Square wave inverters generate a simple, block-shaped output waveform suitable for basic appliances but may cause noise or inefficiency in sensitive electronics, whereas sine wave inverters produce smooth, oscillating waveforms closely mimicking utility power, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance for a wide range of devices. Discover how choosing the right inverter can impact your equipment's safety and efficiency by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
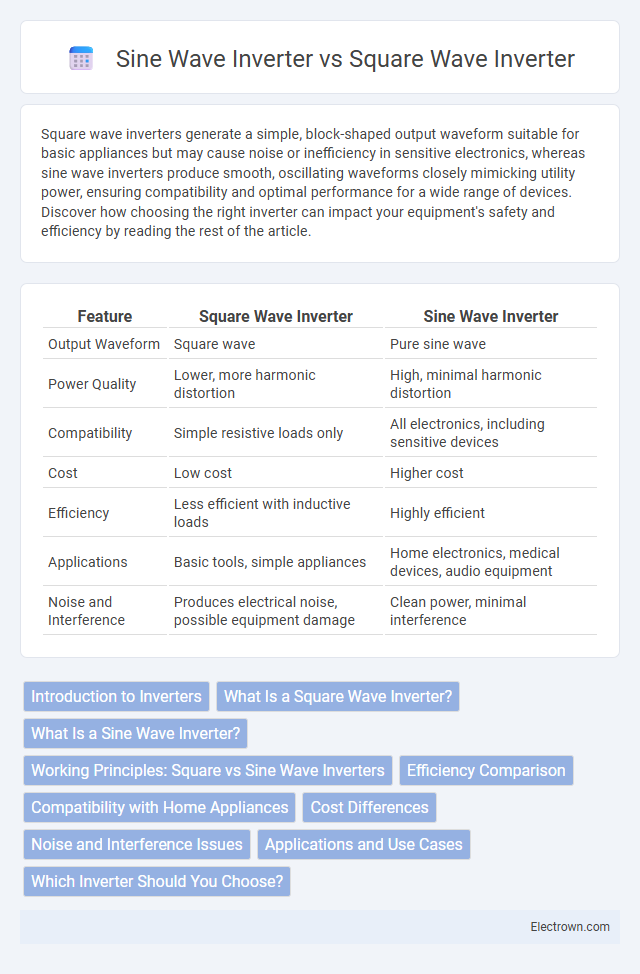
| Feature | Square Wave Inverter | Sine Wave Inverter |
|---|---|---|
| Output Waveform | Square wave | Pure sine wave |
| Power Quality | Lower, more harmonic distortion | High, minimal harmonic distortion |
| Compatibility | Simple resistive loads only | All electronics, including sensitive devices |
| Cost | Low cost | Higher cost |
| Efficiency | Less efficient with inductive loads | Highly efficient |
| Applications | Basic tools, simple appliances | Home electronics, medical devices, audio equipment |
| Noise and Interference | Produces electrical noise, possible equipment damage | Clean power, minimal interference |
Introduction to Inverters
Inverters convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) to power various electrical devices, with Square Wave and Sine Wave inverters being the most common types. Square Wave inverters generate a simple, rectangular waveform ideal for basic resistive loads but may cause noise and inefficiency in sensitive electronics. Sine Wave inverters produce a smooth, sinusoidal output that closely mimics utility power, ensuring compatibility with complex appliances and reducing electromagnetic interference.
What Is a Square Wave Inverter?
A Square Wave Inverter converts direct current (DC) into a simple, non-smooth alternating current (AC) output with abrupt voltage transitions, ideal for basic electronic devices and resistive loads. Its waveform consists of a rapid switch between positive and negative voltages, which can cause noise and reduced efficiency in sensitive equipment. Understanding the characteristics of a square wave inverter helps you choose the right power source for applications requiring cost-effective but less refined AC power.
What Is a Sine Wave Inverter?
A sine wave inverter converts DC power into an AC output that closely mimics the smooth, periodic oscillation of utility-supplied electricity, producing a clean and stable sine wave. This type of inverter is ideal for sensitive electronics and appliances such as medical equipment, audio devices, and variable-speed motors, ensuring optimal performance and reduced electrical noise. Compared to square wave inverters, sine wave inverters provide efficient energy conversion, better compatibility, and safer operation for a wide range of home and industrial applications.
Working Principles: Square vs Sine Wave Inverters
Square wave inverters convert DC to AC by rapidly switching the output voltage between high and low states, creating a stepped waveform that approximates a square shape and is simpler but less compatible with sensitive electronics. Sine wave inverters use pulse width modulation (PWM) to produce a smooth, continuous AC waveform closely matching the natural sine wave of utility power, ensuring higher efficiency and better performance for your devices. The working principle difference impacts efficiency, device compatibility, and output quality, making sine wave inverters ideal for complex electronics and sensitive equipment.
Efficiency Comparison
Square wave inverters typically exhibit lower efficiency due to their simpler waveform, which causes more harmonic distortion and interferes with sensitive electronic devices. Sine wave inverters produce a smooth and pure sinusoidal output, resulting in higher energy efficiency and reduced heat generation, which prolongs device lifespan. The overall performance advantage of sine wave inverters makes them more efficient and reliable for powering complex electronics and household appliances.
Compatibility with Home Appliances
Square wave inverters produce a basic waveform that may cause humming or overheating in sensitive home appliances like microwaves, refrigerators, and audio systems. Sine wave inverters generate a smooth and pure waveform that closely replicates utility power, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance with a wide range of household devices. Choosing a sine wave inverter protects your appliances from potential damage and improves their efficiency and lifespan.
Cost Differences
Square wave inverters typically offer a lower cost option due to their simpler design and fewer components, making them suitable for budget-conscious users or basic electrical appliances. Sine wave inverters, while more expensive, provide cleaner and more reliable power output, which is essential for sensitive electronics and higher efficiency. Choosing the right inverter depends on your specific power quality needs and budget constraints.
Noise and Interference Issues
Square wave inverters generate higher levels of electromagnetic interference (EMI) and audible noise due to their abrupt voltage transitions, which can disrupt sensitive electronic devices and communication equipment. Sine wave inverters produce a smooth and continuous waveform that closely resembles utility power, minimizing noise and interference and ensuring compatibility with a wide range of appliances. This reduction in EMI and audible noise makes sine wave inverters ideal for applications requiring stable and quiet power supply environments.
Applications and Use Cases
Square wave inverters are typically used in simple applications such as powering resistive loads like incandescent bulbs and basic tools, where waveform quality is less critical. Sine wave inverters deliver cleaner, high-quality power essential for sensitive electronics, medical equipment, and audio devices, ensuring optimal performance and reduced interference. Your choice depends on the device sensitivity and power requirements, with sine wave inverters favored for complex, sensitive applications and square wave inverters suited for cost-effective, less demanding uses.
Which Inverter Should You Choose?
Choosing between a square wave inverter and a sine wave inverter depends on your specific power needs and device compatibility. Sine wave inverters produce a smooth, clean waveform ideal for sensitive electronics, making them suitable for appliances, medical equipment, and audio devices, while square wave inverters are more cost-effective but best suited for simple tools and resistive loads. For reliable performance and safety in diverse applications, investing in a pure sine wave inverter is generally recommended.
Square Wave Inverter vs Sine Wave Inverter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com