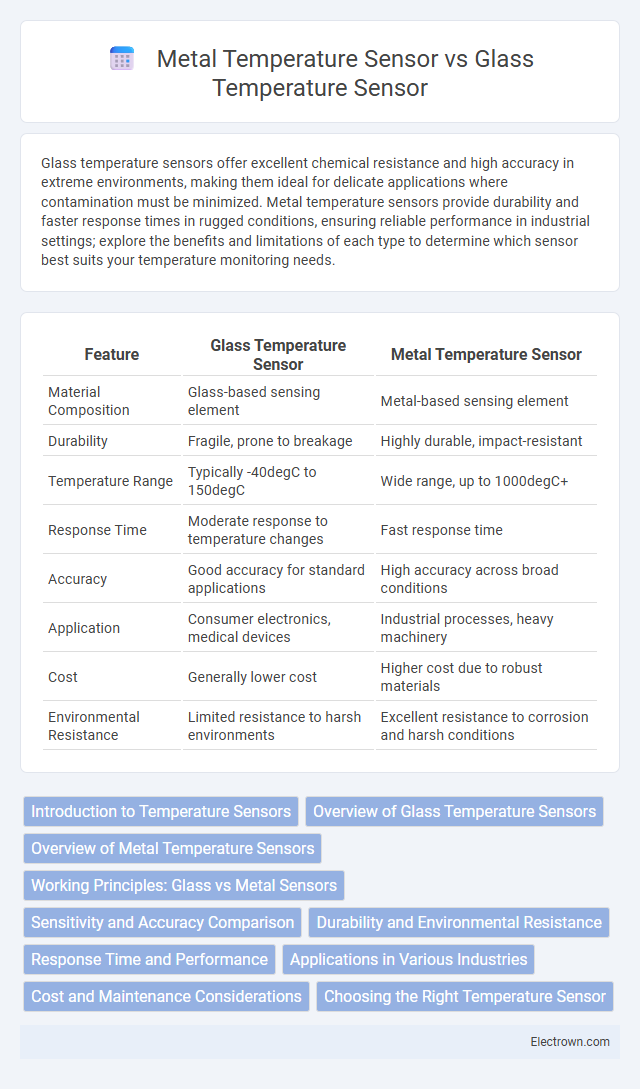
| Feature | Glass Temperature Sensor | Metal Temperature Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Glass-based sensing element | Metal-based sensing element |
| Durability | Fragile, prone to breakage | Highly durable, impact-resistant |
| Temperature Range | Typically -40degC to 150degC | Wide range, up to 1000degC+ |
| Response Time | Moderate response to temperature changes | Fast response time |
| Accuracy | Good accuracy for standard applications | High accuracy across broad conditions |
| Application | Consumer electronics, medical devices | Industrial processes, heavy machinery |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to robust materials |
| Environmental Resistance | Limited resistance to harsh environments | Excellent resistance to corrosion and harsh conditions |
Introduction to Temperature Sensors
Temperature sensors are critical components in monitoring and controlling thermal conditions across various industries. Glass temperature sensors offer high chemical resistance and electrical insulation, making them ideal for harsh environments, while metal temperature sensors provide robust mechanical strength and rapid heat transfer for accurate readings in dynamic conditions. Selecting between glass and metal sensors depends on factors such as temperature range, environmental exposure, and response time requirements.
Overview of Glass Temperature Sensors
Glass temperature sensors consist of a temperature-sensitive element encapsulated within a glass envelope, providing excellent chemical resistance and electrical insulation. These sensors offer high accuracy and stability in harsh environments, making them ideal for applications requiring durability and precise temperature measurement. Their construction ensures minimal interference from electromagnetic noise, enhancing reliability in industrial and scientific settings.
Overview of Metal Temperature Sensors
Metal temperature sensors are renowned for their durability, fast response time, and high accuracy in measuring temperature in extreme environments. Common types include thermocouples and resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), which rely on the electrical properties of metals to detect temperature changes. Your choice of a metal temperature sensor ensures reliable performance in applications requiring precise temperature monitoring and resistance to mechanical stress.
Working Principles: Glass vs Metal Sensors
Glass temperature sensors operate based on the expansion properties of glass, where temperature changes cause measurable changes in the physical dimensions or electrical resistance of the glass material. Metal temperature sensors, such as thermocouples or resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), utilize the predictable variations in electrical resistance or thermoelectric voltage generated in metals as temperature fluctuates. Glass sensors typically offer high chemical resistance and insulation, while metal sensors provide faster response times and greater durability under mechanical stress.
Sensitivity and Accuracy Comparison
Glass temperature sensors offer higher sensitivity due to their responsive thermistor elements, enabling precise detection of minute temperature changes. Metal temperature sensors, such as RTDs or thermocouples, provide superior accuracy over a broad temperature range and exhibit greater stability under harsh conditions. Your choice depends on whether sensitivity to small fluctuations or long-term accuracy is the priority in the application.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Glass temperature sensors offer superior durability and environmental resistance due to their inert material composition, which resists corrosion, moisture, and extreme temperatures effectively. Metal temperature sensors, while robust and highly conductive, are more susceptible to oxidation, corrosion, and mechanical stress in harsh environments. The choice between glass and metal sensors significantly impacts sensor longevity and reliability in applications involving aggressive chemicals, high humidity, or significant temperature fluctuations.
Response Time and Performance
Glass temperature sensors typically offer faster response times due to their low thermal mass, enabling quicker detection of temperature changes. Metal temperature sensors provide robust performance in harsh environments, delivering durability and consistent readings over time. Your choice depends on whether rapid response or long-term resilience is the priority for your application.
Applications in Various Industries
Glass temperature sensors are widely used in pharmaceutical and food industries due to their chemical resistance and high accuracy in sterile environments, while metal temperature sensors, such as thermocouples and RTDs, are preferred in automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing sectors for their durability and rapid response in high-temperature or harsh conditions. Glass sensors excel in laboratory and medical applications where contamination prevention is critical, whereas metal sensors dominate in process control systems, engine monitoring, and HVAC applications due to their robustness and versatility. Industrial automation, energy production, and petrochemical processing rely heavily on metal temperature sensors for durability under pressure and corrosive environments, contrasting with glass sensors' niche in precision and non-reactivity.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Glass temperature sensors typically cost less upfront due to simpler materials and manufacturing processes, making them an economical choice for basic temperature monitoring. Metal temperature sensors, while generally more expensive, offer higher durability and longer service life, which can reduce replacement frequency and maintenance costs over time. Your decision should balance initial investment against expected maintenance demands and operational conditions.
Choosing the Right Temperature Sensor
Selecting the right temperature sensor depends on the application's environment and required accuracy; glass temperature sensors excel in chemical resistance and high-temperature stability, making them ideal for laboratory and industrial settings. Metal temperature sensors, such as thermocouples and RTDs, offer faster response times and durability in rugged conditions, suitable for automotive and manufacturing processes. Understanding factors like temperature range, response time, and environmental exposure ensures optimal performance and sensor longevity.
Glass Temperature Sensor vs Metal Temperature Sensor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com