Three-phase power systems deliver consistent and efficient energy ideal for industrial and large commercial applications, while single-phase systems are simpler and commonly used in residential settings with lower power demands. Explore the differences in performance, cost, and applications to determine which system best suits your energy needs.
Table of Comparison
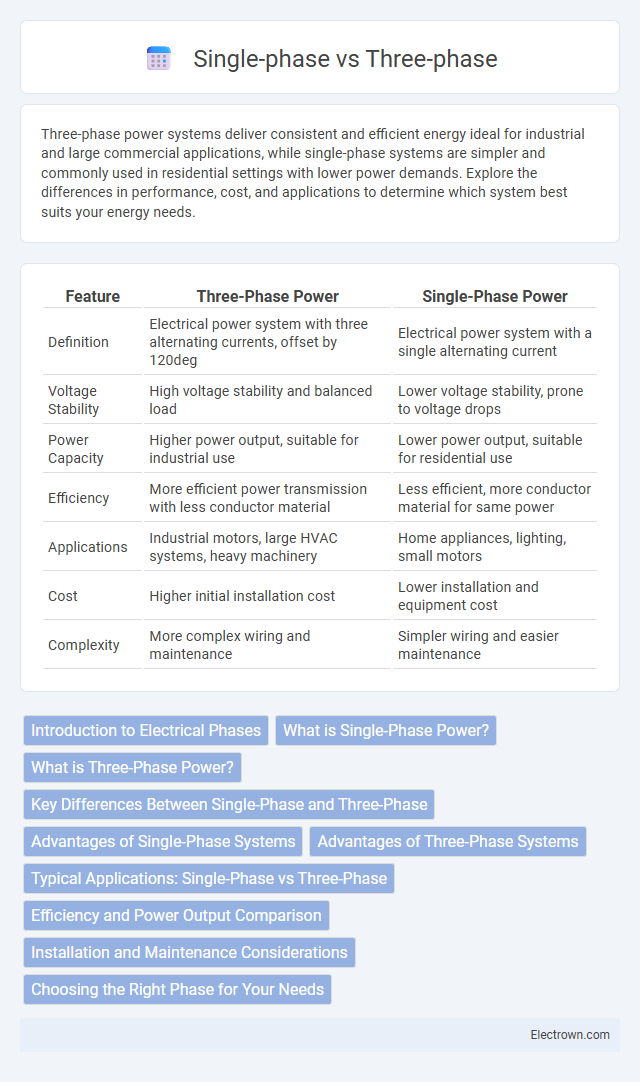
| Feature | Three-Phase Power | Single-Phase Power |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Electrical power system with three alternating currents, offset by 120deg | Electrical power system with a single alternating current |
| Voltage Stability | High voltage stability and balanced load | Lower voltage stability, prone to voltage drops |
| Power Capacity | Higher power output, suitable for industrial use | Lower power output, suitable for residential use |
| Efficiency | More efficient power transmission with less conductor material | Less efficient, more conductor material for same power |
| Applications | Industrial motors, large HVAC systems, heavy machinery | Home appliances, lighting, small motors |
| Cost | Higher initial installation cost | Lower installation and equipment cost |
| Complexity | More complex wiring and maintenance | Simpler wiring and easier maintenance |
Introduction to Electrical Phases
Electrical power systems utilize different phase configurations to distribute electricity efficiently. Single-phase power delivers alternating current through one sine wave, commonly found in residential settings, whereas three-phase power uses three alternating currents offset by 120 degrees, enabling more consistent and reliable energy flow essential for industrial and large-scale applications. Understanding these differences helps you optimize electrical performance based on your specific energy requirements.
What is Single-Phase Power?
Single-phase power consists of a single alternating current (AC) waveform used primarily in residential and light commercial applications, delivering a single voltage cycle at a time. It operates on two wires--one live and one neutral--providing power typically at 120 or 240 volts depending on the region and appliance requirements. Single-phase power is simpler and less expensive to install but offers less efficient energy transmission and lower capacity compared to three-phase power systems.
What is Three-Phase Power?
Three-phase power is an electrical system that uses three alternating currents, each offset by 120 degrees, to deliver consistent and efficient energy transfer. This method is commonly used in industrial and commercial applications due to its ability to provide a balanced load and higher power capacity compared to single-phase power. Understanding three-phase power can help you optimize energy use in large-scale electrical setups.
Key Differences Between Single-Phase and Three-Phase
Single-phase power supply uses one alternating current (AC) waveform, typically found in residential applications and suitable for low power demands. Three-phase power utilizes three AC waveforms offset by 120 degrees, delivering consistent and higher power output essential for industrial and heavy machinery. Understanding the key differences can help you select the appropriate power system for your electrical needs, optimizing efficiency and performance.
Advantages of Single-Phase Systems
Single-phase systems offer simplicity and cost-effectiveness for residential and light commercial applications, reducing installation and maintenance expenses. They require fewer components, making them easier to repair and suitable for smaller power demands. Single-phase power is readily available from standard utility supplies, ensuring widespread compatibility with household appliances and equipment.
Advantages of Three-Phase Systems
Three-phase systems offer higher power efficiency and smoother motor operation compared to single-phase systems, making them ideal for heavy industrial and commercial applications. They provide consistent power delivery with less voltage drop and allow for smaller, more cost-effective wiring and equipment. Your electrical setup benefits from improved reliability and the ability to handle larger loads without the risk of overheating.
Typical Applications: Single-Phase vs Three-Phase
Single-phase power is commonly used in residential homes, small businesses, and light commercial applications due to its simplicity and cost-effectiveness for lower power requirements. Three-phase power is typically deployed in industrial settings, large commercial buildings, and heavy machinery where higher power loads and efficient energy distribution are essential. Understanding Your power needs helps determine whether single-phase or three-phase is the optimal choice for reliable and efficient electricity supply.
Efficiency and Power Output Comparison
Three-phase power systems deliver higher efficiency and more consistent power output compared to single-phase systems, making them ideal for industrial and high-load applications. Single-phase systems are typically sufficient for residential use but can suffer from voltage drops and less stable power delivery under heavy loads. Understanding the efficiency and power output differences can help you select the most suitable option for your energy needs.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Three-phase electrical systems require more complex installation due to the need for three live wires and a neutral, which increases wiring complexity and costs compared to single-phase systems that use only one live wire and a neutral. Maintenance of three-phase systems demands specialized knowledge to handle the balanced load across all three phases and diagnose issues such as phase loss or unbalanced voltages, while single-phase systems have simpler troubleshooting and fewer components to maintain. Proper installation and regular maintenance of three-phase systems often lead to higher efficiency and reliability in industrial settings, whereas single-phase systems are typically adequate and easier to maintain for residential applications.
Choosing the Right Phase for Your Needs
Selecting between three-phase and single-phase power depends on the electrical load and application type; three-phase systems deliver consistent power for heavy machinery and industrial use, while single-phase suits residential and light commercial settings. Three-phase power provides higher efficiency and reduced energy losses for large motors or equipment, making it ideal for manufacturing plants or data centers. Single-phase is cost-effective and simpler to install for everyday appliances, lighting, and smaller machines, offering flexibility for homes and small businesses.
Three-phase vs Single-phase Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com