Slip Power Recovery Drive maximizes energy efficiency by returning slip power from the rotor circuit back to the supply, enhancing motor performance in variable speed applications. Explore the full article to understand how these drives compare in terms of operation, cost, and application suitability for Your industrial needs.
Table of Comparison
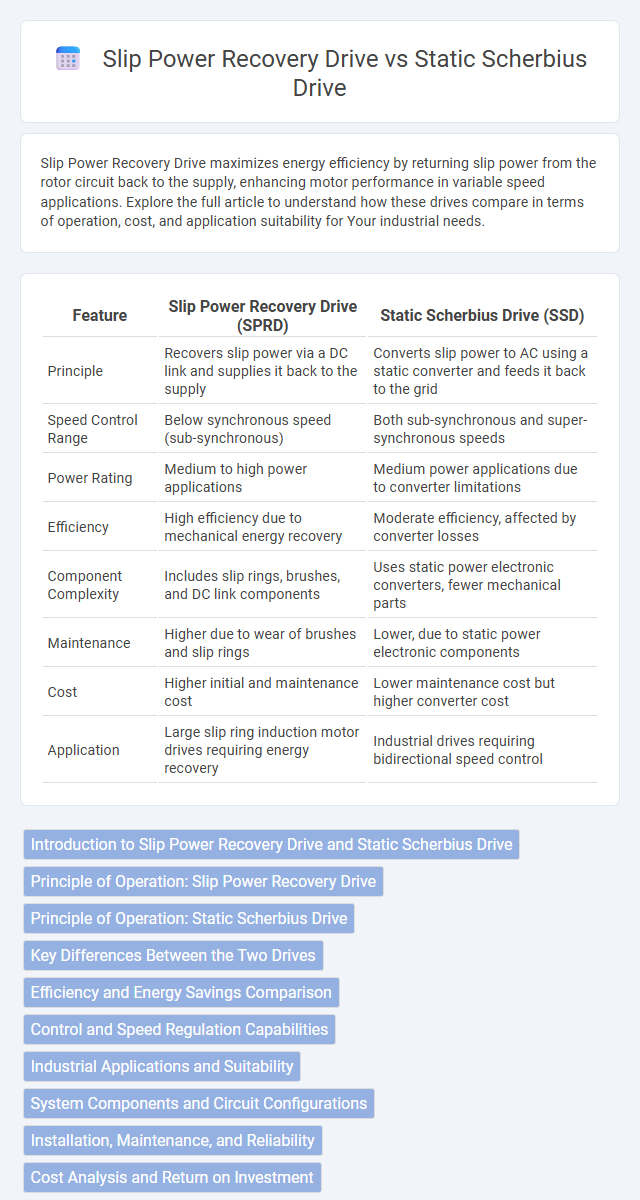
| Feature | Slip Power Recovery Drive (SPRD) | Static Scherbius Drive (SSD) |
|---|---|---|
| Principle | Recovers slip power via a DC link and supplies it back to the supply | Converts slip power to AC using a static converter and feeds it back to the grid |
| Speed Control Range | Below synchronous speed (sub-synchronous) | Both sub-synchronous and super-synchronous speeds |
| Power Rating | Medium to high power applications | Medium power applications due to converter limitations |
| Efficiency | High efficiency due to mechanical energy recovery | Moderate efficiency, affected by converter losses |
| Component Complexity | Includes slip rings, brushes, and DC link components | Uses static power electronic converters, fewer mechanical parts |
| Maintenance | Higher due to wear of brushes and slip rings | Lower, due to static power electronic components |
| Cost | Higher initial and maintenance cost | Lower maintenance cost but higher converter cost |
| Application | Large slip ring induction motor drives requiring energy recovery | Industrial drives requiring bidirectional speed control |
Introduction to Slip Power Recovery Drive and Static Scherbius Drive
Slip Power Recovery Drive and Static Scherbius Drive are advanced methods for improving the efficiency of wound rotor induction motors by recovering slip power. Slip Power Recovery Drive uses a back-to-back converter system to feed the rotor power back to the supply, enabling controlled speed operation with reduced energy loss. In contrast, Static Scherbius Drive employs a static converter connected to the rotor side, allowing precise speed control by injecting or absorbing rotor power without mechanical components.
Principle of Operation: Slip Power Recovery Drive
Slip Power Recovery Drive operates by recovering the slip power from the rotor circuit of a wound rotor induction motor through a static converter or power electronic device, converting it back to the supply or load side. This drive controls rotor speed by adjusting the frequency and amplitude of the slip power, enabling smooth speed variation below synchronous speed with improved efficiency. The system minimizes power losses by feeding the rotor energy back to the supply, unlike traditional methods where slip power is dissipated as heat.
Principle of Operation: Static Scherbius Drive
Static Scherbius Drive operates on the principle of recovering slip power from the rotor circuit of wound rotor induction motors through a back-to-back voltage source converter. This converter allows for bidirectional power flow between the rotor and the supply, enabling smooth speed control and energy regeneration during braking. Your industrial applications benefit from enhanced efficiency and precise motor speed regulation using this drive system.
Key Differences Between the Two Drives
Slip Power Recovery Drive regenerates slip power back to the supply through a back-to-back converter, enhancing energy efficiency in wound rotor induction motors. Static Scherbius Drive uses a frequency converter to control rotor speed and torque by injecting variable frequency voltage into the rotor circuit, enabling smooth speed variation below synchronous speed. Key differences include the Slip Power Recovery Drive's focus on power recovery and simplicity versus the Static Scherbius Drive's advanced speed control and dynamic torque regulation capabilities.
Efficiency and Energy Savings Comparison
Slip Power Recovery Drives offer higher efficiency by recycling slip power back to the supply, often achieving energy savings up to 30% compared to conventional drives. Static Scherbius Drives also provide energy savings by converting slip frequency power into usable electrical energy, but their efficiency is typically lower due to additional conversion losses. Your choice between these technologies should consider the specific application load and cost-benefit analysis for optimal energy performance.
Control and Speed Regulation Capabilities
Slip Power Recovery Drive offers precise control and efficient speed regulation by recovering slip power and feeding it back to the supply, allowing smooth variation of rotor speed in wound rotor motors. Static Scherbius Drive enhances speed control by using power electronic converters to inject controlled voltage into the rotor circuit, providing improved dynamic response and greater efficiency at varying speeds. Both drives enable adjustable speed operation, but Static Scherbius Drives typically achieve finer control and faster response due to advanced semiconductor switching techniques.
Industrial Applications and Suitability
Slip Power Recovery Drive is ideal for industrial applications requiring energy-efficient control of wound-rotor induction motors, such as cranes, hoists, and mills, due to its ability to recover slip power and improve system efficiency. Static Scherbius Drive suits industries demanding precise speed control and smooth torque output, like rolling mills and pumps, by utilizing power electronics to inject controlled voltage into the rotor circuit. Your choice depends on whether energy recovery or fine speed regulation is critical for your industrial process.
System Components and Circuit Configurations
Slip Power Recovery Drive systems consist primarily of a wound rotor induction motor, a power converter (often a voltage source inverter), and a control unit that manages rotor power feedback to the supply. Static Scherbius Drive incorporates a stator-side supply, rotor-side converter, and a common DC link, enabling bidirectional power flow between the rotor circuit and the grid. Your choice between these drives depends on system complexity, with Slip Power Recovery Drive featuring simpler control circuits while Static Scherbius offers improved energy recovery through advanced power electronic converters.
Installation, Maintenance, and Reliability
Slip Power Recovery Drives offer easier installation due to their compact design and fewer components, reducing setup time and space requirements compared to Static Scherbius Drives, which need complex power electronics and cooling systems. Maintenance of Slip Power Recovery Drives is generally lower because of simpler mechanical parts, while Static Scherbius Drives demand frequent inspection and upkeep of power converters to ensure optimal performance. Your choice impacts reliability; Slip Power Recovery Drives provide robust operation with fewer failure points, whereas Static Scherbius Drives, despite higher efficiency, may experience downtime due to electronic component sensitivity and cooling system needs.
Cost Analysis and Return on Investment
Slip Power Recovery Drives generally offer a lower initial cost compared to Static Scherbius Drives due to their simpler mechanical components and established technology. However, Static Scherbius Drives provide higher efficiency and reduced maintenance costs, leading to a better return on investment over the equipment's operational lifespan. Your choice should consider both upfront expenses and long-term energy savings to optimize overall cost-effectiveness.
Slip Power Recovery Drive vs Static Scherbius Drive Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com