Wired industrial communication offers reliable, high-speed data transfer with minimal interference, while wireless solutions provide greater flexibility and ease of installation in dynamic environments. Explore the rest of the article to discover which communication method best suits Your industrial needs.
Table of Comparison
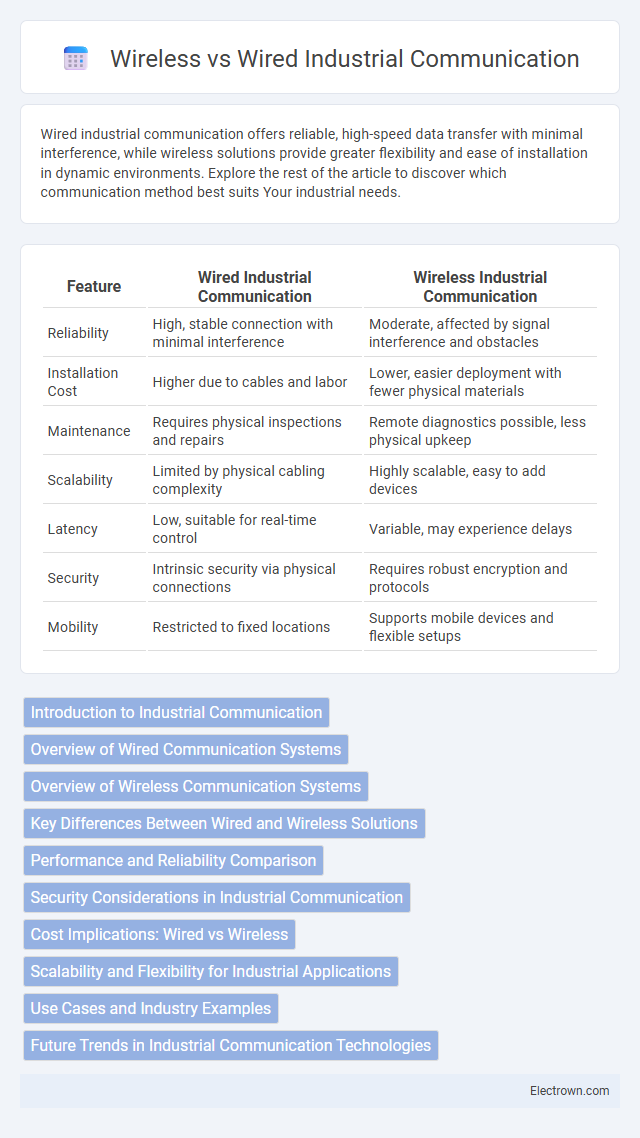
| Feature | Wired Industrial Communication | Wireless Industrial Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Reliability | High, stable connection with minimal interference | Moderate, affected by signal interference and obstacles |
| Installation Cost | Higher due to cables and labor | Lower, easier deployment with fewer physical materials |
| Maintenance | Requires physical inspections and repairs | Remote diagnostics possible, less physical upkeep |
| Scalability | Limited by physical cabling complexity | Highly scalable, easy to add devices |
| Latency | Low, suitable for real-time control | Variable, may experience delays |
| Security | Intrinsic security via physical connections | Requires robust encryption and protocols |
| Mobility | Restricted to fixed locations | Supports mobile devices and flexible setups |
Introduction to Industrial Communication
Industrial communication systems enable seamless data exchange between machinery, control systems, and sensors to optimize manufacturing processes. Wired industrial communication offers high reliability and low latency through physical connections such as Ethernet or fieldbus networks, making it ideal for critical control applications. Wireless communication provides flexibility and ease of installation, supporting remote monitoring and mobile equipment, but it may face challenges with interference and security.
Overview of Wired Communication Systems
Wired communication systems in industrial settings use physical cables such as Ethernet, fiber optics, or coaxial cables to transmit data, offering high reliability and consistent performance in noisy or harsh environments. These systems provide low latency, high data transfer rates, and robust security, making them ideal for critical applications where stability and interference resistance are essential. Your industrial network can benefit from reduced downtime and improved data integrity by leveraging wired communication infrastructure.
Overview of Wireless Communication Systems
Wireless communication systems in industrial settings use technologies such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and 5G to enable real-time data exchange without physical connections. These systems offer enhanced flexibility, scalability, and ease of installation, supporting mobile devices and remote monitoring across large facilities. Your industrial operations can leverage wireless communication to reduce cabling costs and improve system adaptability in dynamic environments.
Key Differences Between Wired and Wireless Solutions
Wired industrial communication offers higher reliability, lower latency, and enhanced security through physical connections, making it ideal for critical systems requiring consistent performance. Wireless solutions provide greater flexibility, easier scalability, and reduced installation costs, allowing for seamless integration across complex or remote industrial environments. Your choice between wired and wireless depends on factors like environmental conditions, data transmission needs, and operational priorities.
Performance and Reliability Comparison
Wired industrial communication offers superior performance with low latency and high data transfer rates, ensuring consistent and reliable connections crucial for mission-critical applications. Wireless communication provides greater flexibility and ease of installation but may suffer from interference, signal loss, and variable latency, impacting overall reliability in harsh industrial environments. Your choice depends on the need for uncompromised reliability versus adaptability and mobility within your industrial network.
Security Considerations in Industrial Communication
Wired industrial communication offers enhanced security due to its physical connections, reducing risks of unauthorized access and interference commonly faced by wireless networks. Wireless communication introduces vulnerabilities like signal interception, jamming, and spoofing, requiring robust encryption and authentication protocols to protect sensitive industrial data. Your choice between wired and wireless should weigh these security considerations against operational flexibility and infrastructure costs to ensure reliable protection.
Cost Implications: Wired vs Wireless
Wired industrial communication systems often entail higher initial installation costs due to extensive cabling, labor, and infrastructure requirements, but provide lower maintenance expenses and greater reliability over time. Wireless systems reduce upfront installation costs by eliminating physical cables and allowing for easier scalability, yet may incur ongoing expenses related to network management, interference mitigation, and security measures. Evaluating total cost of ownership involves balancing the reliability and durability of wired solutions against the flexibility and lower deployment costs of wireless alternatives.
Scalability and Flexibility for Industrial Applications
Wired industrial communication offers robust scalability through structured network expansions, providing consistent performance for large-scale applications with defined infrastructure needs. Wireless industrial communication enhances flexibility by enabling rapid deployment and real-time adaptability, crucial for dynamic industrial environments where mobility and changing layouts are common. Optimizing your industrial communication strategy involves balancing the reliability of wired systems with the scalability and flexibility offered by wireless technologies to meet evolving operational demands.
Use Cases and Industry Examples
Wired industrial communication, utilizing Ethernet and fieldbus systems, excels in applications demanding high reliability and low latency, such as automotive manufacturing and power plant control, where consistent data transfer is critical. Wireless solutions, leveraging technologies like Wi-Fi, 5G, and LPWAN, enable flexible monitoring and predictive maintenance in industries like oil and gas, logistics, and smart factories, supporting asset mobility and remote locations. Your choice between wired and wireless depends on the specific operational environment, scalability needs, and real-time performance requirements in industrial automation.
Future Trends in Industrial Communication Technologies
Future trends in industrial communication technologies emphasize the integration of 5G and edge computing to enhance wireless connectivity, offering ultra-low latency and high reliability for smart factories. Wired communication retains its significance in critical applications requiring deterministic performance and cybersecurity, supported by advancements in Ethernet standards like Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN). Hybrid communication architectures combining wired and wireless solutions are becoming prevalent to optimize flexibility, scalability, and resilience in industrial automation environments.
Wired vs Wireless Industrial Communication Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com