Delta and Wye transformers differ primarily in their winding configurations, impacting voltage levels, phase relationships, and fault tolerance in power systems. Understanding these distinctions can optimize Your electrical system's performance; continue reading to explore their advantages and applications.
Table of Comparison
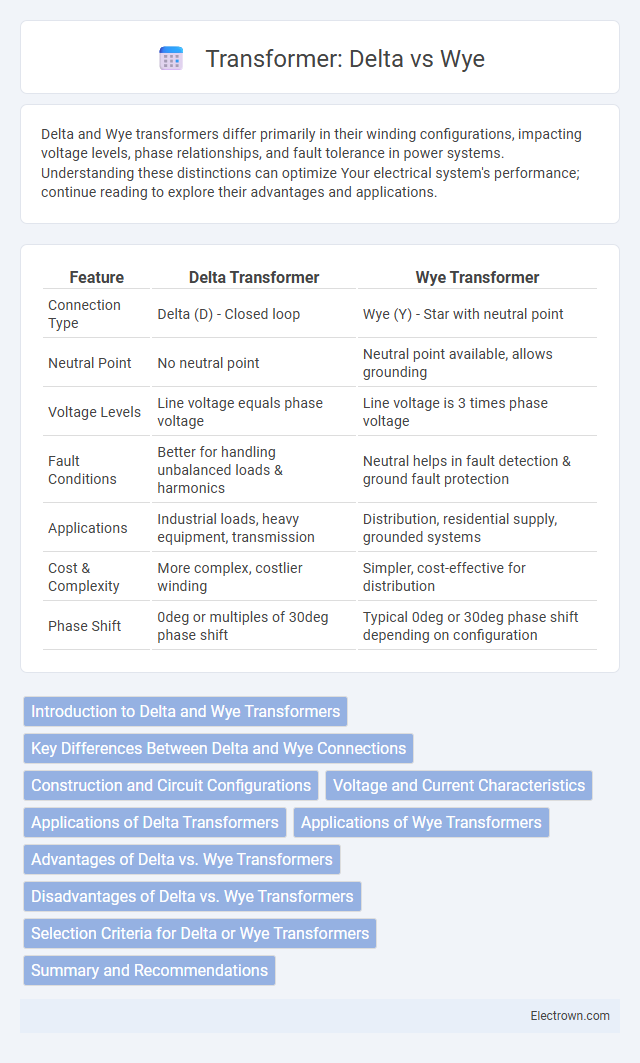
| Feature | Delta Transformer | Wye Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Connection Type | Delta (D) - Closed loop | Wye (Y) - Star with neutral point |
| Neutral Point | No neutral point | Neutral point available, allows grounding |
| Voltage Levels | Line voltage equals phase voltage | Line voltage is 3 times phase voltage |
| Fault Conditions | Better for handling unbalanced loads & harmonics | Neutral helps in fault detection & ground fault protection |
| Applications | Industrial loads, heavy equipment, transmission | Distribution, residential supply, grounded systems |
| Cost & Complexity | More complex, costlier winding | Simpler, cost-effective for distribution |
| Phase Shift | 0deg or multiples of 30deg phase shift | Typical 0deg or 30deg phase shift depending on configuration |
Introduction to Delta and Wye Transformers
Delta and Wye transformers are two common types of transformer winding configurations used in electrical power systems to transfer energy between circuits. Delta transformers connect three windings end-to-end to form a closed loop, allowing for the circulation of current and balanced load distribution. Wye transformers connect one end of each winding to a common neutral point, providing a stable neutral for grounding and enabling multiple voltage levels.
Key Differences Between Delta and Wye Connections
Delta and Wye transformer connections differ primarily in their wiring configurations and phase relationships, affecting voltage and current characteristics. Delta connections feature a closed-loop circuit offering high fault tolerance and suitability for heavy loads, while Wye connections provide a neutral point, enabling the use of multiple voltage levels and improved grounding options. Understanding these distinctions helps you select the appropriate transformer setup for specific power distribution requirements and system stability.
Construction and Circuit Configurations
Delta transformers feature windings connected in a closed loop forming a triangle, allowing three-phase power distribution with no neutral point. Wye transformers have windings connected at a common neutral point, creating a star configuration ideal for providing multiple voltage levels and a neutral connection. The choice between delta and wye configurations impacts fault tolerance, load balancing, and grounding methods in electrical power systems.
Voltage and Current Characteristics
Delta transformers provide higher line voltage and lower line current compared to wye transformers, making them suitable for high-power distribution with less conductor material. Wye transformers offer lower line voltage with higher line current, ideal for balanced loads and grounding capabilities. Your choice between delta and wye configurations directly impacts voltage levels and current flow in electrical systems, influencing efficiency and safety.
Applications of Delta Transformers
Delta transformers are commonly used in industrial settings where heavy machinery requires high starting torque and robust power transfer. Their ability to handle unbalanced loads and provide a stable phase voltage makes them ideal for motor-driven applications and large commercial facilities. These transformers are also preferred in power distribution networks for fault detection and minimizing third harmonic circulation.
Applications of Wye Transformers
Wye transformers are widely utilized in power distribution systems to provide a neutral point for grounding and to facilitate load balancing across three-phase systems. Their application is essential in industrial settings where equipment requires a stable neutral connection for safety and operational reliability. Wye configurations also enable efficient voltage regulation and are commonly used in transmission lines to step down high voltages for commercial and residential use.
Advantages of Delta vs. Wye Transformers
Delta transformers provide superior fault tolerance due to their closed-loop configuration, allowing continuous operation even if one winding fails. They effectively handle unbalanced loads by circulating harmonic currents within the delta, reducing the impact on the power system. Their ability to supply higher starting torque makes them ideal for industrial motors and heavy machinery applications.
Disadvantages of Delta vs. Wye Transformers
Delta transformers face disadvantages such as higher insulation requirements due to circulating currents, which can increase maintenance costs. Their lack of a neutral point limits the ability to provide a stable neutral reference, potentially causing issues in single-phase loads or grounding. When choosing between transformer types, understanding these drawbacks can help you optimize system reliability and efficiency.
Selection Criteria for Delta or Wye Transformers
Selection criteria for Delta or Wye transformers depend primarily on load type, system grounding requirements, and fault tolerance. Delta transformers are preferred for heavy industrial loads due to their ability to handle unbalanced loads and provide a path for triplen harmonics, while Wye transformers are favored in distribution systems for their neutral grounding and easier fault detection. Voltage levels, safety regulations, and system configuration also influence the choice between Delta and Wye connections to optimize efficiency and reliability.
Summary and Recommendations
Delta transformers provide a closed path for triplen harmonics, reducing neutral current issues and improving system stability, making them ideal for industrial applications with heavy motor loads. Wye transformers offer a neutral point for grounding and are better suited for distribution networks requiring balanced loads and easier fault detection. For your setup, select a delta transformer if harmonic mitigation and motor-driven loads dominate, and a wye transformer when grounding and load balancing are critical.
Delta vs Wye Transformer Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com