CAN bus offers a lightweight, flexible communication system ideal for automotive and industrial automation, whereas Profibus provides a robust, high-speed network tailored for complex industrial control environments. Explore the rest of this article to understand which protocol best suits Your specific application needs.
Table of Comparison
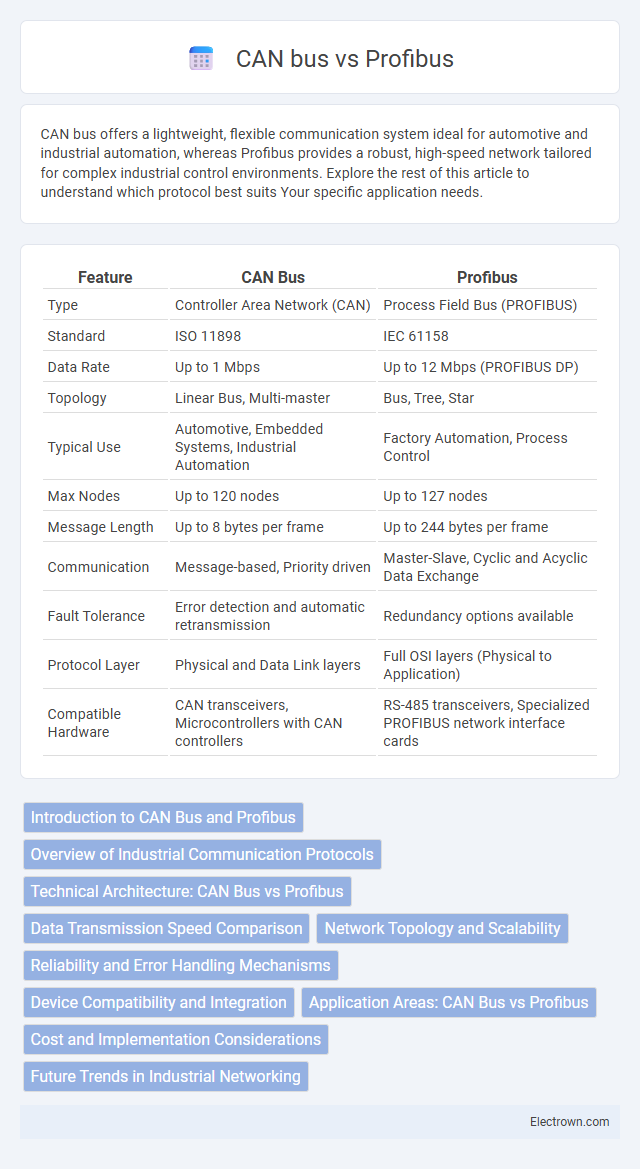
| Feature | CAN Bus | Profibus |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Controller Area Network (CAN) | Process Field Bus (PROFIBUS) |
| Standard | ISO 11898 | IEC 61158 |
| Data Rate | Up to 1 Mbps | Up to 12 Mbps (PROFIBUS DP) |
| Topology | Linear Bus, Multi-master | Bus, Tree, Star |
| Typical Use | Automotive, Embedded Systems, Industrial Automation | Factory Automation, Process Control |
| Max Nodes | Up to 120 nodes | Up to 127 nodes |
| Message Length | Up to 8 bytes per frame | Up to 244 bytes per frame |
| Communication | Message-based, Priority driven | Master-Slave, Cyclic and Acyclic Data Exchange |
| Fault Tolerance | Error detection and automatic retransmission | Redundancy options available |
| Protocol Layer | Physical and Data Link layers | Full OSI layers (Physical to Application) |
| Compatible Hardware | CAN transceivers, Microcontrollers with CAN controllers | RS-485 transceivers, Specialized PROFIBUS network interface cards |
Introduction to CAN Bus and Profibus
CAN Bus is a robust vehicle bus standard designed for microcontrollers and devices to communicate without a host computer, widely used in automotive and industrial automation due to its high-speed data transfer and error detection capabilities. Profibus, short for Process Field Bus, is an industrial communication protocol that facilitates real-time data exchange between controllers and field devices, primarily utilized in factory automation and process control systems. Understanding the differences in communication architectures and protocol applications helps you select the optimal network solution for your automation or automotive project.
Overview of Industrial Communication Protocols
CAN bus offers a robust, real-time communication protocol widely used in automotive and industrial automation for efficient device networking with high fault tolerance. Profibus, a widely adopted fieldbus standard in manufacturing, excels in complex process control and supports large networks with deterministic data exchange and extensive diagnostic capabilities. Understanding the differences in speed, topology, and application areas helps you select the most suitable protocol for your industrial communication needs.
Technical Architecture: CAN Bus vs Profibus
CAN Bus features a multi-master, message-oriented protocol with a lightweight, prioritization-based arbitration scheme, allowing real-time data exchange over a two-wire differential serial bus with speeds up to 1 Mbps. Profibus employs a master-slave or token-passing architecture on a twisted-pair or fiber-optic medium, supporting data rates up to 12 Mbps and structured network topologies such as line, tree, and star. The technical architecture of CAN Bus emphasizes simplicity and real-time control for embedded systems, while Profibus offers complex network management and higher-level protocol layers suited for industrial automation environments.
Data Transmission Speed Comparison
CAN bus typically supports data transmission speeds up to 1 Mbps, making it ideal for automotive and industrial automation applications requiring moderate-speed communication. Profibus, especially Profibus DP, achieves higher data rates up to 12 Mbps, enabling faster and more efficient data exchange in complex automation systems. The choice between CAN bus and Profibus depends on the specific application's speed requirements and network complexity.
Network Topology and Scalability
CAN bus employs a linear bus topology that supports simple wiring and easy device addition but is limited in scalability for large industrial networks. Profibus uses a more flexible tree or line topology, allowing extensive device connections and better scalability across complex automation systems. Your choice between CAN bus and Profibus should consider the required network size and future expansion needs in industrial environments.
Reliability and Error Handling Mechanisms
CAN bus offers high reliability through its robust error detection methods such as cyclic redundancy check (CRC), bit stuffing, and acknowledgment slots, which enable automatic retransmission of corrupted frames to ensure data integrity. Profibus incorporates error handling mechanisms including checksum verification, timeout detection, and diagnostic protocols that provide real-time monitoring and fault isolation to maintain network stability. Both systems support fault-tolerant communication, but CAN bus's deterministic arbitration and extensive error confinement features make it especially suitable for safety-critical applications.
Device Compatibility and Integration
CAN bus supports a wide range of automotive and industrial devices due to its simple protocol and robust error handling, making it highly compatible with sensor and control modules. Profibus offers extensive integration with industrial automation equipment, including PLCs, drives, and field devices, through standardized profiles that ensure seamless interoperability. Device compatibility in CAN bus emphasizes flexibility and low-level control, whereas Profibus prioritizes structured integration for complex factory automation systems.
Application Areas: CAN Bus vs Profibus
CAN bus excels in automotive and industrial automation due to its robust, real-time communication capabilities and resistance to electrical interference. Profibus is widely used in factory automation and process control environments, offering high-speed data exchange and seamless integration with programmable logic controllers (PLCs). Your choice depends on the specific requirements of your application, with CAN bus suited for embedded systems and Profibus ideal for complex industrial networks.
Cost and Implementation Considerations
CAN bus offers lower implementation costs due to its simple wiring and widespread use in automotive and industrial applications, making it ideal for cost-sensitive projects. Profibus requires more complex infrastructure and specialized components, increasing installation expenses but providing robust diagnostics and higher data rates suited for large-scale automation systems. Your choice should balance budget constraints with performance needs, considering future scalability and maintenance costs.
Future Trends in Industrial Networking
CAN bus and Profibus are evolving to meet future industrial networking demands with a focus on higher data rates and enhanced real-time performance. Integration with Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) platforms and increased support for cybersecurity measures are driving advancements in both protocols. Profibus is shifting towards Profinet technologies for Ethernet-based communication, while CAN bus is adapting through CAN FD and CAN XL to handle larger data payloads and faster communication speeds.
CAN bus vs Profibus Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com