Copper ground rods offer superior corrosion resistance and conductivity compared to galvanized ground rods, making them ideal for long-term electrical grounding solutions. To understand which grounding rod best suits your needs and environment, explore the detailed comparison in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
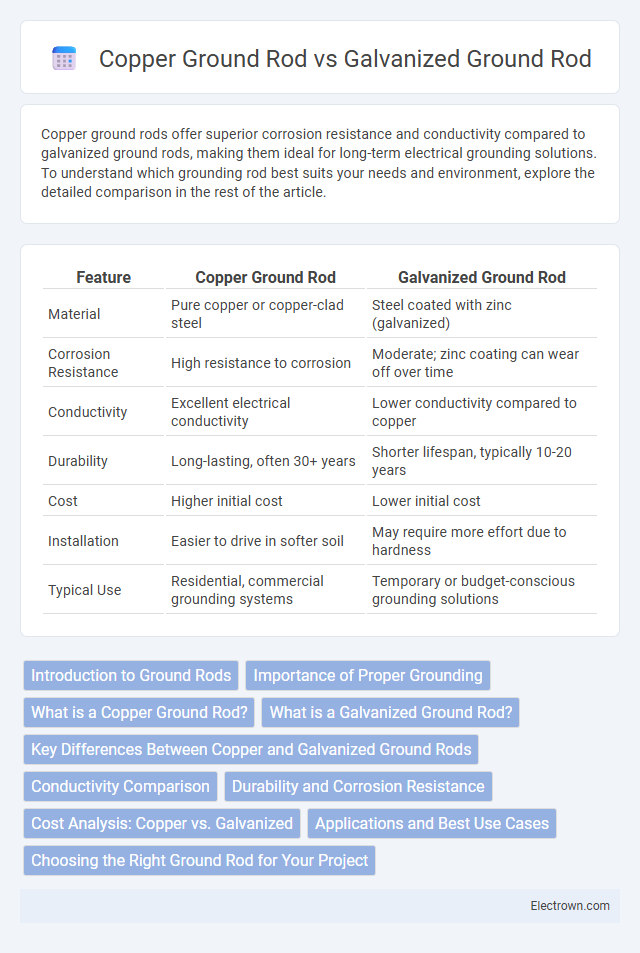
| Feature | Copper Ground Rod | Galvanized Ground Rod |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Pure copper or copper-clad steel | Steel coated with zinc (galvanized) |
| Corrosion Resistance | High resistance to corrosion | Moderate; zinc coating can wear off over time |
| Conductivity | Excellent electrical conductivity | Lower conductivity compared to copper |
| Durability | Long-lasting, often 30+ years | Shorter lifespan, typically 10-20 years |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Installation | Easier to drive in softer soil | May require more effort due to hardness |
| Typical Use | Residential, commercial grounding systems | Temporary or budget-conscious grounding solutions |
Introduction to Ground Rods
Ground rods are essential components for electrical grounding systems, providing a low-resistance path to dissipate electrical currents safely into the earth. Copper ground rods offer superior corrosion resistance and conductivity, ensuring long-term durability and effective grounding performance. Your choice between copper and galvanized ground rods will impact the efficiency and lifespan of the grounding system, with galvanized rods being more affordable but prone to corrosion over time.
Importance of Proper Grounding
Proper grounding ensures electrical safety by effectively dissipating fault currents and preventing electrical shock hazards. Copper ground rods offer superior conductivity and corrosion resistance, providing reliable long-term grounding performance compared to galvanized ground rods, which may corrode over time and reduce effectiveness. Selecting an appropriate grounding rod material is critical for maintaining system integrity and preventing equipment damage in electrical installations.
What is a Copper Ground Rod?
A copper ground rod is a solid copper or copper-clad rod used to safely dissipate electrical currents into the earth, providing effective grounding for electrical systems. Known for its superior conductivity and corrosion resistance, copper ground rods ensure long-term reliability in grounding applications compared to galvanized steel rods. These rods typically measure 8 feet in length and are installed vertically into the soil to establish a low-resistance path for fault currents.
What is a Galvanized Ground Rod?
A galvanized ground rod is a steel rod coated with a layer of zinc to prevent corrosion and ensure durability when used as a grounding electrode in electrical systems. Your choice between a copper ground rod and a galvanized ground rod depends on factors like soil resistivity, budget, and corrosion resistance requirements, with galvanized rods offering a more cost-effective but less conductive option compared to copper. Galvanized rods are commonly used in residential and commercial grounding applications where moderate corrosion protection is sufficient.
Key Differences Between Copper and Galvanized Ground Rods
Copper ground rods offer superior corrosion resistance and conductivity compared to galvanized ground rods, making them ideal for long-lasting grounding systems. Galvanized ground rods are coated with zinc, which can deteriorate over time, reducing their effectiveness and lifespan. When choosing your grounding solution, consider the environmental conditions, as copper rods perform better in highly corrosive soils, while galvanized rods may suffice in less aggressive environments.
Conductivity Comparison
Copper ground rods exhibit superior conductivity compared to galvanized ground rods, ensuring more efficient grounding and safer electrical systems. The high electrical conductivity of copper allows for quicker dissipation of electrical currents into the earth, reducing the risk of electrical faults and equipment damage. Your choice of copper ground rod can significantly enhance grounding performance in sensitive or high-demand installations.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Copper ground rods exhibit superior durability and corrosion resistance due to their inherent resistance to oxidation and rust, ensuring long-term electrical conductivity even in harsh soil conditions. Galvanized ground rods, coated with a layer of zinc, offer moderate corrosion protection but tend to degrade faster as the zinc layer wears away, leading to potential rust and reduced lifespan. For environments with high moisture or acidic soil, copper rods provide a more reliable grounding solution that maintains performance over decades.
Cost Analysis: Copper vs. Galvanized
Copper ground rods generally have a higher upfront cost compared to galvanized ground rods due to the premium price of copper material. Galvanized rods, while cheaper initially, may require more frequent replacements or maintenance because they are prone to corrosion over time. When considering the total cost of ownership, copper rods often provide better long-term value by reducing repair costs and improving grounding efficiency in electrical systems.
Applications and Best Use Cases
Copper ground rods excel in providing superior conductivity and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for residential and commercial electrical grounding systems where long-term durability is crucial. Galvanized ground rods offer a cost-effective alternative suited for temporary installations or environments with less corrosive soil conditions. Selecting the right rod depends on your grounding requirements, soil composition, and budget considerations to ensure optimal electrical safety and system performance.
Choosing the Right Ground Rod for Your Project
Copper ground rods offer superior corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity, ensuring long-term durability and reliable grounding performance for your project. Galvanized ground rods provide a cost-effective alternative but may corrode faster in certain soil conditions, which can reduce their lifespan and effectiveness. Evaluate soil chemistry, budget constraints, and project requirements to choose the optimal ground rod material that meets your grounding system's safety and efficiency standards.
Copper Ground Rod vs Galvanized Ground Rod Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com