Conventional motor starters deliver immediate full voltage to motors, causing sudden current surges and mechanical stress, whereas soft starters gradually ramp up voltage to reduce inrush current and protect your equipment. Discover how choosing the right starter can enhance your motor's performance and lifespan by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
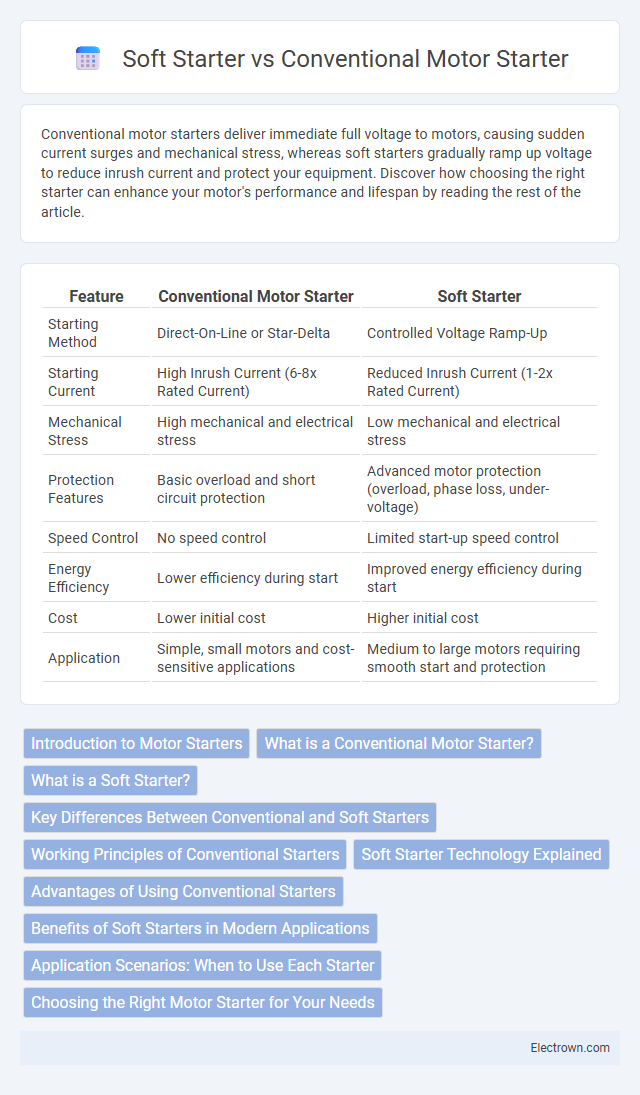
| Feature | Conventional Motor Starter | Soft Starter |
|---|---|---|
| Starting Method | Direct-On-Line or Star-Delta | Controlled Voltage Ramp-Up |
| Starting Current | High Inrush Current (6-8x Rated Current) | Reduced Inrush Current (1-2x Rated Current) |
| Mechanical Stress | High mechanical and electrical stress | Low mechanical and electrical stress |
| Protection Features | Basic overload and short circuit protection | Advanced motor protection (overload, phase loss, under-voltage) |
| Speed Control | No speed control | Limited start-up speed control |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower efficiency during start | Improved energy efficiency during start |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Application | Simple, small motors and cost-sensitive applications | Medium to large motors requiring smooth start and protection |
Introduction to Motor Starters
Motor starters are essential devices in industrial and commercial settings designed to safely start and stop electric motors while protecting against overloads. Conventional motor starters use electromechanical contactors and overload relays to control motor operation, providing simple and robust functionality for many applications. Soft starters, on the other hand, employ solid-state electronics to gradually ramp up voltage, reducing mechanical stress and enhancing the longevity of your motor and connected equipment.
What is a Conventional Motor Starter?
A conventional motor starter is an electromechanical device used to start and stop electric motors by directly connecting them to the power supply, typically involving components like contactors and overload relays to provide basic protection. It operates by applying full voltage immediately to the motor, resulting in a high inrush current that can cause mechanical stress and electrical disturbances. This traditional starting method is simple and cost-effective but lacks the ability to control acceleration and torque smoothly compared to advanced solutions like soft starters.
What is a Soft Starter?
A soft starter is an advanced electrical device designed to regulate the initial voltage applied to an electric motor, enabling a gradual ramp-up in speed and reducing mechanical stress and electrical surges. Unlike conventional motor starters that apply full voltage instantly, soft starters use solid-state components such as thyristors to modulate power during startup. This technology extends motor lifespan, minimizes energy consumption, and enhances overall operational efficiency in industrial applications.
Key Differences Between Conventional and Soft Starters
Conventional motor starters use direct-on-line or star-delta methods to start motors, causing high inrush currents and mechanical stress, while soft starters gradually ramp up voltage to minimize electrical and mechanical shock. Soft starters provide improved motor protection, energy efficiency, and reduced maintenance costs compared to conventional starters. Your choice affects system longevity, operational smoothness, and overall performance depending on load requirements and startup frequency.
Working Principles of Conventional Starters
Conventional motor starters operate using electromagnetic relays or contactors combined with overload protection to directly connect the motor to the power supply, enabling full voltage start. These starters rely on mechanical switching to rapidly apply and remove electrical power, which can cause high inrush currents and mechanical stress on the motor. Their straightforward design contrasts with soft starters that gradually ramp up voltage, minimizing current surges and enhancing motor longevity.
Soft Starter Technology Explained
Soft starter technology uses controlled voltage ramp-up to gradually increase motor speed, reducing inrush current and mechanical stress compared to conventional motor starters that apply full voltage instantly. This precise voltage control minimizes electrical and mechanical wear, extending equipment lifespan and improving operational efficiency. Your motor benefits from smoother startups, enhanced protection, and lower maintenance costs when using soft starters.
Advantages of Using Conventional Starters
Conventional motor starters offer reliable and straightforward operation with proven durability, making them ideal for simple applications requiring frequent motor starts and stops. They provide robust overload protection and are typically more cost-effective than soft starters, reducing initial investment and maintenance expenses. Your equipment benefits from their ease of installation and compatibility with various motor types, ensuring dependable performance in demanding industrial environments.
Benefits of Soft Starters in Modern Applications
Soft starters provide precise control of motor starting current and torque, reducing electrical and mechanical stress on equipment while extending motor lifespan. Your machinery benefits from smoother acceleration, minimizing power surges and preventing damage to connected systems in modern industrial applications. This results in lower maintenance costs and improved overall efficiency compared to conventional motor starters.
Application Scenarios: When to Use Each Starter
Conventional motor starters are ideal for applications requiring simple on/off control and robust protection in environments with minimal need for reducing inrush current, such as pumps, compressors, and conveyors. Soft starters are best used in scenarios where minimizing mechanical stress and electrical peaks during motor startup is critical, including HVAC systems, fans, and applications involving frequent starts and stops. Selecting the appropriate starter for your motor depends on the operational demands and the need to enhance equipment lifespan and energy efficiency.
Choosing the Right Motor Starter for Your Needs
Choosing the right motor starter depends on your application's requirements for torque control, energy efficiency, and equipment protection. Conventional motor starters provide basic on/off control and are suitable for simple, low-cost applications, while soft starters offer smoother motor acceleration and reduced mechanical stress, enhancing equipment lifespan and operational efficiency. Understanding your load characteristics and startup demands ensures you select a motor starter that balances performance, cost, and durability for your specific needs.
Conventional Motor Starter vs Soft Starter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com