A vibration damper reduces mechanical vibrations by absorbing energy and preventing structural damage, while a snubber circuit protects electrical components by controlling voltage spikes and transient currents. Explore this article to understand how each device enhances your system's performance and longevity.
Table of Comparison
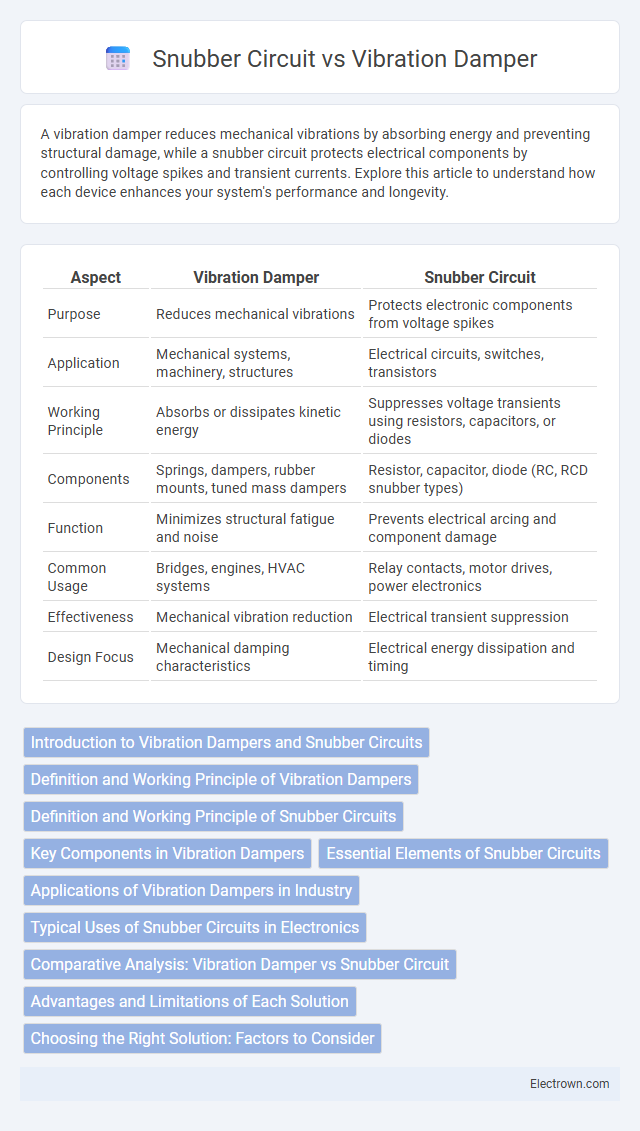
| Aspect | Vibration Damper | Snubber Circuit |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Reduces mechanical vibrations | Protects electronic components from voltage spikes |
| Application | Mechanical systems, machinery, structures | Electrical circuits, switches, transistors |
| Working Principle | Absorbs or dissipates kinetic energy | Suppresses voltage transients using resistors, capacitors, or diodes |
| Components | Springs, dampers, rubber mounts, tuned mass dampers | Resistor, capacitor, diode (RC, RCD snubber types) |
| Function | Minimizes structural fatigue and noise | Prevents electrical arcing and component damage |
| Common Usage | Bridges, engines, HVAC systems | Relay contacts, motor drives, power electronics |
| Effectiveness | Mechanical vibration reduction | Electrical transient suppression |
| Design Focus | Mechanical damping characteristics | Electrical energy dissipation and timing |
Introduction to Vibration Dampers and Snubber Circuits
Vibration dampers are mechanical devices designed to reduce unwanted oscillations in structures or machinery by converting vibrational energy into heat, thereby enhancing stability and longevity. Snubber circuits, on the other hand, are electrical components used to suppress voltage spikes and transient signals in power electronics, protecting sensitive devices from damage. Both serve critical roles in their respective domains, with vibration dampers focused on mechanical vibration control and snubber circuits aimed at electrical noise mitigation.
Definition and Working Principle of Vibration Dampers
Vibration dampers are devices designed to reduce or eliminate the amplitude of mechanical vibrations through energy dissipation, typically using materials like rubber, springs, or viscoelastic substances that absorb kinetic energy. They work by converting vibrational energy into heat or other forms of energy, thereby minimizing oscillations and protecting structures or machinery from damage. Unlike snubber circuits, which are electrical components used to suppress voltage spikes, vibration dampers are purely mechanical systems focused on controlling physical motion and vibration.
Definition and Working Principle of Snubber Circuits
Snubber circuits are electronic devices designed to suppress voltage spikes and absorb transient energy in electrical systems, protecting components such as semiconductors from damage. They operate by using resistors, capacitors, and sometimes diodes to control the rate of voltage change (dv/dt) and clamp voltage surges, thereby reducing electromagnetic interference and enhancing circuit reliability. Unlike vibration dampers that minimize mechanical oscillations, snubber circuits focus on managing electrical transients in power electronics and switching applications.
Key Components in Vibration Dampers
Vibration dampers primarily consist of a mass, spring, and damping element that work together to reduce oscillations and dissipate energy from mechanical vibrations. The damping element, often made of viscoelastic materials or hydraulic fluids, is crucial for converting kinetic energy into heat, thereby minimizing amplitude and preventing structural damage. Understanding these key components helps you select the right vibration damper to protect your machinery or structure effectively.
Essential Elements of Snubber Circuits
Snubber circuits, critical for protecting semiconductor devices, primarily consist of a resistor and capacitor working together to suppress voltage spikes and absorb transient energy. These essential elements reduce electromagnetic interference and prevent damage caused by sudden inductive load changes in power electronics. Your efficient circuit design depends on selecting the right snubber components to balance energy dissipation and protection effectiveness.
Applications of Vibration Dampers in Industry
Vibration dampers are crucial in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing to reduce mechanical oscillations and enhance equipment lifespan. They are commonly used in machinery mounting, bridge cables, and precision instruments to mitigate resonance and prevent structural damage. These devices improve operational stability and safety by absorbing excess vibrational energy and minimizing noise pollution.
Typical Uses of Snubber Circuits in Electronics
Snubber circuits are essential in electronics to protect switching devices such as transistors and thyristors from voltage spikes caused by inductive loads during switching operations. They are commonly used in power supplies, motor controllers, and relay drive circuits to suppress transient voltage and reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI). Unlike vibration dampers used to reduce mechanical vibrations, snubber circuits specifically manage electrical disturbances and enhance component longevity.
Comparative Analysis: Vibration Damper vs Snubber Circuit
Vibration dampers reduce mechanical oscillations by absorbing and dissipating kinetic energy, often utilizing materials like viscoelastic polymers or tuned mass systems, whereas snubber circuits protect electrical components by limiting voltage spikes and controlling transient currents using resistors, capacitors, or diodes. While vibration dampers optimize structural integrity in machinery, snubber circuits enhance electrical circuit reliability by preventing damage from inductive load switching. The effectiveness of each depends on the application: vibration dampers excel in mechanical vibration control, whereas snubber circuits are critical in electronic transient suppression.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Solution
Vibration dampers effectively reduce mechanical oscillations and extend equipment lifespan by absorbing and dissipating energy, but they can be bulky and less precise for high-frequency vibrations. Snubber circuits excel in protecting electrical components from voltage spikes and transient surges by providing controlled damping, yet they may introduce power losses and require careful design to avoid component stress. Choosing between vibration dampers and snubber circuits depends on whether mechanical vibration reduction or electrical transient suppression is the primary concern.
Choosing the Right Solution: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right solution between a vibration damper and a snubber circuit depends on your specific application requirements, such as the type of mechanical or electrical noise you need to control and the frequency range involved. Vibration dampers are ideal for reducing physical oscillations and mechanical resonance, while snubber circuits excel in protecting electrical components from voltage spikes and transient surges. Assess factors like environmental conditions, system sensitivity, and cost-effectiveness to ensure optimal performance and longevity of your equipment.
Vibration Damper vs Snubber Circuit Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com