Inverter duty motors are specifically designed to handle variable frequency drives with enhanced insulation and cooling systems, resulting in improved performance and longevity compared to standard motors that operate optimally only at fixed speeds. Discover how choosing the right motor can impact Your application's efficiency and reliability by reading the rest of the article.
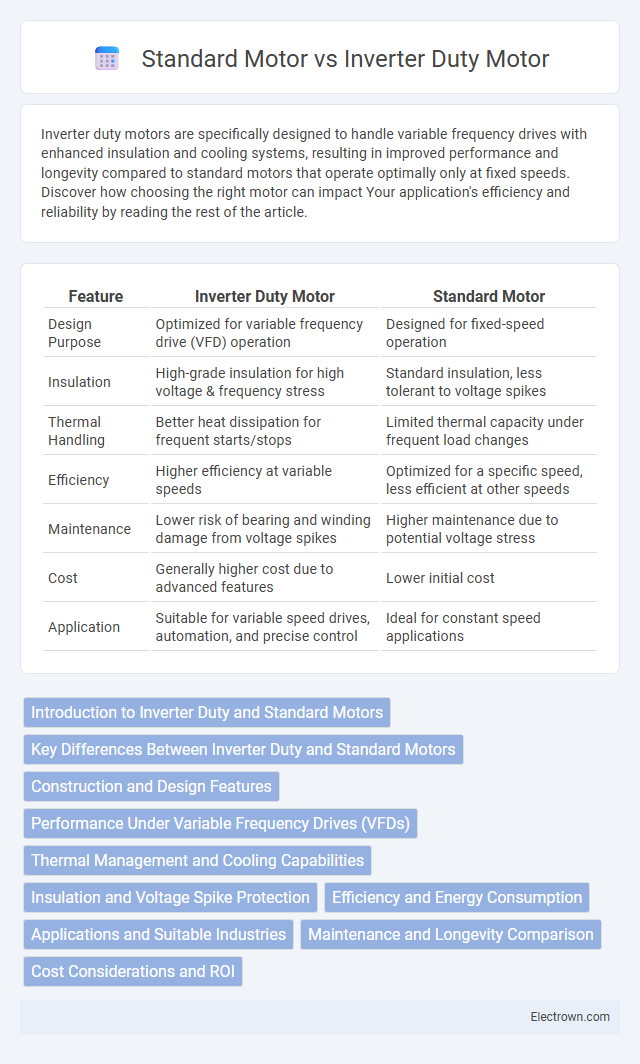
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Inverter Duty Motor | Standard Motor |
|---|---|---|
| Design Purpose | Optimized for variable frequency drive (VFD) operation | Designed for fixed-speed operation |
| Insulation | High-grade insulation for high voltage & frequency stress | Standard insulation, less tolerant to voltage spikes |
| Thermal Handling | Better heat dissipation for frequent starts/stops | Limited thermal capacity under frequent load changes |
| Efficiency | Higher efficiency at variable speeds | Optimized for a specific speed, less efficient at other speeds |
| Maintenance | Lower risk of bearing and winding damage from voltage spikes | Higher maintenance due to potential voltage stress |
| Cost | Generally higher cost due to advanced features | Lower initial cost |
| Application | Suitable for variable speed drives, automation, and precise control | Ideal for constant speed applications |
Introduction to Inverter Duty and Standard Motors
Inverter duty motors are specifically designed to operate efficiently with variable frequency drives (VFDs), providing enhanced thermal insulation, robust construction, and superior performance under fluctuating speeds and voltages. Standard motors, in contrast, are optimized for fixed-speed operation on constant voltage power supplies and may suffer from overheating or premature wear when used with VFDs. Key differentiators include inverter duty motors' ability to handle variable speed control and prevent insulation breakdown caused by harmonics and voltage spikes generated by inverters.
Key Differences Between Inverter Duty and Standard Motors
Inverter duty motors are specifically designed to handle variable frequency drives (VFDs), providing superior insulation, cooling, and construction to withstand voltage spikes and overheating, unlike standard motors which are optimized for constant-speed operation. You benefit from enhanced durability and efficiency with inverter duty motors in applications requiring precise speed control and frequent starts and stops. The key differences lie in the motor's insulation class, thermal rating, and rotor design, enabling inverter duty motors to operate reliably under varying speeds and loads where standard motors might fail prematurely.
Construction and Design Features
Inverter duty motors are engineered with reinforced insulation systems and enhanced cooling mechanisms to withstand voltage spikes and variable frequency drives, unlike standard motors that lack these robust features. Their stator windings use high-grade materials and tighter tolerances, ensuring durability under fluctuating speeds and non-sinusoidal currents common in inverter applications. You benefit from inverter duty motors' superior construction that promotes reliable performance and extended lifespan in demanding environments.
Performance Under Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs)
Inverter Duty Motors are specifically designed to handle the rapid frequency changes and voltage spikes produced by Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs), ensuring consistent torque and reduced heat buildup. Standard Motors, on the other hand, may suffer from insulation damage, overheating, and decreased lifespan when operated under VFD conditions due to their inability to manage high voltage surges and harmonic distortions. Optimizing motor selection for VFD applications enhances energy efficiency, reliability, and overall system performance in variable speed operations.
Thermal Management and Cooling Capabilities
Inverter Duty Motors feature advanced thermal management systems designed to handle the fluctuating speeds and variable frequencies common in inverter applications, preventing overheating during extended operation. Their enhanced cooling capabilities, often incorporating superior fan designs and optimized airflow paths, ensure consistent temperature control even under heavy load conditions. You benefit from improved motor longevity and reliable performance in demanding environments compared to Standard Motors, which typically have less robust cooling mechanisms and may experience thermal stress under variable speed conditions.
Insulation and Voltage Spike Protection
Inverter Duty Motors feature advanced insulation systems designed to withstand the high-frequency voltage spikes generated by variable frequency drives (VFDs), ensuring enhanced durability and performance. Standard Motors typically lack this reinforced insulation, making them more susceptible to insulation breakdown and premature failure under VFD operation. Choosing an Inverter Duty Motor safeguards Your equipment by providing superior voltage spike protection and extending motor lifespan in demanding variable-speed applications.
Efficiency and Energy Consumption
Inverter duty motors are designed to operate efficiently under variable speeds, significantly reducing energy consumption compared to standard motors that run at fixed speeds. Their enhanced insulation and cooling systems optimize performance, increasing overall efficiency during fluctuating load conditions. Your energy costs can be lowered by choosing an inverter duty motor for applications requiring speed control and frequent starts or stops.
Applications and Suitable Industries
Inverter duty motors are designed for variable frequency drive (VFD) applications, providing precise speed control and enhanced performance in industries such as HVAC, manufacturing, and automation. Standard motors are suitable for fixed-speed applications with consistent load demands, commonly used in pumps, fans, and conveyor systems within industries like agriculture and general manufacturing. Your choice depends on whether your application requires flexibility and efficiency at varying speeds or straightforward, constant-speed operation.
Maintenance and Longevity Comparison
Inverter duty motors are designed with enhanced insulation systems and robust bearings that withstand variable frequency drive (VFD) vibrations and thermal stresses, significantly reducing maintenance requirements compared to standard motors. Standard motors often face premature wear due to harmonics and rapid speed changes common in VFD applications, leading to increased downtime and frequent servicing. Consequently, inverter duty motors offer extended operational longevity, minimizing total lifecycle costs and supporting continuous industrial processes.
Cost Considerations and ROI
Inverter duty motors typically incur higher upfront costs than standard motors due to specialized insulation and design features that allow them to handle variable frequency drive (VFD) operations. The increased initial investment is often offset by longer service life, improved energy efficiency, and reduced maintenance expenses, resulting in a favorable return on investment (ROI) over time. Evaluating total cost of ownership, inverter duty motors deliver significant economic benefits in applications requiring speed control and frequent startups compared to standard motors.
Inverter Duty Motor vs Standard Motor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com