Rotary sensors measure angular position or rotation, ideal for detecting circular movements, while linear sensors track straight-line displacement, perfect for monitoring linear motion in applications like robotics or automation. Explore the rest of the article to understand which sensor fits your specific needs and how to optimize your system's performance.
Table of Comparison
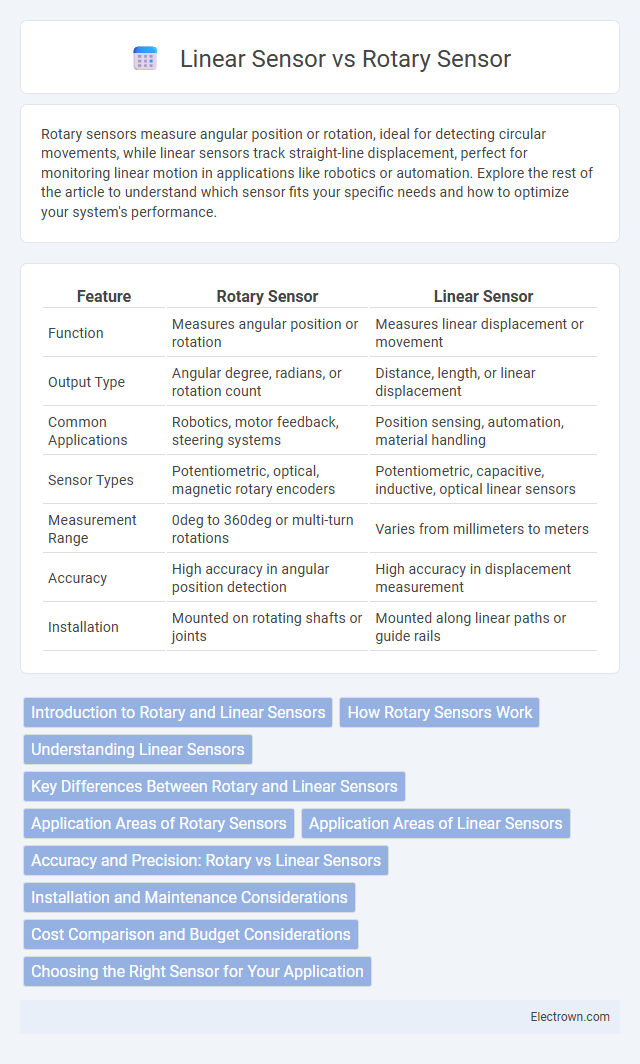
| Feature | Rotary Sensor | Linear Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Measures angular position or rotation | Measures linear displacement or movement |
| Output Type | Angular degree, radians, or rotation count | Distance, length, or linear displacement |
| Common Applications | Robotics, motor feedback, steering systems | Position sensing, automation, material handling |
| Sensor Types | Potentiometric, optical, magnetic rotary encoders | Potentiometric, capacitive, inductive, optical linear sensors |
| Measurement Range | 0deg to 360deg or multi-turn rotations | Varies from millimeters to meters |
| Accuracy | High accuracy in angular position detection | High accuracy in displacement measurement |
| Installation | Mounted on rotating shafts or joints | Mounted along linear paths or guide rails |
Introduction to Rotary and Linear Sensors
Rotary sensors measure angular position or rotation of a shaft, commonly used for applications involving rotational motion detection. Linear sensors detect displacement or position along a straight path, ideal for monitoring linear movement in machinery or automation systems. Both sensors convert physical motion into electrical signals for precise control and measurement in various industrial and robotic applications.
How Rotary Sensors Work
Rotary sensors measure angular position or displacement by detecting changes in an object's rotational movement, often using potentiometers, optical encoders, or magnetic fields. They convert the mechanical rotation into an electrical signal proportional to the angle of rotation, enabling precise control in applications like robotics and industrial machinery. This measurement method differs from linear sensors, which track straight-line displacement rather than rotational motion.
Understanding Linear Sensors
Linear sensors measure displacement or position along a straight path, converting physical movement into electrical signals with high accuracy. These sensors are essential for applications requiring precise measurement of linear motion, such as automation, robotics, and industrial machinery. Your choice between rotary and linear sensors depends on whether rotational or straight-line position tracking is needed.
Key Differences Between Rotary and Linear Sensors
Rotary sensors measure angular displacement, detecting rotational position or speed with components like potentiometers or encoders, while linear sensors track straight-line displacement, using technologies such as LVDTs or linear encoders. Rotary sensors are ideal for applications requiring precise angle feedback, machinery control, and motor shaft position, whereas linear sensors excel in monitoring linear motion and position in automation and material handling. The primary distinction lies in their sensing orientation--rotary sensors focus on circular motion, while linear sensors target straight-line movements, influencing their design, installation, and application suitability.
Application Areas of Rotary Sensors
Rotary sensors are widely used in robotics, automotive systems, and industrial machinery for precise angle measurement and rotational position feedback. Their applications extend to motor speed control, volume control knobs, and steering systems where accurate rotational movement monitoring is critical. These sensors enable enhanced performance in automation processes, ensuring reliable and repeatable angular position detection.
Application Areas of Linear Sensors
Linear sensors are extensively used in industrial automation for precise position feedback in machinery, robotics, and assembly lines. They are crucial in medical devices, ensuring accurate measurements in imaging equipment and patient monitoring systems. Additionally, linear sensors enable reliable control in automotive applications such as throttle position sensing and suspension system adjustments.
Accuracy and Precision: Rotary vs Linear Sensors
Rotary sensors provide high accuracy and precision in detecting angular positions, often measured in degrees or fractions of a degree, making them ideal for applications requiring exact rotational movement. Linear sensors measure displacement along a straight path with precision typically expressed in micrometers or millimeters, excelling in environments where linear position tracking is critical. Your choice depends on whether precise angular or straight-line measurement aligns better with your system's requirements.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Rotary sensors require precise shaft alignment during installation to ensure accurate angular position measurement, while linear sensors demand accurate positioning along the measurement axis to detect displacement effectively. Maintenance of rotary sensors often involves inspecting bearings and seals to prevent mechanical wear, whereas linear sensors typically need regular cleaning of the sensing path to avoid debris interference. Both sensor types benefit from calibration checks to maintain measurement accuracy, but rotary sensors may require more frequent servicing in high-torque environments.
Cost Comparison and Budget Considerations
Rotary sensors generally have lower initial costs compared to linear sensors due to simpler design and widespread availability, making them suitable for budget-conscious projects requiring angular position measurement. Linear sensors tend to be more expensive because of their complex construction and specialized applications, which adds to development and maintenance expenses. Evaluating project requirements against sensor precision and durability is crucial to balance cost-effectiveness with performance in sensor selection.
Choosing the Right Sensor for Your Application
Selecting the right sensor for your application depends on the type of motion you need to measure; rotary sensors are ideal for detecting angular positions, while linear sensors excel in measuring straight-line displacement. Consider factors such as accuracy requirements, environmental conditions, and space constraints when deciding between a rotary sensor and a linear sensor. Your choice will impact system performance, so evaluate sensor specifications like resolution, range, and durability to ensure optimal results.
Rotary Sensor vs Linear Sensor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com