Fieldbus offers a robust, real-time, and deterministic communication protocol specifically designed for industrial automation, enabling seamless integration of multiple devices over a single network, whereas Modbus is a simpler, widely-used serial communication protocol that supports basic data exchange between controllers and devices. Discover how your choice between Fieldbus and Modbus can impact system performance and scalability by exploring the detailed comparisons in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
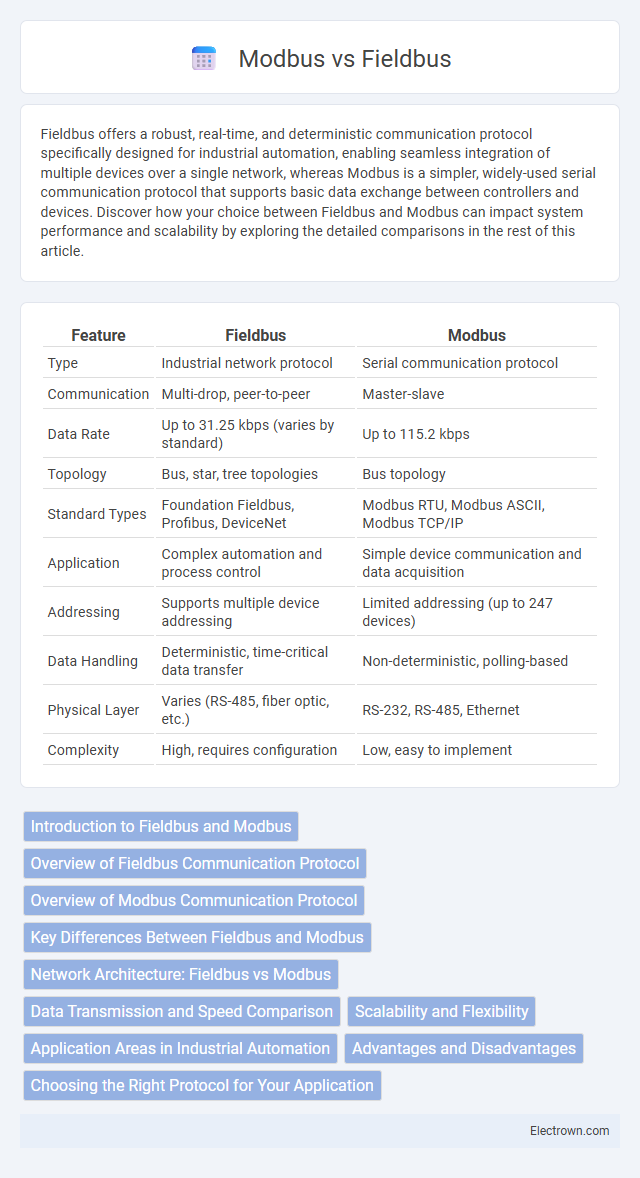
| Feature | Fieldbus | Modbus |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Industrial network protocol | Serial communication protocol |
| Communication | Multi-drop, peer-to-peer | Master-slave |
| Data Rate | Up to 31.25 kbps (varies by standard) | Up to 115.2 kbps |
| Topology | Bus, star, tree topologies | Bus topology |
| Standard Types | Foundation Fieldbus, Profibus, DeviceNet | Modbus RTU, Modbus ASCII, Modbus TCP/IP |
| Application | Complex automation and process control | Simple device communication and data acquisition |
| Addressing | Supports multiple device addressing | Limited addressing (up to 247 devices) |
| Data Handling | Deterministic, time-critical data transfer | Non-deterministic, polling-based |
| Physical Layer | Varies (RS-485, fiber optic, etc.) | RS-232, RS-485, Ethernet |
| Complexity | High, requires configuration | Low, easy to implement |
Introduction to Fieldbus and Modbus
Fieldbus and Modbus are essential communication protocols in industrial automation, enabling seamless data exchange between control devices. Fieldbus is a digital, real-time, multi-drop communication system designed for complex automation networks, offering high-speed data transmission and enhanced diagnostics. Modbus, by contrast, is a simpler serial communication protocol widely used for connecting industrial electronic devices and allowing You to monitor and control various processes efficiently.
Overview of Fieldbus Communication Protocol
Fieldbus is an industrial network protocol designed for real-time distributed control, enabling multiple devices to communicate on a single cable within automation systems. It supports deterministic data transmission and integrates field-level instruments, such as sensors and actuators, improving process control efficiency. Unlike Modbus, which is simpler and primarily master-slave, Fieldbus offers complex device interoperability and enhanced diagnostic capabilities for your industrial communication needs.
Overview of Modbus Communication Protocol
Modbus is a widely used serial communication protocol designed for industrial automation systems, enabling communication between electronic devices. It supports master-slave architecture and functions primarily over RS-232, RS-485, or Ethernet networks, facilitating data exchange in a simple and reliable manner. Its open standard nature and ease of implementation make Modbus a preferred choice for connecting sensors, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and other field devices.
Key Differences Between Fieldbus and Modbus
Fieldbus is a digital, multi-drop network designed for real-time distributed control in industrial systems, enabling multiple devices to communicate over a single cable with deterministic timing. Modbus is a simpler, master-slave protocol primarily used for serial communication in automation, supporting point-to-point or multi-drop configurations but lacking real-time deterministic control. Fieldbus supports complex device profiles and diagnostics, while Modbus offers widespread compatibility and ease of implementation, making them suited for different industrial automation needs.
Network Architecture: Fieldbus vs Modbus
Fieldbus offers a decentralized network architecture where intelligent devices communicate directly through a single cable, enhancing real-time data exchange and reducing wiring complexity. Modbus operates on a master-slave architecture, relying on a master controller to poll slave devices sequentially, limiting communication speed and flexibility. Your choice between Fieldbus and Modbus will impact network scalability and device interoperability based on specific industrial automation needs.
Data Transmission and Speed Comparison
Fieldbus protocols typically offer deterministic data transmission with cycle times ranging from milliseconds to microseconds, ensuring real-time control in industrial automation. Modbus, often implemented over serial or TCP/IP networks, provides slower data rates generally between 9600 bps to 115.2 kbps for serial versions and up to 100 Mbps for Modbus TCP, but it lacks the inherent timing guarantees of Fieldbus systems. The choice between Fieldbus and Modbus depends on the required network speed and timing precision, with Fieldbus excelling in time-critical applications and Modbus serving well in simpler, non-real-time data communication scenarios.
Scalability and Flexibility
Fieldbus systems offer high scalability through segmented network architecture, enabling easy addition of devices without compromising performance, while Modbus provides flexibility with its simple master-slave communication suitable for small to medium-sized networks. Fieldbus protocols support complex topologies and extensive device interoperability, making them ideal for large-scale industrial automation requiring modular expansion. Modbus, however, allows flexible implementation across a variety of hardware and software platforms, favoring straightforward integration in diverse control systems.
Application Areas in Industrial Automation
Fieldbus is extensively used in complex process industries such as chemical plants and power generation, where real-time, deterministic communication is critical for control and safety systems. Modbus, favored for its simplicity and ease of integration, is widely applied in factory automation, building management, and smaller-scale industrial environments where cost-effective serial communication between controllers and devices is sufficient. Both protocols facilitate interoperability among industrial devices but differ in scalability and communication speed, influencing their suitability for specific automation tasks.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Fieldbus offers high-speed, deterministic communication ideal for complex industrial automation with real-time data exchange, but it requires more sophisticated hardware and higher initial costs. Modbus is simpler to implement, widely supported, and cost-effective for basic control and monitoring tasks, though it lacks advanced features and slower performance compared to Fieldbus. Your choice depends on the complexity and scalability needs of your industrial network.
Choosing the Right Protocol for Your Application
Selecting between Fieldbus and Modbus depends on application requirements such as network size, speed, and complexity. Fieldbus excels in complex, real-time, multi-device environments with advanced diagnostics, whereas Modbus suits simpler, smaller-scale systems needing straightforward communication. Evaluating factors like protocol compatibility, installation cost, and scalability ensures optimal performance and integration in industrial automation setups.
Fieldbus vs Modbus Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com