A PID controller continuously adjusts the control output based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms to maintain precise system stability, while an on-off controller simply switches the output fully on or off, causing more oscillations and less accuracy. Discover how choosing the right controller can optimize your system's performance by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
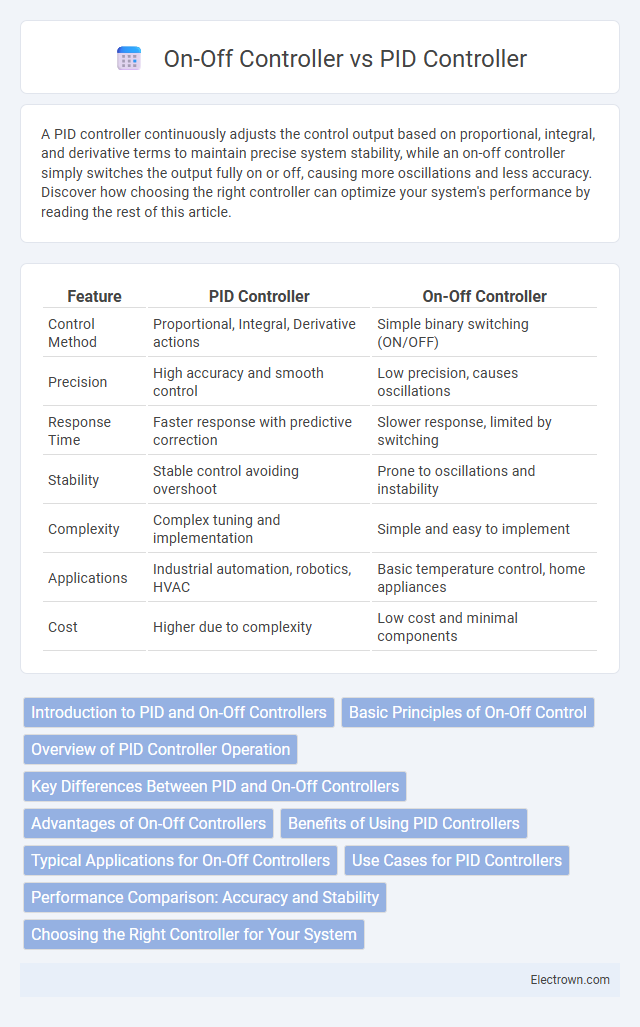
| Feature | PID Controller | On-Off Controller |
|---|---|---|
| Control Method | Proportional, Integral, Derivative actions | Simple binary switching (ON/OFF) |
| Precision | High accuracy and smooth control | Low precision, causes oscillations |
| Response Time | Faster response with predictive correction | Slower response, limited by switching |
| Stability | Stable control avoiding overshoot | Prone to oscillations and instability |
| Complexity | Complex tuning and implementation | Simple and easy to implement |
| Applications | Industrial automation, robotics, HVAC | Basic temperature control, home appliances |
| Cost | Higher due to complexity | Low cost and minimal components |
Introduction to PID and On-Off Controllers
PID controllers use proportional, integral, and derivative calculations to continuously adjust control outputs for precise system regulation, minimizing errors over time. On-off controllers operate with simple binary signals, switching outputs fully on or off based on threshold values, ideal for basic control tasks with less sensitivity. The choice between PID and on-off controllers depends on system complexity, accuracy requirements, and response time demands.
Basic Principles of On-Off Control
On-Off control operates by switching the output fully on or off based on whether the process variable is above or below a setpoint, creating a binary control signal without intermediate states. This method is simple and cost-effective, commonly used in applications where precise control is not critical, such as thermostats or basic heating systems. Its fundamental principle relies on hysteresis to prevent excessive switching and reduce wear on mechanical components.
Overview of PID Controller Operation
A PID controller continuously calculates an error value as the difference between a desired setpoint and a measured process variable, using proportional, integral, and derivative terms to minimize this error over time. The proportional term addresses present error, the integral term corrects accumulated past errors, and the derivative term predicts future error trends to improve stability and response. Understanding your PID controller's ability to fine-tune these three parameters helps achieve precise and smooth process control compared to the simpler On-Off controller.
Key Differences Between PID and On-Off Controllers
PID controllers use proportional, integral, and derivative actions to continuously adjust control output for precise regulation, while on-off controllers operate with simple two-state outputs, switching fully on or off based on setpoint deviation. PID controllers minimize steady-state error and oscillations, offering smoother and more stable control, whereas on-off controllers often cause frequent switching and potential wear on mechanical components. Your choice depends on the required control accuracy, system dynamics, and tolerance for output fluctuations.
Advantages of On-Off Controllers
On-Off Controllers offer simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for applications where basic temperature or pressure regulation is sufficient. Their straightforward operation reduces the need for complex tuning and maintenance, ensuring consistent performance in environments with minimal precision requirements. You can rely on On-Off Controllers for reliable control in systems where slight oscillations around the setpoint are acceptable.
Benefits of Using PID Controllers
PID controllers provide precise and stable control by continuously adjusting output based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms, minimizing errors and overshoot. Unlike on-off controllers that can cause oscillations and wear due to frequent switching, PID controllers enhance system performance and longevity by maintaining smoother operation. Your process benefits from improved accuracy, reduced energy consumption, and consistent quality control when using PID controllers.
Typical Applications for On-Off Controllers
On-off controllers are commonly used in applications requiring simple temperature regulation, such as household thermostats, ovens, and refrigeration systems, where precise control is not critical. They are ideal for systems with slow dynamics or those that can tolerate some degree of temperature fluctuation, like water heaters and incubators. These controllers offer cost-effectiveness and ease of implementation, making them suitable for basic industrial processes and HVAC systems.
Use Cases for PID Controllers
PID controllers excel in applications requiring precise control and stability, such as temperature regulation in industrial furnaces and speed control in motors. Their ability to continuously adjust output based on proportional, integral, and derivative actions makes them ideal for processes with dynamic changes and minimal overshoot. PID controllers are preferred in sectors like manufacturing automation, chemical processing, and robotics where accuracy and smooth control are critical.
Performance Comparison: Accuracy and Stability
PID controllers provide superior accuracy and stability compared to On-Off controllers by continuously adjusting output based on proportional, integral, and derivative calculations, minimizing error and overshoot. On-Off controllers, while simpler and cost-effective, often lead to persistent oscillations and less precise control due to their binary nature. Your choice of controller impacts system responsiveness, with PID controllers delivering smoother, more stable performance in complex or sensitive applications.
Choosing the Right Controller for Your System
Selecting the right controller depends on the specific requirements of your system, such as precision, response time, and complexity. PID controllers offer precise, continuous control by adjusting output based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms, ideal for processes needing stable and accurate regulation. On-off controllers provide simpler, binary control suited for applications with less stringent accuracy demands or where cost and simplicity are priorities.
PID Controller vs On-Off Controller Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com